ESET Analysis
ESET’s expert analysts have conducted an exhaustive technical assessment of the Gamaredon group’s cyberespionage toolkit, focusing on their malicious activities aimed specifically at Ukrainian targets.

The ongoing crisis in Ukraine, sparked by the Euromaidan protests in late 2013 that toppled President Viktor Yanukovych’s government in February 2014, took a catastrophic turn on February 24, 2022, when Russia launched a large-scale invasion of Ukrainian territory.thIn 2022, the complex conflict unfolded as a tangled web of misinformation and cyber attacks, highlighting the critical need for accurate information and robust digital defenses. Throughout multiple years, ESET analysis has uncovered numerous campaigns conducted by Russia-aligned advanced persistent threat (APT) groups targeting Ukrainian entities and speakers; we have analyzed various operations and closely monitored several APT teams focusing on this region amid the ongoing conflict.
Based on our analysis, we examined the activities of Gamaredon, an actor that has demonstrated remarkable energy since at least 2013 and currently represents the most active Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group in Ukraine. Since 2022, the intensity of Russia’s bodily aggression has noticeably increased; however, it is crucial to acknowledge that Gamaredon’s cyber operations have maintained a consistent level of activity – the group has been deliberately deploying its malicious tools against targets since well before the invasion commenced.
Having scrutinized thousands of samples, we present the conclusive findings from a comprehensive technical evaluation of Gamaredon’s toolset employed for cyberespionage in 2022 and 2023 within our recently published white paper, accessible in its entirety below:
In this whitepaper, we delve into the evolving techniques employed by Gamaredon to evade detection and circumvent domain-based blocking measures, including their tactics for obfuscation. The proliferation of these innovative tactics poses significant challenges to monitoring initiatives, rendering traditional methods less effective in identifying and countering the group’s sophisticated tools. Notwithstanding our investigation, we successfully identified and documented the tactics employed by Gamaredon, meticulously monitoring their activities. We delve deeper into the instrument families, highlighting their most prominent and intriguing members to illuminate the intricate relationships between them, ultimately fostering a richer understanding of the instruments’ interconnected ecosystem?
Victimology and group background
Gamaredon to the 18th The Heart of Information Security, operating from occupied Crimea, an agency of the Federal Security Service. We regard this particular grouping alongside a second malevolent entity that we identified and dubbed.
According to ESET telemetry data and corroborated by various official Ukrainian sources, a significant proportion of Gamaredon’s attacks have been consistently targeted at Ukrainian government institutions. In April 2022 and again in February 2023, our monitoring systems detected multiple attempts to infiltrate strategic targets in several NATO member countries, including Bulgaria, Latvia, Lithuania, and Poland, although none of these efforts resulted in successful breaches.
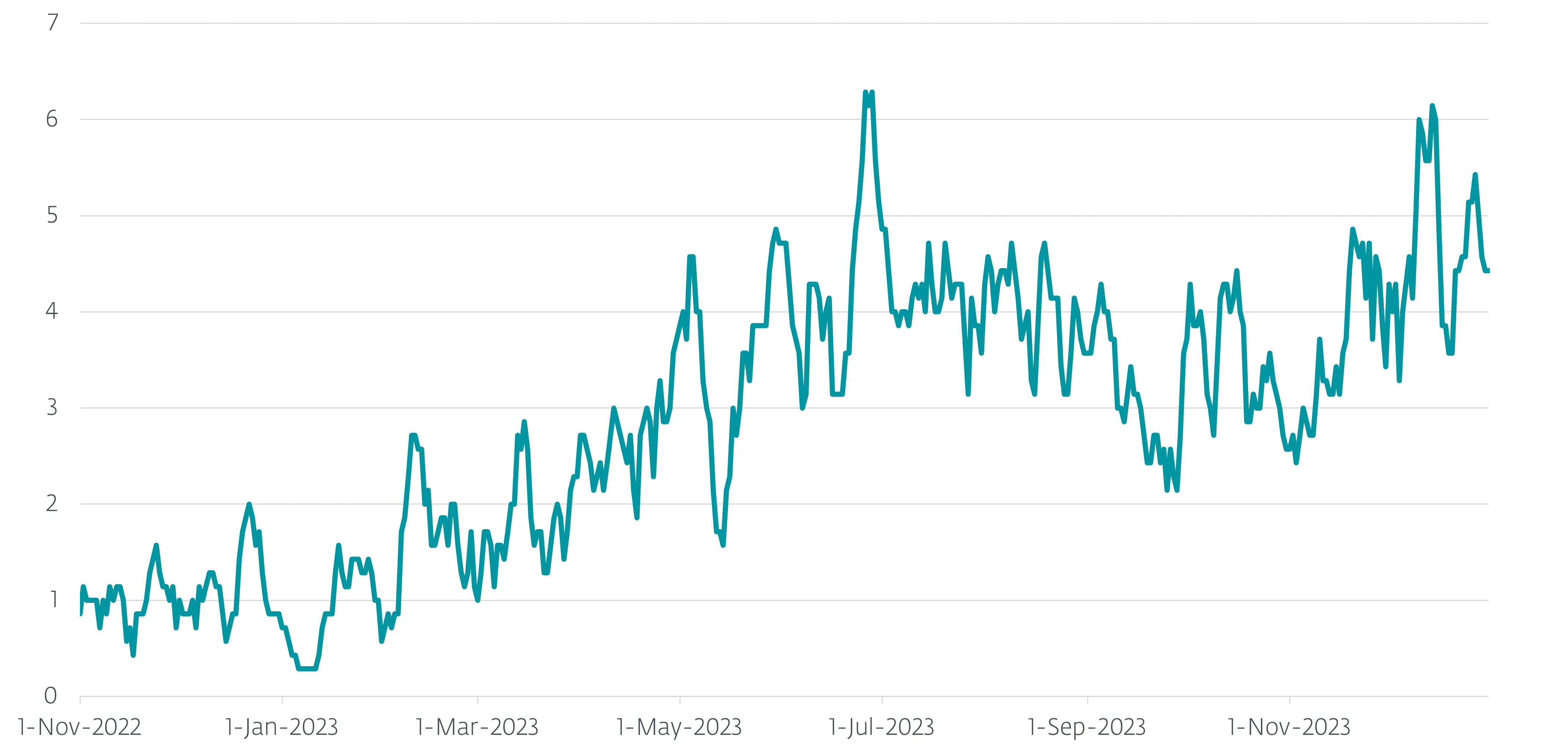
Between November 1st, 2022 and December 31st In 2023, it was observed that over a thousand unique computer systems in Ukraine were targeted by the malicious actor Gamaredon. The daily cumulative trend over a seven-day period is illustrated in Figure 1.
Chaotic and destructive, yet undeniably perilous
Gamaredon orchestrates sophisticated spear-phishing operations, exploiting unsuspecting targets through customized malware-infected phrase documents and USB drives that are unwittingly shared among potential victims.
Uncharacteristically, Gamaredon’s APT tactics eschew traditional stealthiness, instead opting for brazen methods that intentionally seek to evade detection during cyberespionage operations, often leaving a trail that invites discovery by vigilant defenders. Although they’re not particularly concerned with noise levels, they go to great lengths to avoid triggering security measures and diligently monitor access to vulnerable programs.
Occasionally, Gamaredon resorts to deploying multiple concurrent easy downloaders or backdoors in a bid to safeguard its entry point. The lack of refinement in Gamaredon’s instruments is mitigated by regular software updates and the deployment of adaptive encryption methods that periodically change complexity.
As technology continues to evolve, scripting languages like VBScript and PowerShell are also adapting to meet the changing needs of developers. In recent years, there has been a significant shift in the focus of these two scripting languages.
While VBScript was initially designed for Windows-specific tasks, its popularity has waned due to the rise of other technologies and the decline of ActiveX controls. On the other hand, PowerShell has emerged as a powerful tool for managing and automating Windows systems, leveraging its strong integration with .NET framework.
PowerShell’s versatility, along with its ability to automate administrative tasks, has made it a go-to choice for many system administrators. Its extensive library of cmdlets, or commandlets, provides a wide range of functionality for managing servers, databases, and other IT infrastructure.
The shift towards PowerShell can be attributed to Microsoft’s increased focus on developing cross-platform solutions that integrate seamlessly with Windows systems. As a result, developers are increasingly opting for PowerShell over VBScript due to its improved performance, reliability, and flexibility.
SKIP
Gamaredon’s toolset has undergone numerous modifications throughout its history. By 2022, the group incrementally transitioned their tactics to incorporate both VBScript and PowerShell, effectively phasing out reliance on SFX archives that had previously been a staple of their operations. In 2023, Gamaredon significantly enhanced its cyberespionage capabilities by developing novel tools within PowerShell, focusing primarily on pilfering valuable information from internet applications running within web browsers, email clients, and instant messaging platforms such as Signal and Telegram.
Notwithstanding this, an information stealer discovered in August 2023 also targets sensitive data related to Ukraine’s naval system and a web-based email service used by the country’s government. The timeline of recent instruments launched in 2022 and 2023, as depicted in Figure 2, has been validated by ESET Research, with the exception of PteroScreen.
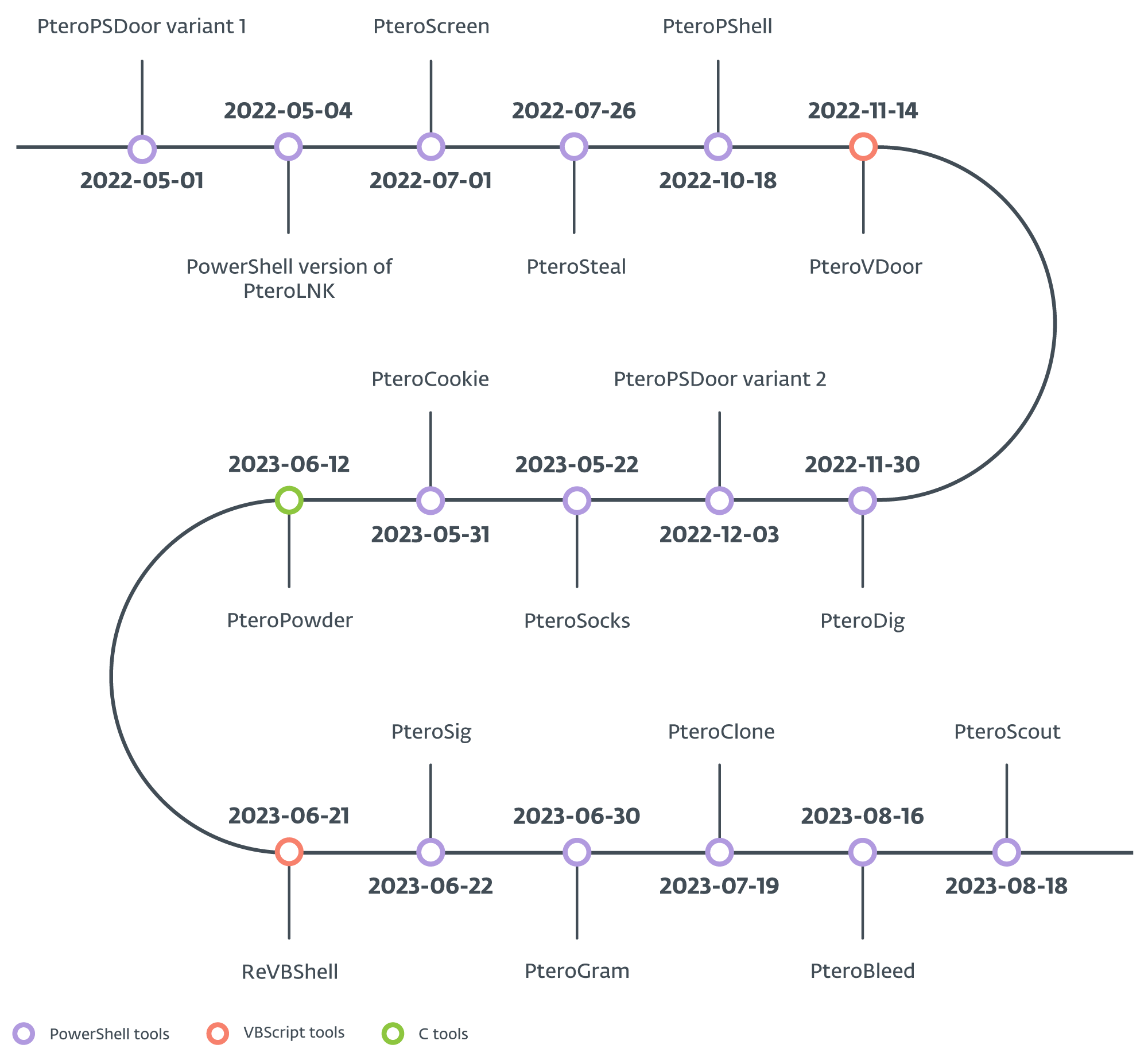
Tightly clustered, Gamaredon’s arsenal is often partitioned into six distinct categories: downloaders, droppers, weaponizers, stealers, backdoors, and ad-hoc tools. The group leverages a combination of both general-purpose and specialized downloaders to distribute malicious payloads. Attackers employ droppers to deliver diverse VBScript payloads; weaponizers modify attributes of existing files or generate new ones on connected USB drives, thereby pilfering specific files from the file system. Moreover, backdoors facilitate distant shell access, while ad-hoc tools execute specific capabilities, such as reverse SOCKS proxies or payload delivery via reliable command-line programs.
Quick switching of C&C IP addresses and domains
Our assessment also provides insight into the organization’s community framework. Gamaredon makes use of a way generally known as – often altering its command and management (C&C) servers’ IP addresses, normally a number of instances per day, to keep away from IP-based blocking. The group additionally often registers and updates many new C&C domains to keep away from domain-based blocking, primarily utilizing because the top-level area (TLD).
Gamaredon’s adaptability is further exemplified through its implementation of diverse tactics to circumvent network-based detection mechanisms, collaborating with external entities such as Telegram, Cloudflare, and other relevant organizations.
Despite its relatively unsophisticated arsenal, Gamaredon’s relentless aggression and unwavering determination render it a significant threat. As tensions persist in the region, we expect Gamaredon to maintain its focus on Ukraine, given the ongoing conflict.
Access the comprehensive ESET Analysis white paper for a meticulous examination and technical dissection of Gamaredon’s tools and activities.
A comprehensive record of indicators of compromise (IoCs) may exist within the Gamaredon Group’s tactics, techniques, and procedures.

