Necessities
- Reliable and scalable storage: To ensure seamless operations, the system must be designed to horizontally scale and accommodate increasing data volumes from various functions, thereby maintaining dependable performance and meeting Service Level Agreements (SLAs) with zero downtime or interruptions.
- Efficiency: To optimize performance, software requires a storage service that can effectively manage varying demands while maintaining low latency and high throughput, even in situations where usage patterns fluctuate wildly.
- The infrastructure group must clearly define, continuously monitor, and rigorously enforce stringent Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to ensure the reliability, scalability, and responsiveness of the storage service, thereby guaranteeing the required levels of efficiency and availability?
- Elevate value delivery: By harnessing intensive resources efficiently, the platform should strike a balance between cost effectiveness and quality while maintaining operational efficiency.
- Elevating user experience: Seamless entry and intuitive interaction with the storage system are vital components for streamlined access. Skilled builders from various organizations should find the system intuitive, featuring streamlined procedures for provisioning, seamless access, and effortless management of knowledge assets.
- Knowledge segregation and entry management: To ensure utmost safety and compliance, the platform must guarantee strict knowledge segmentation. To effectively prevent unauthorized access to sensitive information, robust and finely tuned entry controls are essential for segregating disparate functional areas.
Further issues
- Knowledge governance is crucial because a centralized storage platform must comply with established policies to ensure the integrity, quality, and regulatory compliance of stored data?
- A reliable backup and disaster recovery strategy is essential, providing assurance against data loss and facilitating swift business continuity in the event of an outage or cyberattack.
- The platform should provide adaptable features that accommodate diverse software requirements, including support for various data formats and structures, as well as offer customisation options tailored to specific software needs?
- Ongoing monitoring and optimisation are crucial to ensure the sustained effectiveness of the platform, proactively addressing potential issues to maintain optimal performance and efficiency.
Operational knowledge retailer
A Data-as-a-Service (DaaS) platform, operating as an operational knowledge hub, aggregates disparate data sources into a unified repository, providing a seamless gateway for diverse business applications. The integration of disparate data sources to provide a comprehensive understanding of customer behavior is crucial for functions such as buyer 360 software, aggregating information from CRM, order management, support systems, and more, thereby offering a holistic view.
Structure
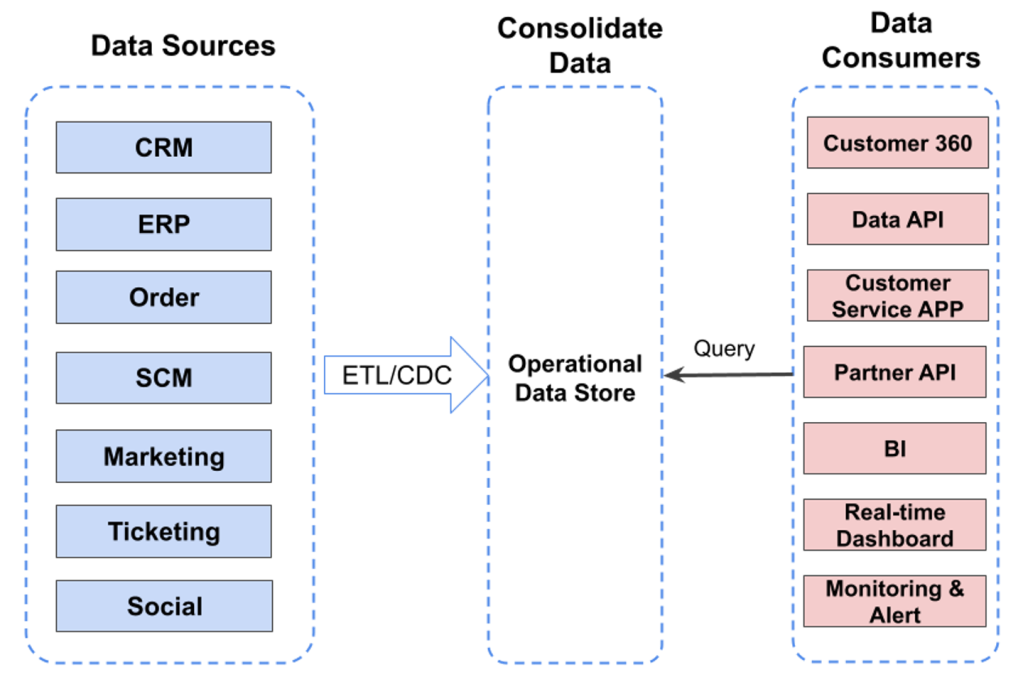
IDG
The typical architecture comprises three fundamental components: knowledge repositories, a central data warehouse (ODS), and end-user consumers. Data from various systems, including CRM, ERP, and SCM, is aggregated in the ODS via Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) procedures or Change Data Capture (CDC) methods, making it accessible for querying and analytics through multiple data consumer applications.
Necessities
- Effective data unification through efficient ETL/CDC processes ensures seamless integration of diverse knowledge sources while ensuring the highest standards of quality and consistency.
- Consolidating and transforming knowledge, the central repository ensures seamless access, presenting information in a readily consumable format that meets diverse functional needs.
- Low-latency data access enables real-time insights by quickly processing and serving information requests, fostering timely decision-making and swift action.
- To deliver optimal user experiences, the system must efficiently handle numerous customers posing complex inquiries without compromising performance and introducing latency?
- Knowledge security and privacy: With a centralised platform, it is crucial to implement robust safeguards and privacy protocols to protect sensitive information and conform to regulatory requirements.
- Scalable and dependable infrastructure is crucial, as the central hub for organisational knowledge must be able to handle increasing knowledge volumes while ensuring consistent availability?
Further issues
- Proactive knowledge governance demands the establishment of crystal-clear insurance policies and procedures, ensuring seamless management throughout the entire information lifecycle, thereby fostering transparency, accountability, and regulatory compliance.
- The platform should be capable of providing advanced analytics and robust business intelligence capabilities, delivering actionable insights across the organization.
- Customisable entry patterns: The platform’s ability to adapt to diverse requirements is crucial, as various functions may necessitate distinct entry patterns to ensure seamless operation.
- Monitoring and alert capabilities should encompass comprehensive detection and response mechanisms to ensure prompt identification and resolution of issues, thereby maintaining system health and data integrity?
Multi-tenant software design patterns
| SaaS software | Exterior tenant | A few hundred | Scale effortlessly across a diverse range of buyers and personas while ensuring rock-solid multi-tenancy, robust security, and steadfast compliance with Service Level Agreements (SLAs), all within the framework of an agile architecture. | 1. Large tenant rely 2. Tenant Isolation 3. Whole price 4. Schema adjustments 5. Availability 6. Scalability of a vast array of enormous tenants. |
| Centralized storage platform | Inside tenant | Tens to hundred | Streamline a diverse range of database scenarios within a secure and fiscally responsible framework. That is database consolidation. | 1. Scalability for big companies 2. Reliability for important companies 3. Elevating efficiency for large volumes of non-strategic entities 4. What are the costs associated with maintaining our database platform? |
| Operational knowledge retailer | Many tenants possess a shared body of knowledge. Isolating writing ingestion and processing tasks for separate tenants reduces the risk of cross-tenancy data contamination. | 1. Scalability 2. Flexibility in querying knowledge 3. The relationship between ingestion pace and its impact on learning? 4. Navigating Complex Queries Across Comprehensive Knowledge Bases Isolation between the companies 1. Scalability 2. Flexibility in querying knowledge 3. The impact of ingestion pace on learning? 4. Eliciting precise information from vast repositories of knowledge often proves daunting, as intricate questions necessitate a deep understanding of interconnected concepts and nuanced relationships. 5. Isolation between the companies |
Multi-tenant knowledge administration design patterns
Now that we’ve defined the key scenarios for multi-tenancy, let’s explore various architectural designs that cater to distinct requirements.

