Scientists have lengthy tried to grasp the human mind by evaluating it to different primates. Researchers are nonetheless making an attempt to grasp what makes our mind completely different to our closest family. Our current examine might have introduced us one step nearer by taking a brand new strategy—evaluating the best way brains are internally related.
The Victorian palaeontologist Richard Owen incorrectly argued that the human mind was the one mind to comprise a small space known as the Hippocampus minor. He claimed that made it distinctive among the many animal kingdom, and he argued, the human mind was subsequently clearly unrelated to different species. We’ve realized quite a bit since then in regards to the group and performance of our mind, however there’s nonetheless a lot to study.
Most research evaluating the human mind to that of different species deal with measurement. This may be the scale of the mind, measurement of the mind relative to the physique, or the scale of components of the mind to the remainder of it. Nonetheless, measures of measurement don’t inform us something in regards to the inside group of the mind. For example, though the large mind of an elephant incorporates 3 times as many neurons because the human mind, these are predominantly situated within the cerebellum, not within the neocortex, which is often related to human cognitive talents.
Till lately, learning the mind’s inside group was painstaking work. The arrival of medical imaging strategies, nonetheless, has opened up new prospects to look contained in the brains of animals rapidly, in nice element, and with out harming the animal.
Our group used publicly out there MRI information of white matter, the fibers connecting components of the mind’s cortex. Communication between mind cells runs alongside these fibers. This prices vitality and the mammalian mind is subsequently comparatively sparsely related, concentrating communications down just a few central pathways.
The connections of every mind area inform us quite a bit about its capabilities. The set of connections of any mind area is so particular that mind areas have a distinctive connectivity fingerprint.
In our examine, we in contrast these connectivity fingerprints throughout the human, chimpanzee, and macaque monkey mind. The chimpanzee is, along with the bonobo, our closest dwelling relative. The macaque monkey is the non-human primate finest identified to science. Evaluating the human mind to each species meant we couldn’t solely assess which components of our mind are distinctive to us, but additionally which components are more likely to be shared heritage with our non-human family.
A lot of the earlier analysis on human mind uniqueness has targeted on the prefrontal cortex, a gaggle of areas on the entrance of our mind linked to complicated thought and determination making. We certainly discovered that facets of the prefrontal cortex had a connectivity fingerprint within the human that we couldn’t discover within the different animals, notably once we in contrast the human to the macaque monkey.
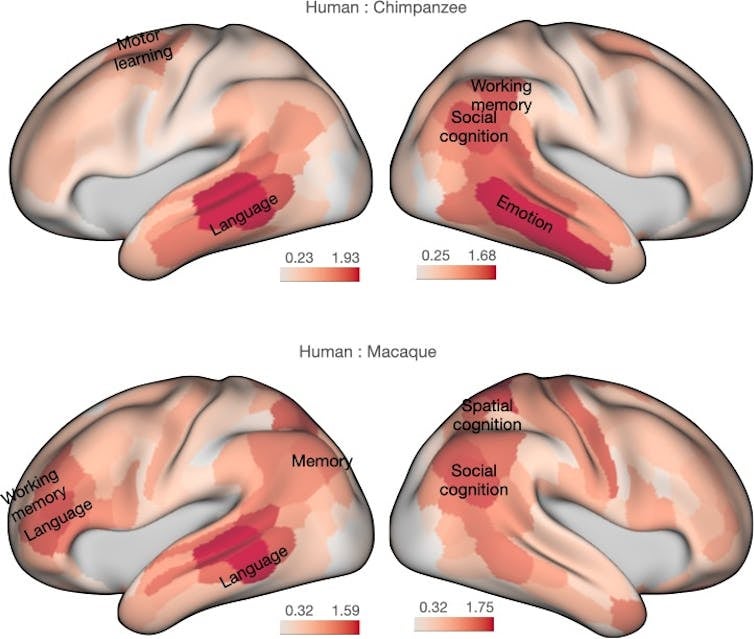
A better worth means the brains are extra completely different. JNeurosci/Rogier Mars and Katherine Bryant, CC BY-NC-ND
However the primary variations we discovered weren’t within the prefrontal cortex. They have been within the temporal lobe, a big a part of cortex situated roughly behind the ear. Within the primate mind, this space is dedicated to deep processing of data from our two principal senses: imaginative and prescient and listening to. One of the vital dramatic findings was within the center a part of the temporal cortex.
The function driving this distinction was the arcuate fasciculus, a white matter tract connecting the frontal and temporal cortex and historically related to processing language in people. Most if not all primates have an arcuate fasciculus however it’s a lot bigger in human brains.
Nonetheless, we discovered that focusing solely on language could also be too slim. The mind areas which can be related by way of the arcuate fasciculus are additionally concerned in different cognitive capabilities, corresponding to integrating sensory info and processing complicated social conduct. Our examine was the primary to search out the arcuate fasciculus is concerned in these capabilities. This perception underscores the complexity of human mind evolution, suggesting that our superior cognitive talents arose not from a single change, as scientists thought, however by a number of, interrelated adjustments in mind connectivity.
Whereas the center temporal arcuate fasciculus is a key participant in language processing, we additionally discovered variations between the species in a area extra in the back of the temporal cortex. This temporoparietal junction space is vital in processing details about others, corresponding to understanding others’ beliefs and intentions, a cornerstone of human social interplay.
In people, this mind space has far more intensive connections to different components of the mind processing complicated visible info, corresponding to facial expressions and behavioral cues. This means that our mind is wired to deal with extra intricate social processing than these of our primate family. Our mind is wired as much as be social.
These findings problem the thought of a single evolutionary occasion driving the emergence of human intelligence. As a substitute, our examine suggests mind evolution occurred in steps. Our findings counsel adjustments in frontal cortex group occurred in apes, adopted by adjustments in temporal cortex within the lineage resulting in people.
Richard Owen was proper about one factor. Our brains are completely different from these of different species—to an extent. We have now a primate mind, but it surely’s wired as much as make us much more social than different primates, permitting us to speak by spoken language.
This text is republished from The Dialog below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the authentic article.

