
New variations of the XWorm backdoor are being distributed in phishing campaigns after the unique developer, XCoder, deserted the mission final 12 months.
The newest variants, XWorm 6.0, 6.4, and 6.5, look like adopted by a number of menace actors and have help for plugins that enable a variety of malicious actions.
Malware operators can use the modules to steal information from browsers and functions, take management of the host by distant desktop and shell entry, and encrypt or decrypt information.
The final recognized model of the malware developed by XCoder is 5.6, which was susceptible to a distant code execution flaw, addressed within the current variants.
Versatile and standard
XWorm is a distant entry trojan first noticed in 2022. It gained a popularity as a extremely efficient malware because of its modular structure and intensive capabilities.
It’s usually used to gather delicate information (passwords, crypto wallets, monetary data), monitor keystrokes, steal info within the clipboard,
Nevertheless, it can be used to launch distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) assaults and cargo different malware.
After XCoder deleted their Telegram accounts, the place they shared common updates, a number of menace actors began to unfold cracked variations of the malware.
XWorm was so standard {that a} menace actor used it as a lure to focus on less-skilled cybercriminals with a backdoor that stole information.
That marketing campaign counted 18,459 infections, most of them in Russia, america, India, Ukraine, and Turkey.
Number of supply strategies
Since June, researchers at cybersecurity firm Trellix have observed a rise in XWorm samples on the VirusTotal scanning platform, which additionally signifies a excessive adoption price amongst cybercriminals.
In a single phishing marketing campaign, the malware was deployed by a malicious JavaScript that initiated a PowerShell script, which might bypass the Antimalware Scan Interface safety and deploy XWorm.
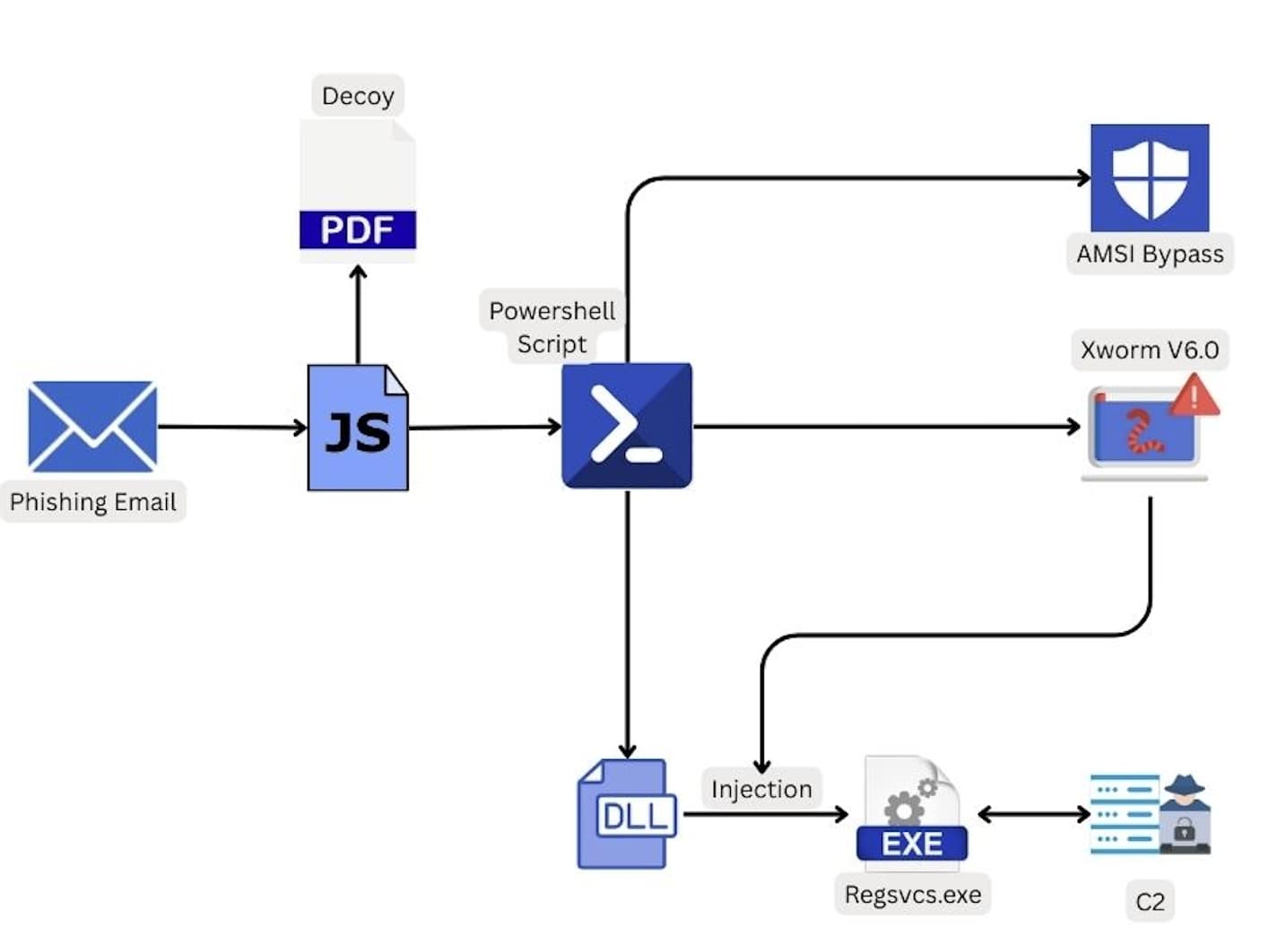
supply: Trellix
In a report from September, the researchers mentioned that “the XWorm malware an infection chain has advanced to incorporate extra strategies past conventional email-based assaults.”
Electronic mail and .LNK information are nonetheless a typical preliminary entry vector, however the malware additionally makes use of “legitimate-looking .exe filenames to disguise itself as innocent functions” akin to Discord.
“This marks a shift in direction of combining social engineering with technical assault vectors for higher effectiveness,” Trellix mentioned.
Different researchers detected campaigns that delivered XWorm utilizing AI-themed lures and a modified variant of the ScreenConnect distant entry device.
One other analysis supplies technical particulars on an phishing marketing campaign delivering XWorm by shellcode embedded in a Microsoft Excel file (.XLAM).
Ransomware menace amongst dozens of modules
In keeping with Trellix researchers, XWorm now has greater than 35 plugins that reach its capabilities from stealing delicate info to ransomware.
The file encrypting performance, Ransomware.dll, lets malware operators set a desktop wallpaper after locking the information, the ransom quantity, pockets deal with, and speak to e-mail.
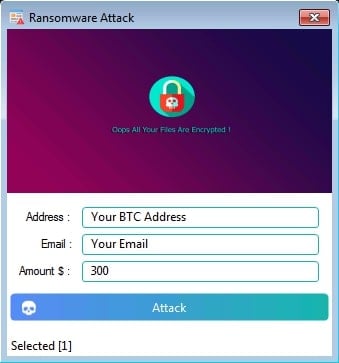
supply: Trellix
The encryption course of avoids system information and folders and focuses on information within the %USERPROFILE% and Paperwork areas, deletes the unique file, and provides the .ENC extension to the locked information.
Victims additionally get directions to decrypt the information in an HTML file dropped on the desktop. Particulars embody the BTC deal with, e-mail ID, and ransom quantity.

supply: Trellix
Trellix researchers discovered code overlaps between XWorm’s ransomware module and the .NET-based NoCry ransomware first noticed in 2021.
Each items of malicious code use the identical algorithm to generate the initialization vector (IV) and the encryption/decryption key, the encryption course of (AES with CBC mode in blocks of 4096 bytes).
The researchers additionally observed that the 2 items of malware ran the identical set of verifications towards evaluation environments.
Other than the ransomware element, Trellix analyzed 14 different plugins for XWorm:
- RemoteDesktop.dll: creates a distant session to work together with the sufferer’s machine
- WindowsUpdate.dll, Stealer.dll, Restoration.dll, merged.dll, Chromium.dll, and SystemCheck.Merged.dll: steal victims’ information
- FileManager.dll: supplies the operator filesystem entry and manipulation capabilities
- Shell.dll: executes system instructions the operator sends in a hidden cmd.exe course of
- Informations.dll: gathers system details about the sufferer’s machine
- Webcam.dll: Used to report the sufferer. It’s also utilized by the operator to confirm if an contaminated machine is actual
- TCPConnections.dll, ActiveWindows.dll, and StartupManager.dll: ship an inventory of lively TCP connections, lively home windows, and startup packages, respectively, to the C2 server
The researchers say that the information theft modules alone enable an XWorm operator to steal login information from a number of functions that embody greater than 35 net browsers, e-mail shoppers, messaging apps, FTP shoppers, and crypto wallets.
Since plugins serve a particular operate, Trellix recommends that organizations use a multi-layered protection strategy that may reply to malicious exercise after compromise.
Endpoint detection and response (EDR) options can determine the habits of XWorm’s modules, whereas proactive e-mail and net protections can block the preliminary malware droppers.
Moreover, a community monitoring answer might detect the communication with the command and management server for downloading extra plugins or information exfiltration.


