As severe weather events like atmospheric rivers and tornado outbreaks swept across the country, it’s eerily reminiscent of what homebuyers experienced in March. Despite “turbulent” aptly describing the market’s volatile nature since the Fed began hiking interest rates a year ago, things reached a frenzied pitch last month, largely driven by three bank failures that sparked global panic, triggered significant deposit outflows, and precipitated a sudden but severe downturn as a crisis of confidence seized world markets. Despite the excitement surrounding March Madness, the first quarter ultimately proved decisive in determining the victor. The ROBO International Indexes continued their upward trend, with all indicators flashing green across the board.
Does this 20th-century model of progress truly have a lasting shelf life? While recent events have highlighted certain peculiarities, we believe it’s challenging to convincingly argue that the system itself is imperiled by anything beyond more stringent global economic conditions – although these would undoubtedly be significant. Despite technology’s dominant role in driving recent market trends and expertise seemingly plateauing – what’s to halt sustained, rapid growth if the Fed’s established tactics fail to temper investors’ exuberance? A closer examination of events that transpired during this quarter may yield valuable insights.
In light of a precipitous decline in rate-of-interest expectations during 2022, the Q1 landscape was defined by an implied reversion from prior market dynamics. As cracks begin to emerge within the banking system, accompanied by easing inflationary pressures and signs of a potential slowdown in US consumer spending, market participants are increasingly predicting that the Federal Reserve’s hiking cycle may be nearing its end within the current year. Simultaneously, a notable turnaround occurred in stock valuations, as many of the biggest 2022 losers transformed into top performers in the first quarter. While the development shares regained their market prominence, fueled by mega-cap tech, unprofitable tech, and pricey software stocks, smaller companies, healthcare, and defensive sectors lagged behind. Within the US, mega-cap tech shares returned a whopping +31%, with the remainder of the S&P returning simply +2%.
The first quarter’s performance in the ROBO International Indexes underscored the remarkable growth prospects and developmental momentum of companies driving innovation in robotics, artificial intelligence, and healthcare technologies.
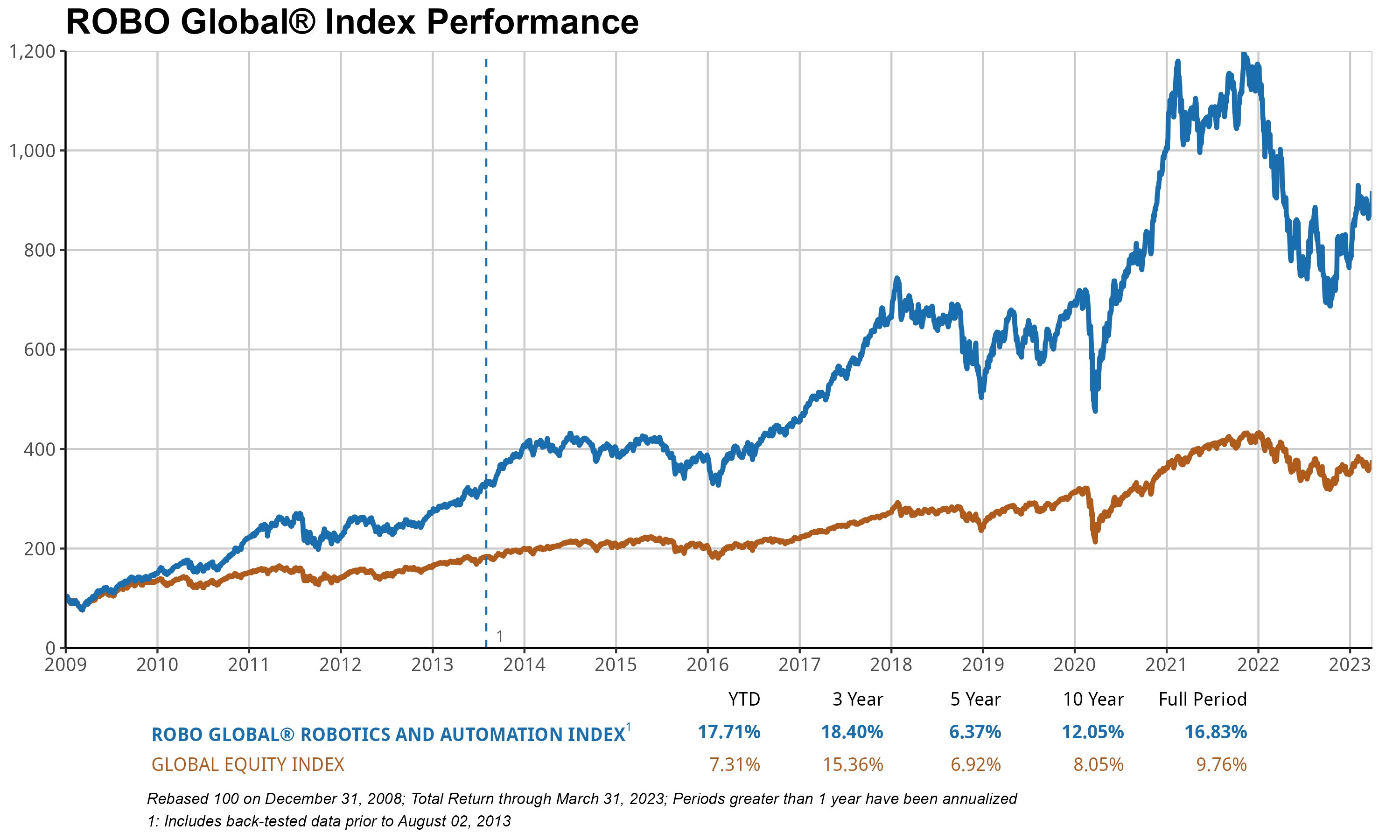
The ROBO International Robotics & Automation Index (ROBO) logged double-digit share positive factors for the second consecutive quarter, returning +17.71% and handily outperforming the 7.3% acquire for the MSCI AC World Index (ACWI)1 Surpassed by more than a 10 percentage point margin throughout the quarter. The ROBO index of best-in-class robotics and automation equities world wide was led by robust positive factors in Computing & AI (+25%), Actuation (+22%), and Logistics Automation (+18%), whereas European (+12%) and Healthcare (+4%) shares lagged.
In a quarter marked by market volatility, AI and semiconductor stocks proved resilient, with iFlyTek’s explosive gain of +95% leading the charge, followed closely by Nvidia’s impressive performance at +90%, while International Unichip and Samsara also notched notable gains of +71% and +59%, respectively. As generative AI innovations, the ChatGPT phenomenon, and advancements in groundbreaking capabilities have converged, a palpable sense of revitalized enthusiasm has spread throughout the community, prompting valuations to surge to unprecedented heights once again. Nvidia’s market capitalization is currently trading at a premium of approximately 60 times its forward earnings, a valuation multiple that is unusually high even by the standards of the technology sector.2 and a staggering 24.5 times gross sales, remarkably close to its 2021 record of 70x P/E ratio3.
While the majority of the portfolio exhibits relatively modest valuations compared to other areas, cyclical shares within industrial end-markets such as manufacturing and industrial automation, with a price-to-earnings ratio of 17 times, food and agriculture at 16 times, and Japanese shares at 15 times, stand out for their particularly low cost. Non-US shares, comprising 56% of the ROBO portfolio, exhibit a significant valuation disparity compared to US shares, trading at an attractive low multiple of 18x versus their US counterparts’ more expensive 36x. In Japan, this phenomenon holds remarkable significance. Japanese corporations, which comprise 22% of the ROBO index and hold a mixed 40% stake in the world’s industrial robotic market, are well-positioned to capitalize on China’s sturdy financial recovery following its chaotic exit from COVID-19 restrictions, as well as the dramatic depreciation of the Japanese Yen, which will yield a substantial value boost and potentially lead to margin expansion.
ROBO’s forward-looking P/E ratio stands at 26x, significantly different from its historical average of around 24x since inception roughly a decade ago, and even lower than the 36x peak reached in 2021. Meanwhile, earnings growth remains resilient compared to broader market indexes, with projections indicating a 10% increase in earnings per share.4 EPS is expected to improve in 2023, mirroring the notable growth observed in 2022, with a robust 8% increase in gross sales aligned with our long-term trajectory. The increasing interest in automation technology appears to manifest its energy demand. As adoption accelerates across increasingly diverse sectors of the financial landscape.
Regardless of the speedy improve in the price of capital, M&A exercise is powerful within the Robotics & Automation area, with two index members, Stratasys and Nationwide Devices, receiving takeover bids because the begin of 2023. Since 2013, takeover attempts against ROBO index members have totalled 30, averaging roughly three per year.
As part of the quarterly rebalancing process, March witnessed three notable changes to the ROBO index: Symbotic was added, while Amano and Shenzhen Inovance were removed from the roster. It is likely that Symbotic has rapidly established itself as a pioneer in logistics and warehouse automation due to its comprehensive solution for automating pallet processing and case handling for retailers. Over a remarkably short period, the company has accumulated an astronomical order backlog valued at more than $12 billion, spanning over 170 programs – the majority of which are in partnership with Walmart.5. Despite Amano’s limitations in income and expertise management, it ultimately fell out due to those deficiencies, while Shenzhen Inovance was disqualiied following an increase in foreign ownership that effectively rendered it no longer eligible for further consideration. Since listing on the ROBO index in 2019, Shenzhen Inovance has yielded a remarkable 279% return, an impressive performance that has underscored its growth potential.
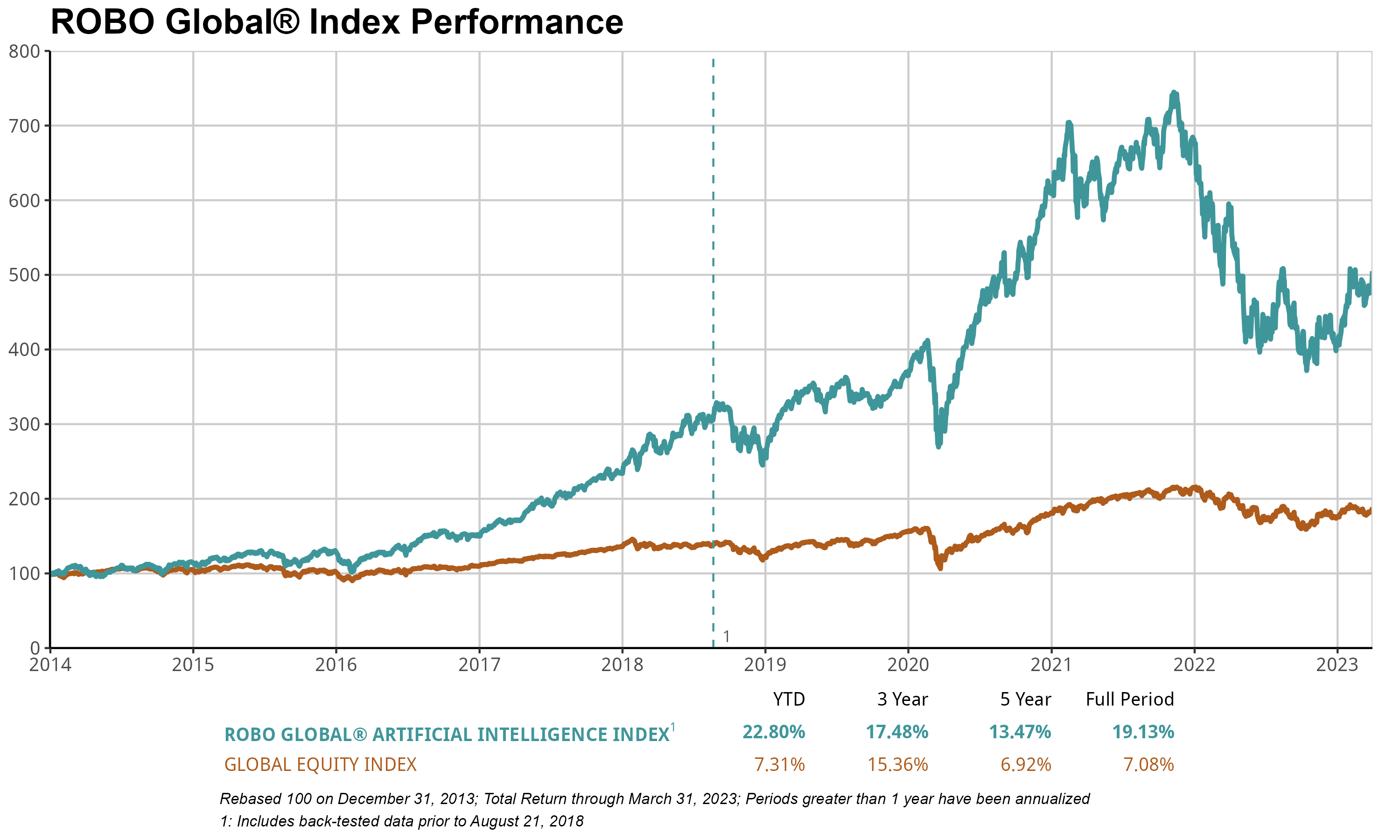
The Robo International Synthetic Intelligence Index (THNQ) surged 22.8% in the first quarter, a significant outperformance of the ACWI, which rose by just 5%. The rapid progress of ChatGPT has sparked widespread enthusiasm, leading us to conclude that a strategic approach like THNQ is well-positioned to capitalize on the unfolding transformation of this landscape. As many of the world’s most influential thought leaders have posited, artificial intelligence represents the most revolutionary technological advancement of our era. Companies are increasingly leveraging artificial intelligence to unlock the vast potential of diverse knowledge and streamline operations across all facets of business, transcending industry boundaries. The comprehensive checklist of functions boasts an impressive scale.
ChatGPT, a prominent member of the generative pre-trained transformer (GPT) family of language models, has garnered widespread acclaim in recent years for its remarkable ability to produce human-like text. This type of artificial intelligence uses machine learning algorithms to analyze vast amounts of text-based data, generating responses in a conversational manner. The primary driver behind the ChatGPT phenomenon lies in its ability to engage in genuine, captivating discussions with clients. The AI system potentially acknowledges and responds to diverse topics and could possibly produce tailored reactions grounded on individual input. This versatility renders it an ideal tool for tasks comparable to customer service, conversational AI, and generating content for online platforms or websites. Another factor contributing to ChatGPT’s acclaim is its ease of adoption, with a user-friendly interface requiring little to no initial configuration. As a result, software developers and companies are increasingly integrating ChatGPT into their offerings, making it more widely available and accessible to a broader audience.
Nvidia is widely regarded as the undisputed leader in artificial intelligence (AI), a field expected to experience explosive growth in the near future. According to a recent report, the global AI market has been valued at $119 billion in 2022 and is forecasted to surge to $1.59 trillion by 2030, driven by an estimated compound annual growth rate of6 What will be the compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of a specific value between 2022 and 2030? The drivers of this development span a vast landscape of AI applications, encompassing industries such as healthcare, finance, retail, automotive, and many others. As AI’s digital “goldrush” gains momentum, NVIDIA assumes its role as leading AI chip provider, equipping the industry with the essential tools to strike gold.
NVDA’s AI portfolio encompasses a comprehensive range of hardware and software solutions, spanning from NVIDIA GPU Cloud, focused on cloud-based applications, to NVIDIA Jetson, targeting autonomous machines, to NVIDIA TensorRT, optimizing high-performance deep learning. The corporation reported a remarkable 90-plus percent increase in 1Q performance, driving the THNQ index to notch consecutive double-digit gains for the quarter.
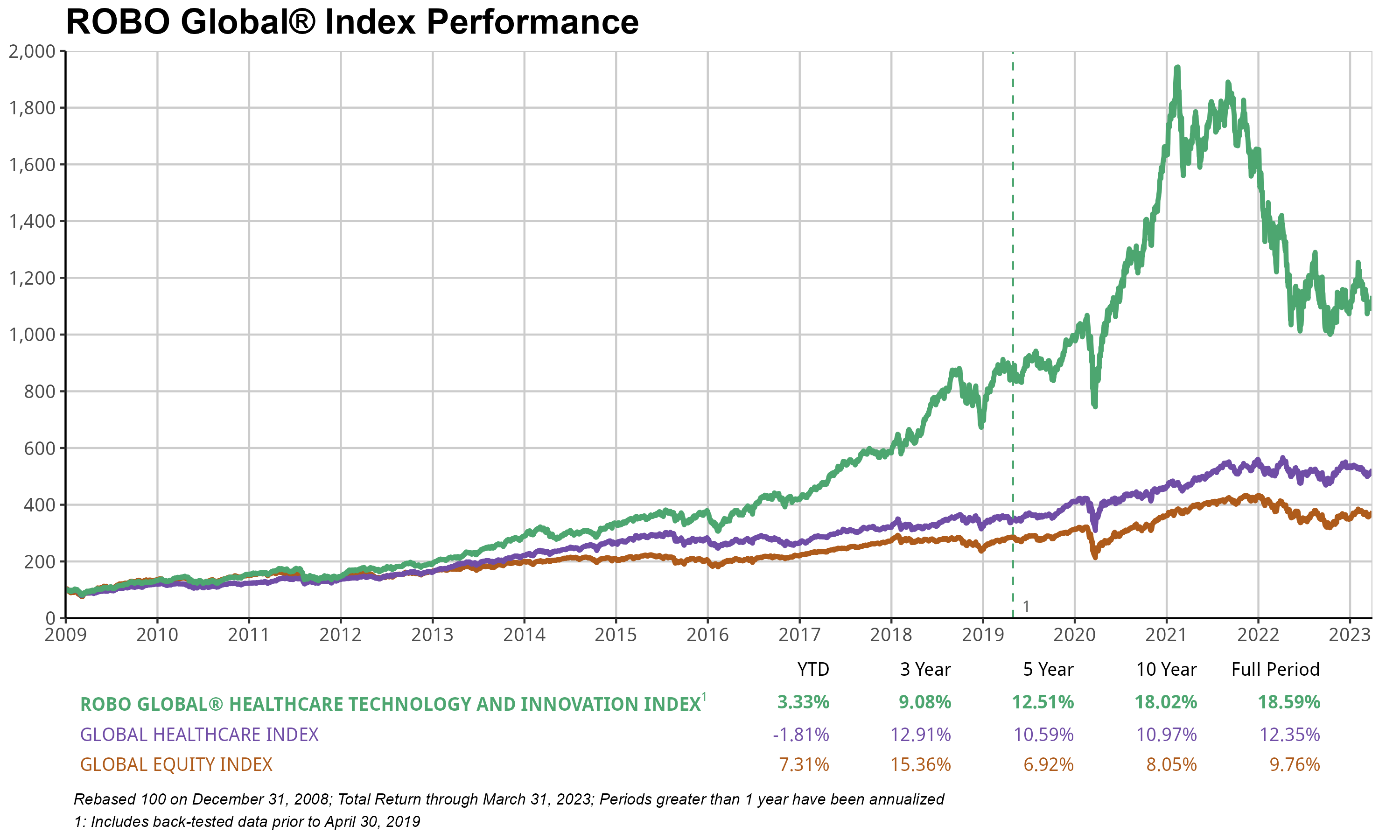
The ROBO International Healthcare Know-how & Innovation Index (HTEC) gained +3.18% in 1Q, barely underperforming ACWI’s +5% acquire. While optimistic positive factors in Information Analytics drove growth (+12%), the impact was tempered by underperformance from Regenerative Medicine (-17%) and Precision Medicine (-13%). Importantly, we witnessed significant innovation milestones throughout the quarter, including Vertex’s collaboration with CRISPR Therapeutics, which builds on its focus of developing cell and genetic therapies to eradicate critical diseases. A new licensing agreement between the two companies will accelerate the development of Vertex’s hypo-immune cell therapies for the treatment of type 1 diabetes, a crucial step in cementing their leadership in these modalities as they expand their broad gene and cell-based therapeutics portfolio.
Natera’s announcement of enhanced MRM capabilities came surprisingly soon, within six months of securing VA approval for its minimal residual disease monitoring solution. A novel molecular diagnostics program (MolDX) has expanded its coverage to include Signatera’s molecular minimal residual disease (MRD) testing for patients with stage IIb or higher breast cancer, encompassing HR-positive, HER2-negative, triple-negative, and other subtypes. This move builds upon MolDX’s existing colorectal, bladder, and pan-cancer monitoring offerings, further solidifying its position in the market. The announcement has sparked a positive impact on both top- and bottom-line projections for 2023 and beyond, driven by the average selling price (ASP) of approximately $5,500.7 (ASP) is predicted to range from $2,500 to $3,500, with tens of thousands of eligible patients annually, potentially generating $30 million in accretion this year – a possible 3-5% increase to the top line relying on adoption velocity. The outcome: the stock soared 17% upon announcement.
As catastrophic climate fluctuations intensify across the United States and worldwide, it’s futile to expect respite from turbulent weather patterns in the near future. As crises unfold, the propensity for consumers to respond with caution remains unwavering. As simultaneously as ever, it’s evident that technology brings value to nearly everything it encounters; consequently, when companies deliver technologies driving value, customers ultimately enjoy the benefits. Despite short-term market fluctuations triggered by financial systems, the Fed, or unforeseen events, investors should focus on long-term opportunities in sectors such as robotics, automation, and healthcare technologies, which have the potential to drive portfolio growth and stability over time.
Synthetic Intelligence (AI) Market Size: Opportunities and Challenges, January 2023 – A Comprehensive Report Covering 2022-2030
1 The MSCI ACWI Index is MSCI’s flagship global equity benchmark, tracking the performance of over 2,900 large- and mid-capitalization stocks across 47 developed and emerging market countries.
2 The forward price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio estimates the relative value of future earnings.
3 The price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio compares a company’s stock price to its earnings per share.
4
Earnings per share (EPS) is an organization’s net income from internet sales divided by the number of outstanding shares it has issued.
5 Supply: Symbotic
6 The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) represents the rate of return (RoR) necessary for an investment to grow from its initial balance to its final balance, assuming all earnings were reinvested at the end of each period throughout the investment’s lifespan.
7 The term “average selling price” (ASP) denotes the typical cost at which a product or service is commonly sold.

