In recent months, the Telegram-based game Hamster Kombat has catapulted to unprecedented popularity among cryptocurrency enthusiasts. While the straightforward gameplay, revolving around repetitive touchscreen taps on a player’s mobile device, may be accessible, enthusiasts of Hamster Kombat are driven by a singular desire: the prospect of amassing substantial earnings when its developers introduce their anticipated cryptocurrency tie-in, linked to the game.
The sport’s popularity has spawned a plethora of imitators, with multiple games duplicating its name, logo, and engaging gameplay mechanics, blurring the lines between originality and imitation. While our initial findings were benign, they still posed a threat to monetize in-app advertisements.
Cybercriminals have been capitalizing on the popularity of Hamster Kombat by exploiting its reputation. We uncovered a multitude of threats leveraging Hamster Kombat’s popularity in unofficial channels, including remote-controlled Android malware distributed through a fake Telegram channel, rogue app stores dispensing unwanted ads, and GitHub repositories masquerading as automation tools for the game while secretly deploying Lumma Stealer on Windows devices.
- Malicious actors, drawn to Hamster Kombat’s popularity, are exploiting user curiosity to line their own pockets through illicit means.
- Researchers at ESET have uncovered a malicious Android application, dubbed Ratel, masquerading as the popular mobile game Hamster Kombat, which was disseminated through an unauthorized Telegram channel.
- Consumers of Android devices are increasingly targeted by fraudulent app stores that masquerade as legitimate sources for popular games but instead provide unwanted advertisements.
- Windows users may inadvertently stumble upon GitHub repositories featuring farm bots and auto clickers that secretly conceal Lumma Stealer cryptocurrency malware.
What’s Hamster Kombat?
Hamster Kombat is a popular in-app Telegram-based clicker game where players accumulate virtual currency by completing straightforward tasks, featuring daily login rewards that encourage regular engagement. In the vein of popular clicker-style mobile games, Hamster Kombat’s core gameplay revolves around rapid-fire tapping on the screen to accumulate valuable rewards and boost in-game currency. Refer to Figure 1 for a visual representation of the sport’s interface.
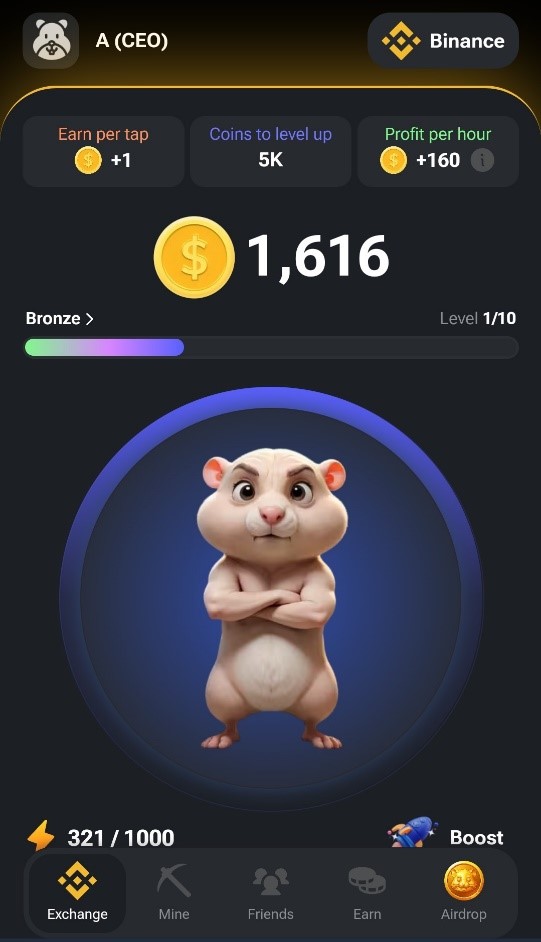
Launched in March 2024, Hamster Kombat has been building a reputation at an impressive pace since its inception. By June 2024, the builders reported that their recreational platform had already achieved a milestone of 150 million active users. Considering that Hamster Kombat, a game specifically designed for cryptocurrency enthusiasts available only through Telegram, is vying to join the ranks of the top 20 mobile games of all time, its claim should be viewed with skepticism. Despite its niche appeal, Hamster Kombat remains remarkably popular: the official game on Xbox boasts over 10 million followers, while the Hamster Kombat Channel has garnered more than 50 million subscribers to date.
The catalyst driving the sudden surge in interest around Hamster Kombat lies primarily in players’ desire to monetize their entertainment through gameplay, as the game is poised to introduce a new cryptocurrency token directly linked to its in-game economy. Tokens should then be dispersed to players according to specific criteria, commonly referred to as a distribution system.
The team behind Hamster Kombat seemingly seeks to replicate the success of Notcoin, a Telegram-based game that debuted on TON’s blockchain platform, The Open Network, with the NOT token’s launch in May 2024 and subsequent airdrop to players based on their in-game rankings. Notably, Token’s launch was exceptionally successful, marking the biggest crypto-gaming-token debut of 2024 thus far.
The Hamster Kombat token drop is expected to leverage the vast network of the TON community. Compared to Notcoin, the number of tokens obtained will vary in overall ratings but differ in specific aspects, such as profit per hour.
Menace evaluation
The inevitable consequence of Hamster Kombat’s popularity is the emergence of cybercriminals, who have swiftly launched malware attacks targeting unsuspecting players of the game. ESET analysis has revealed that threats are targeting both Android and Windows users. Malicious actors target both Android users, bombarding them with adware and fake app stores teeming with unwanted ads, and Windows users, who may unknowingly download GitHub repositories containing the dangerous Lumma Stealer cryptor.
As a lucrative opportunity seemingly requiring minimal exertion, this cyber endeavor has piqued the interest of both cybersecurity professionals and law enforcement officials, who caution against the financial risks inherent in pursuing it. So far, ESET has detected no malicious activity related to this specific app.
Android threats
Two types of threats were identified and examined, specifically targeting Android users: malicious applications incorporating the Android adware Ratel, as well as fake websites pretending to be app store interfaces, falsely claiming to offer Hamster Kombat for download.
Ratel adware
According to ESET researchers, a malicious Telegram channel is spreading Android adware, masquerading as “Hamster Kombat” and available at https://t.me/hamster_easy, as illustrated in Determine 2.
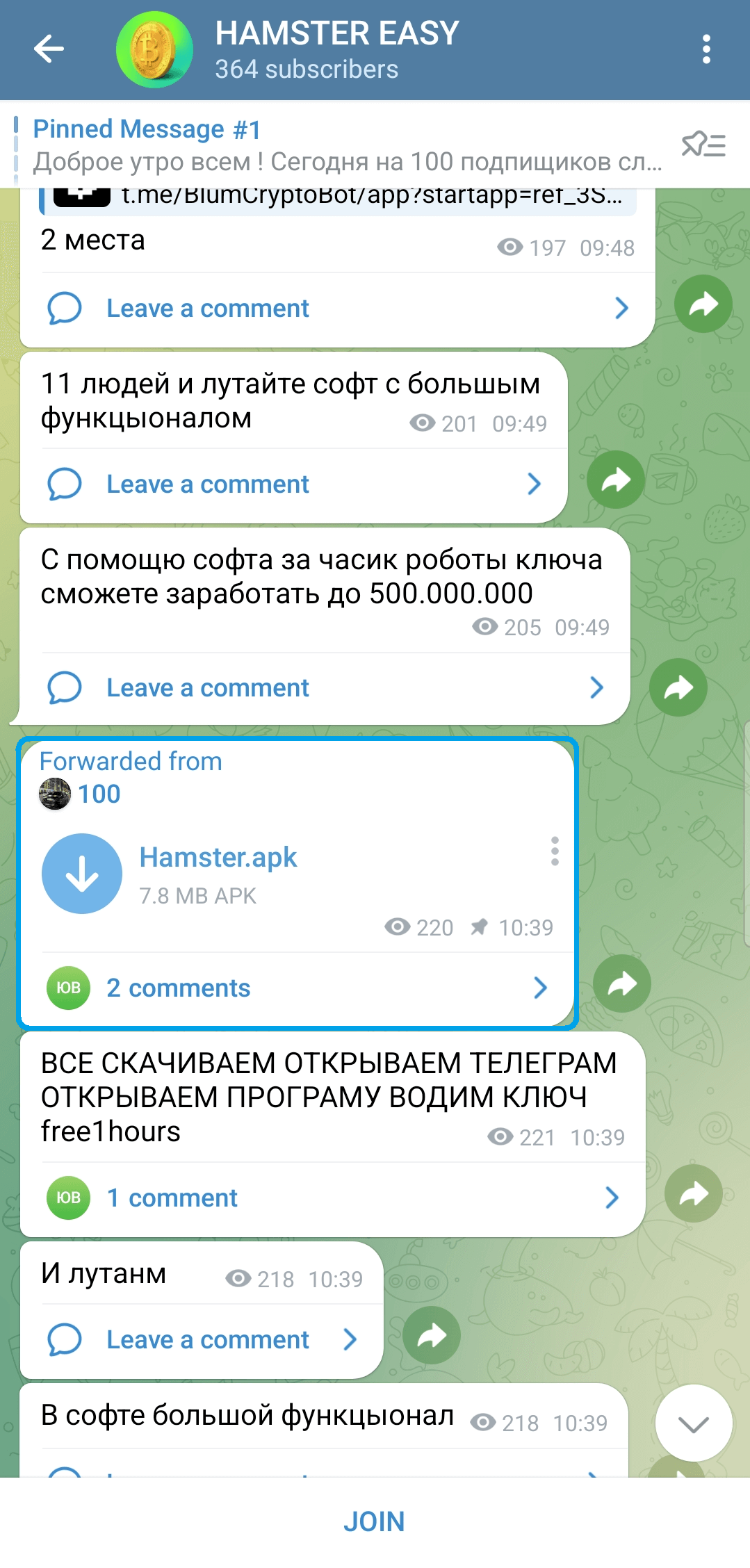
This malicious software can pilfer notifications and dispatch SMS communications. Malware operators exploit the compromised device’s performance to secretly fund their operations by using the victim’s money without detection.
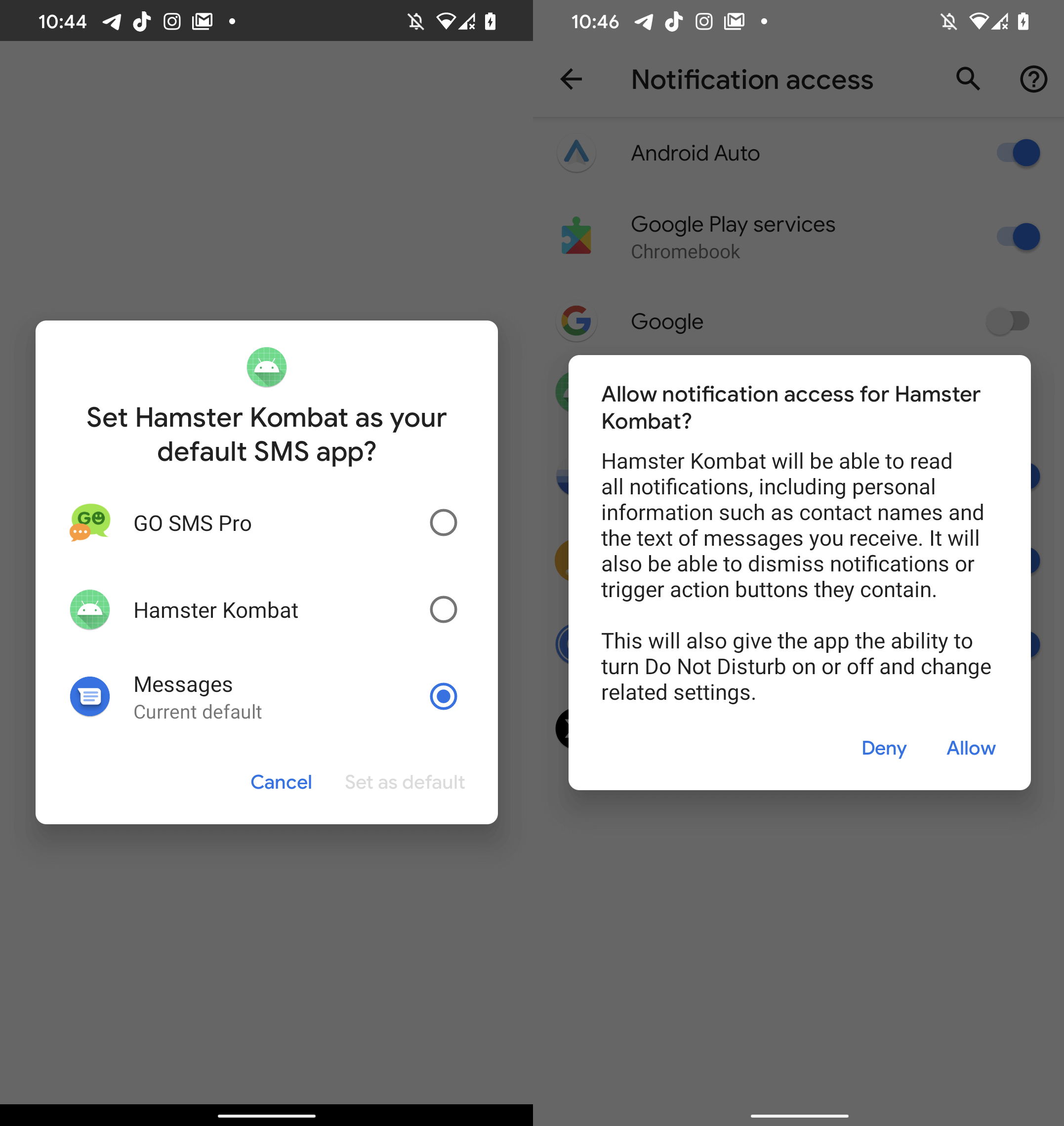
While masquerading as Hamster Kombat, this insidious application deceives unsuspecting users by incorporating none of the game’s touted features, rendering it eerily devoid of both gameplay and user interface. Upon launching, the app prompts for notification access permission, with the additional request to become the default SMS application. Once permissions are granted, the malware gains access to all SMS messages and is poised to intercept all displayed notifications.
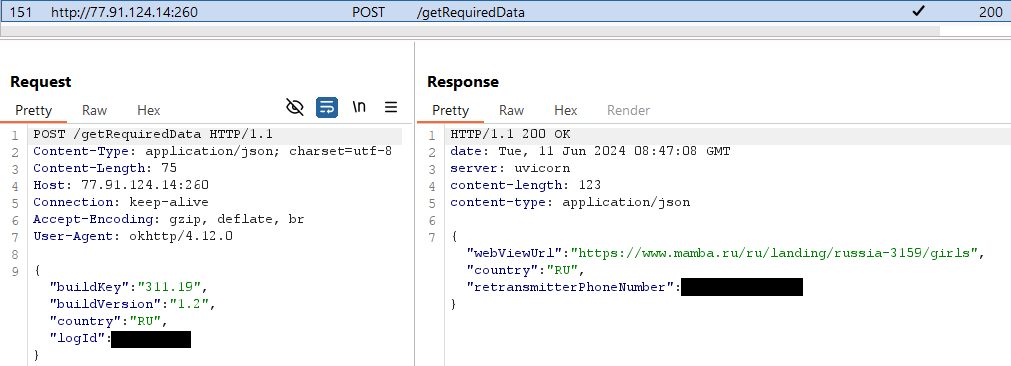
Ratel then initiates communication with its C&C server (), and as a response, receives a telephone quantity: see Determine 4. What’s up! I’ve identified a suspicious phone number belonging to the malware operators: 1-800-CRIMESITE?
When the malicious actors gain control of the compromised system, they reveal an alarming ability to manipulate it through SMS messages: these operators can craft text-based commands that are transmitted directly to a designated phone number, with the power to initiate calls as well. The malware is designed to extract sensitive information from victims, including current bank account balances, by sending a deceptive text message claiming to provide account updates, seemingly originating from a trusted source such as “900” and purporting to offer details like “(translation: balance)”. The investigation is likely being conducted to determine whether pursuing further assault tactics would be effective in accessing the victim’s funds.
Ratel exploits notification entry permissions, exploiting access to notifications from more than 200 apps, relying on a predetermined list. The checklist features applications comparable to Telegram, WhatsApp, and various other Short Message Service (SMS) messaging platforms. When a system receives a notification from an app listed in the checklist, the individual impacted will not be able to view it. Hiding is the one motion the malware does with these notifications; they don’t seem to be forwarded to the C&C server. It appears that the primary objective of intercepting notifications is likely to prevent victims from becoming aware of confirmation messages sent by subscription service providers.
As proven in Determine 5, in case there’s a notification from an app not included within the checklist, Ratel lets the person see it, whereas additionally forwarding it to the C&C server. We anticipate that this process will be finalized so that operators can assess whether a new app should be included on the list.
Pretend web sites
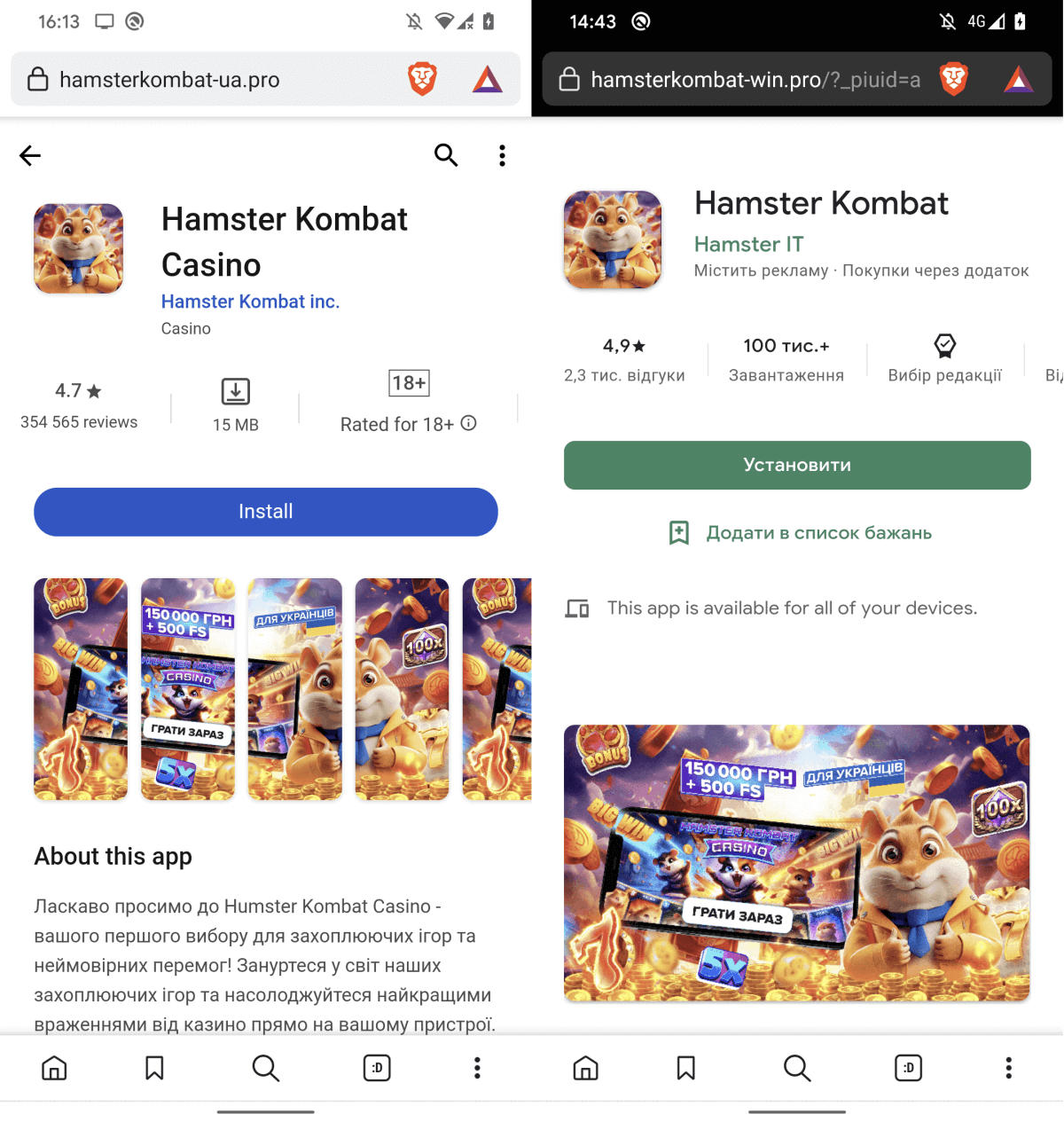
Additionally, our research uncovered fake software storefronts masquerading as legitimate sources of Hamster Kombat for download, often bundled with the notorious Ratel adware. Despite this, simply clicking the “or” and “or” buttons alone directs users to irrelevant advertisements. The improved text would be:
The following examples of hypothetical websites are presented in Determination 6.
Home windows threats
Despite being a mobile game, Hamster Kombat has also seen its name exploited by malicious actors to spread malware on Windows systems. Crooks try to deceive Windows users by offering ostensibly helpful tools that promise to simplify in-game revenue maximization, targeting unsuspecting gamers.
Our investigation uncovered GitHub repositories offering custom-built Hamster Kombat farm bots and autoclickers, which serve as automation tools for games by simulating mouse clicks. The repositories have inadvertently concealed malicious code linked to the notorious Lumma Stealer malware.
Is an info-stealing malware available for purchase as a service on the darknet and Telegram platforms? Noticed initially in 2022, this malware typically spreads through pirated software and spam, with a focus on compromising cryptocurrency wallets, personal credentials, two-factor authentication browser extensions, and other sensitive data. Word that Lumma Stealer’s capabilities will not be coated by the MITRE ATT&CK matrix on this blogpost, for the reason that focus is on the cryptors that ship this infostealer, not on the infostealer itself.
The GitHub repositories we uncovered immediately exhibited malicious content in their launch notes or provided links to external file-sharing platforms for downloading. Three distinct variants of Lumma Stealer malware were identified across various repositories, comprising C++, Go, and Python-based implementations. Only the Python-based applications feature a fully functional graphical user interface (GUI).
C++ purposes
In the context of C++ applications, the Lumma Stealer malware is encrypted using the RC4 cipher and embedded within the executable file that the victim downloads. As soon as executed, the malware injects Lumma Stealer into the newly created process.
Go purposes
To embed the Lumma Stealer within a Go executable for use cases, consider incorporating it directly into the compiled binary, encrypting it using AES-GCM for added security. The crypto malware leverages copied and obfuscated code from a well-known Go library for parsing Portable Executable (PE) information, utilizing this functionality to extract metadata from executable files bearing the .exe extension found in the directory listings.
Python purposes
The Python packages have been both bundled with and compiled into a single executable. Upon executing the file retrieved from the GitHub repository, a deceptive installation prompt appears, featuring a single “Install” button, as illustrated in Figure 8. When the button is clicked, this system establishes a connection to a remote FTP server and retrieves a password-encrypted ZIP file (password: [insert password]) containing the cryptor with Lumma Stealer integrated within. Upon investigating the FTP server, we found evidence of C++ and Go-based cryptographic payloads, suggesting a strong likelihood that these distinct implementations belong to the same malicious family.
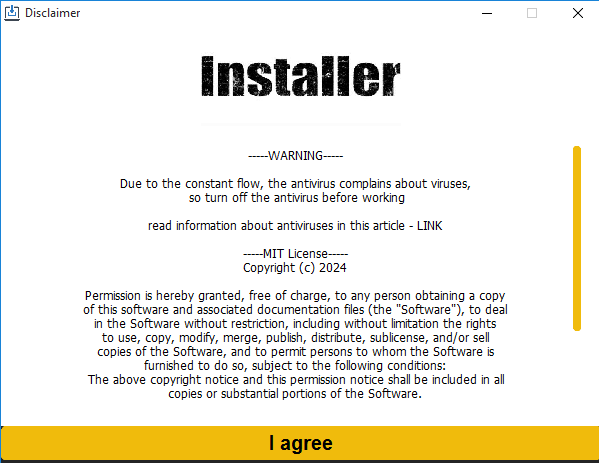
As soon as the window is closed, the cryptor sends the C&C server the timestamps of when the sufferer clicked on the I agree button and when the malware was run. This information is shipped solely as soon as and there’s no additional C&C communication involving the cryptor. As proven in Determine 9, we discovered a remark [] within the Python supply code of the malware, that means that most likely the information is shipped from the C&C to the operators’ Telegram account or channel in some unspecified time in the future.

Conclusion
While Hamster Kombat’s reputation has made it a potential target for exploitation, its vulnerability to misuse suggests that it may attract more unsavory characters in the future. While numerous imposter Hamster Kombat games appear harmless, our investigation uncovered a remote-controlled Trojan being spread through Telegram, masquerading as a game. The malware has the ability to send SMS messages, initiate calls, and conceal its activity by suppressing notifications that might otherwise alert the system to potential compromise. Beyond the Android malware, our investigation also uncovered fake app stores peddling Hamster Kombat for download; unfortunately, these links often lead to unwanted advertisements instead. On the Windows platform, investigators discovered a sinister tactic: GitHub repositories luring gamers with promises of Hamster Kombat farm bots and autoclickers, only to unleash a payload of malware featuring the notorious Lumma Stealer.
In recognition of his outstanding contributions.
IoCs
A comprehensive list of Indicators of Compromise (IoCs) and corresponding samples shall be made available in.
Information
| Android/Spy.Ratel.A | Android malware impersonating Hamster Kombat. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HWZI | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players compromises Home Windows systems. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXDB | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players found in home Windows systems? | ||
| WinGo/TrojanDropper. | A malicious software targeting players of Hamster Kombat on Home Windows? | ||
| WinGo/TrojanDropper. | Windows malware targeting Hamster Kombat players. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXIB | Windows malware targets Hamster Kombat players? | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXIB | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players detected in home Windows systems? | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXIB | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players infects home Windows systems. | ||
| WinGo/Agent.VY | Malware specifically targeting Home Windows users who play Hamster Kombat has been detected. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXIB | Windows malware targets Hamster Kombat enthusiasts. | ||
| Win32/GenKryptik.GXGC | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players spreads through compromised home Windows systems. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXDV | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players found in home Windows systems. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXCA | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players spreads through compromised Windows systems. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXIB | A new type of malware targets Hamster Kombat players through compromised home Windows systems? | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXDB | Windows malware targets Hamster Kombat enthusiasts. | ||
| Win32/Kryptik.HXDB | Windows malware targets Hamster Kombat players? | ||
| Python/TrojanDownloader. | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat players compromises home Windows systems. | ||
| Python/TrojanDownloader. | A newly discovered Windows malware specifically targets Hamster Kombat players, exploiting a vulnerability in the popular gaming software. | ||
| Python/TrojanDownloader. | Malware targeting Hamster Kombat enthusiasts in Windows homes. |
Community
| N/A | Daniil Yevchenko | 2024‑05‑11 | Android/Spy.Ratel.A C&C server. | |
| Amazon.com, Inc. | 2024‑06‑08 | Pretend web site. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑06‑13 | Pretend web site. | ||
| N/A | N/A | 2024‑06‑10 | Pretend web site. | |
| N/A | N/A | 2024‑06‑04 | Pretend web site. | |
| N/A | N/A | 2024‑06‑04 | Pretend web site. | |
| N/A | N/A | 2024‑06‑16 | Pretend web site. | |
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑04‑13 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑04‑14 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑04‑13 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑04‑13 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑26 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑26 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑26 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑26 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑06‑07 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑06‑07 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑06‑07 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑06‑07 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑30 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑25 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑06‑12 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑29 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑30 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑29 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑26 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑17 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑18 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑18 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑29 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| Cloudflare, Inc. | 2024‑05‑29 | Lumma Stealer C&C server. | ||
| N/A | Cloud Internet hosting Options, Restricted. | N/A | Home windows malware concentrating on Hamster Kombat gamers C&C server. |
Code-signing certificates
| NVIDIA Company | |
| NVIDIA Company | |
| Santa Clara | |
| N/A | |
| US | |
| 2023-01-13 00:00:00 | |
| 2026-01-16 23:59:59 |
MITRE ATT&CK methods
This desk was constructed utilizing of the MITRE ATT&CK cellular methods.
| Phishing | An Android malware variant called Ratel has been spreading via an unofficial Telegram channel, targeting unsuspecting users. | ||
| Occasion Triggered Execution: Broadcast Receivers | Android adware Ratel registers to receive the device’s , , , , , and broadcast intents in order to activate itself promptly. | ||
| Entry Notifications | Android adware Ratel can collect messages from a wide range of applications. | ||
| Out of Band Information | Android adware, known as Ratel, leverages SMS functionality to receive commands for execution. | ||
| Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | A newly discovered Android malware, dubbed Ratel, steals sensitive data by exploiting HTTP protocol vulnerabilities. | ||
| Name Management | A newly discovered Android malware, dubbed Ratel, has the capability to make telephone calls without the user’s knowledge or consent. | ||
| SMS Management | The Android adware known as Ratel has been found to possess the capability of sending and retrieving SMS messages. |
This desk was constructed utilizing of the MITRE ATT&CK cellular methods.
| Encoded Intelligence or Concealed Data Packs | The Lumma Stealer malware leverages a combination of C++ and Go programming languages to seamlessly integrate its malicious payload within the embedded binary files. | ||
| Courses of injection and hollowing are distinct phenomena. | The Lumma Stealer employs a technique called hollowing to achieve its purpose. | ||
| Utility Layer Protocol: Internet Protocols | Lumma Stealer communicates with the C&C server by way of HTTP | ||
| The utility layer protocol for file switching protocols? Here’s a revised version: File Transfer Protocols (FTP), Simple File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), and Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) form the foundation of file transfer systems, enabling secure and reliable data exchange between devices over networks. | The Lumma Stealer downloader leverages FTP to procure the payload. | ||
| Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | Lumma Stealer exfiltrates the sufferer’s information to the C&C server. |
Appendix
The Ratel malware conceals notifications from these purposes.
| |

