After a decade or extra the place Single-Web page-Purposes generated by
JavaScript frameworks have
develop into the norm, we see that server-side rendered HTML is changing into
common once more, additionally due to libraries corresponding to HTMX or Turbo. Writing a wealthy internet UI in a
historically server-side language like Go or Java is not simply potential,
however a really enticing proposition.
We then face the issue of learn how to write automated checks for the HTML
elements of our internet functions. Whereas the JavaScript world has advanced highly effective and subtle methods to check the UI,
ranging in dimension from unit-level to integration to end-to-end, in different
languages we don’t have such a richness of instruments out there.
When writing an online utility in Go or Java, HTML is often generated
by means of templates, which comprise small fragments of logic. It’s actually
potential to check them not directly by means of end-to-end checks, however these checks
are sluggish and costly.
We will as a substitute write unit checks that use CSS selectors to probe the
presence and proper content material of particular HTML parts inside a doc.
Parameterizing these checks makes it simple so as to add new checks and to obviously
point out what particulars every take a look at is verifying. This strategy works with any
language that has entry to an HTML parsing library that helps CSS
selectors; examples are supplied in Go and Java.
Degree 1: checking for sound HTML
The primary factor we wish to verify is that the HTML we produce is
principally sound. I do not imply to verify that HTML is legitimate in accordance with the
W3C; it might be cool to do it, nevertheless it’s higher to start out with a lot easier and sooner checks.
As an example, we would like our checks to
break if the template generates one thing like
<div>foo</p>
Let’s have a look at learn how to do it in phases: we begin with the next take a look at that
tries to compile the template. In Go we use the usual html/template bundle.
Go
func Test_wellFormedHtml(t *testing.T) { templ := template.Should(template.ParseFiles("index.tmpl")) _ = templ } In Java, we use jmustache
as a result of it is quite simple to make use of; Freemarker or
Velocity are different widespread decisions.
Java
@Take a look at void indexIsSoundHtml() { var template = Mustache.compiler().compile( new InputStreamReader( getClass().getResourceAsStream("/index.tmpl"))); } If we run this take a look at, it would fail, as a result of the index.tmpl file does
not exist. So we create it, with the above damaged HTML. Now the take a look at ought to move.
Then we create a mannequin for the template to make use of. The appliance manages a todo-list, and
we are able to create a minimal mannequin for demonstration functions.
Go
func Test_wellFormedHtml(t *testing.T) { templ := template.Should(template.ParseFiles("index.tmpl")) mannequin := todo.NewList() _ = templ _ = mannequin } Java
@Take a look at void indexIsSoundHtml() { var template = Mustache.compiler().compile( new InputStreamReader( getClass().getResourceAsStream("/index.tmpl"))); var mannequin = new TodoList(); } Now we render the template, saving the ends in a bytes buffer (Go) or as a String (Java).
Go
func Test_wellFormedHtml(t *testing.T) { templ := template.Should(template.ParseFiles("index.tmpl")) mannequin := todo.NewList() var buf bytes.Buffer err := templ.Execute(&buf, mannequin) if err != nil { panic(err) } } Java
@Take a look at void indexIsSoundHtml() { var template = Mustache.compiler().compile( new InputStreamReader( getClass().getResourceAsStream("/index.tmpl"))); var mannequin = new TodoList(); var html = template.execute(mannequin); } At this level, we wish to parse the HTML and we anticipate to see an
error, as a result of in our damaged HTML there’s a div aspect that
is closed by a p aspect. There may be an HTML parser within the Go
customary library, however it’s too lenient: if we run it on our damaged HTML, we do not get an
error. Fortunately, the Go customary library additionally has an XML parser that may be
configured to parse HTML (due to this Stack Overflow reply)
Go
func Test_wellFormedHtml(t *testing.T) { templ := template.Should(template.ParseFiles("index.tmpl")) mannequin := todo.NewList() // render the template right into a buffer var buf bytes.Buffer err := templ.Execute(&buf, mannequin) if err != nil { panic(err) } // verify that the template might be parsed as (lenient) XML decoder := xml.NewDecoder(bytes.NewReader(buf.Bytes())) decoder.Strict = false decoder.AutoClose = xml.HTMLAutoClose decoder.Entity = xml.HTMLEntity for { _, err := decoder.Token() swap err { case io.EOF: return // We're performed, it is legitimate! case nil: // do nothing default: t.Fatalf("Error parsing html: %s", err) } } } This code configures the HTML parser to have the fitting degree of leniency
for HTML, after which parses the HTML token by token. Certainly, we see the error
message we needed:
--- FAIL: Test_wellFormedHtml (0.00s) index_template_test.go:61: Error parsing html: XML syntax error on line 4: sudden finish aspect </p>
In Java, a flexible library to make use of is jsoup:
Java
@Take a look at void indexIsSoundHtml() { var template = Mustache.compiler().compile( new InputStreamReader( getClass().getResourceAsStream("/index.tmpl"))); var mannequin = new TodoList(); var html = template.execute(mannequin); var parser = Parser.htmlParser().setTrackErrors(10); Jsoup.parse(html, "", parser); assertThat(parser.getErrors()).isEmpty(); } And we see it fail:
java.lang.AssertionError: Anticipating empty however was:<[<1:13>: Unexpected EndTag token [</p>] when in state [InBody],
Success! Now if we copy over the contents of the TodoMVC
template to our index.tmpl file, the take a look at passes.
The take a look at, nonetheless, is simply too verbose: we extract two helper features, in
order to make the intention of the take a look at clearer, and we get
Go
func Test_wellFormedHtml(t *testing.T) { mannequin := todo.NewList() buf := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin) assertWellFormedHtml(t, buf) } Java
@Take a look at void indexIsSoundHtml() { var mannequin = new TodoList(); var html = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin); assertSoundHtml(html); } Degree 2: testing HTML construction
What else ought to we take a look at?
We all know that the seems of a web page can solely be examined, in the end, by a
human taking a look at how it’s rendered in a browser. Nevertheless, there’s typically
logic in templates, and we would like to have the ability to take a look at that logic.
One may be tempted to check the rendered HTML with string equality,
however this method fails in observe, as a result of templates comprise a whole lot of
particulars that make string equality assertions impractical. The assertions
develop into very verbose, and when studying the assertion, it turns into troublesome
to grasp what it’s that we’re making an attempt to show.
What we’d like
is a method to claim that some elements of the rendered HTML
correspond to what we anticipate, and to ignore all the main points we do not
care about. A technique to do that is by working queries with the CSS selector language:
it’s a highly effective language that enables us to pick out the
parts that we care about from the entire HTML doc. As soon as we now have
chosen these parts, we (1) rely that the variety of aspect returned
is what we anticipate, and (2) that they comprise the textual content or different content material
that we anticipate.
The UI that we’re purported to generate seems like this:
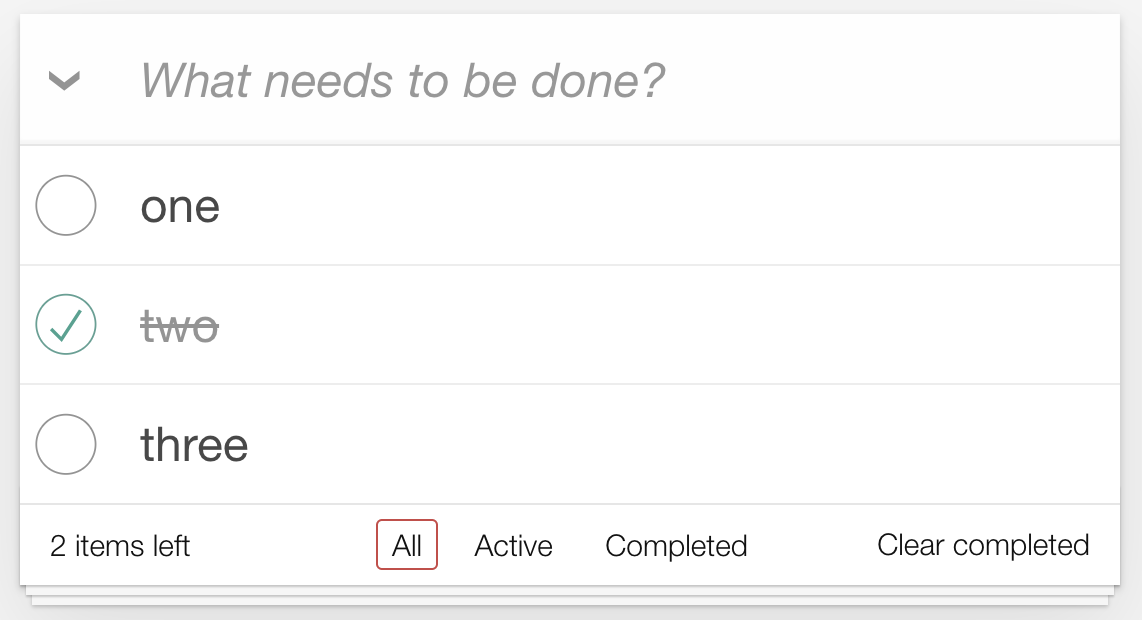
There are a number of particulars which can be rendered dynamically:
- The variety of gadgets and their textual content content material change, clearly
- The fashion of the todo-item modifications when it is accomplished (e.g., the
second) - The “2 gadgets left” textual content will change with the variety of non-completed
gadgets - One of many three buttons “All”, “Energetic”, “Accomplished” can be
highlighted, relying on the present url; as an illustration if we resolve that the
url that reveals solely the “Energetic” gadgets is/lively, then when the present url
is/lively, the “Energetic” button ought to be surrounded by a skinny pink
rectangle - The “Clear accomplished” button ought to solely be seen if any merchandise is
accomplished
Every of this issues might be examined with the assistance of CSS selectors.
This can be a snippet from the TodoMVC template (barely simplified). I
haven’t but added the dynamic bits, so what we see right here is static
content material, supplied for instance:
index.tmpl
<part class="todoapp"> <ul class="todo-list"> <!-- These are right here simply to indicate the construction of the record gadgets --> <!-- Record gadgets ought to get the category `accomplished` when marked as accomplished --> <li class="accomplished"> ② <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox" checked> <label>Style JavaScript</label> ① <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> <li> <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label>Purchase a unicorn</label> ① <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> </ul> <footer class="footer"> <!-- This ought to be `0 gadgets left` by default --> <span class="todo-count"><robust>0</robust> merchandise left</span> ⓷ <ul class="filters"> <li> <a class="chosen" href="#/">All</a> ④ </li> <li> <a href="#/lively">Energetic</a> </li> <li> <a href="#/accomplished">Accomplished</a> </li> </ul> <!-- Hidden if no accomplished gadgets are left ↓ --> <button class="clear-completed">Clear accomplished</button> ⑤ </footer> </part>
By trying on the static model of the template, we are able to deduce which
CSS selectors can be utilized to establish the related parts for the 5 dynamic
options listed above:
| function | CSS selector | |
|---|---|---|
| ① | All of the gadgets | ul.todo-list li |
| ② | Accomplished gadgets | ul.todo-list li.accomplished |
| ⓷ | Objects left | span.todo-count |
| ④ | Highlighted navigation hyperlink | ul.filters a.chosen |
| ⑤ | Clear accomplished button | button.clear-completed |
We will use these selectors to focus our checks on simply the issues we wish to take a look at.
Testing HTML content material
The primary take a look at will search for all of the gadgets, and show that the info
arrange by the take a look at is rendered accurately.
func Test_todoItemsAreShown(t *testing.T) { mannequin := todo.NewList() mannequin.Add("Foo") mannequin.Add("Bar") buf := renderTemplate(mannequin) // assert there are two <li> parts contained in the <ul class="todo-list"> // assert the primary <li> textual content is "Foo" // assert the second <li> textual content is "Bar" } We want a technique to question the HTML doc with our CSS selector; a very good
library for Go is goquery, that implements an API impressed by jQuery.
In Java, we preserve utilizing the identical library we used to check for sound HTML, particularly
jsoup. Our take a look at turns into:
Go
func Test_todoItemsAreShown(t *testing.T) { mannequin := todo.NewList() mannequin.Add("Foo") mannequin.Add("Bar") buf := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin) // parse the HTML with goquery doc, err := goquery.NewDocumentFromReader(bytes.NewReader(buf.Bytes())) if err != nil { // if parsing fails, we cease the take a look at right here with t.FatalF t.Fatalf("Error rendering template %s", err) } // assert there are two <li> parts contained in the <ul class="todo-list"> choice := doc.Discover("ul.todo-list li") assert.Equal(t, 2, choice.Size()) // assert the primary <li> textual content is "Foo" assert.Equal(t, "Foo", textual content(choice.Nodes[0])) // assert the second <li> textual content is "Bar" assert.Equal(t, "Bar", textual content(choice.Nodes[1])) } func textual content(node *html.Node) string { // Just a little mess attributable to the truth that goquery has // a .Textual content() methodology on Choice however not on html.Node sel := goquery.Choice{Nodes: []*html.Node{node}} return strings.TrimSpace(sel.Textual content()) } Java
@Take a look at void todoItemsAreShown() throws IOException { var mannequin = new TodoList(); mannequin.add("Foo"); mannequin.add("Bar"); var html = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin); // parse the HTML with jsoup Doc doc = Jsoup.parse(html, ""); // assert there are two <li> parts contained in the <ul class="todo-list"> var choice = doc.choose("ul.todo-list li"); assertThat(choice).hasSize(2); // assert the primary <li> textual content is "Foo" assertThat(choice.get(0).textual content()).isEqualTo("Foo"); // assert the second <li> textual content is "Bar" assertThat(choice.get(1).textual content()).isEqualTo("Bar"); } If we nonetheless have not modified the template to populate the record from the
mannequin, this take a look at will fail, as a result of the static template
todo gadgets have completely different textual content:
Go
--- FAIL: Test_todoItemsAreShown (0.00s) index_template_test.go:44: First record merchandise: need Foo, bought Style JavaScript index_template_test.go:49: Second record merchandise: need Bar, bought Purchase a unicorn
Java
IndexTemplateTest > todoItemsAreShown() FAILED org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError: Anticipating: <"Style JavaScript"> to be equal to: <"Foo"> however was not.
We repair it by making the template use the mannequin information:
Go
<ul class="todo-list"> {{ vary .Objects }} <li> <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label>{{ .Title }}</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> {{ finish }} </ul>
Java – jmustache
<ul class="todo-list"> {{ #allItems }} <li> <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label>{{ title }}</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> {{ /allItems }} </ul>
Take a look at each content material and soundness on the identical time
Our take a look at works, however it’s a bit verbose, particularly the Go model. If we will have extra
checks, they’ll develop into repetitive and troublesome to learn, so we make it extra concise by extracting a helper operate for parsing the html. We additionally take away the
feedback, because the code ought to be clear sufficient
Go
func Test_todoItemsAreShown(t *testing.T) { mannequin := todo.NewList() mannequin.Add("Foo") mannequin.Add("Bar") buf := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin) doc := parseHtml(t, buf) choice := doc.Discover("ul.todo-list li") assert.Equal(t, 2, choice.Size()) assert.Equal(t, "Foo", textual content(choice.Nodes[0])) assert.Equal(t, "Bar", textual content(choice.Nodes[1])) } func parseHtml(t *testing.T, buf bytes.Buffer) *goquery.Doc { doc, err := goquery.NewDocumentFromReader(bytes.NewReader(buf.Bytes())) if err != nil { // if parsing fails, we cease the take a look at right here with t.FatalF t.Fatalf("Error rendering template %s", err) } return doc } Java
@Take a look at void todoItemsAreShown() throws IOException { var mannequin = new TodoList(); mannequin.add("Foo"); mannequin.add("Bar"); var html = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin); var doc = parseHtml(html); var choice = doc.choose("ul.todo-list li"); assertThat(choice).hasSize(2); assertThat(choice.get(0).textual content()).isEqualTo("Foo"); assertThat(choice.get(1).textual content()).isEqualTo("Bar"); } non-public static Doc parseHtml(String html) { return Jsoup.parse(html, ""); } Significantly better! A minimum of for my part. Now that we extracted the parseHtml helper, it is
a good suggestion to verify for sound HTML within the helper:
Go
func parseHtml(t *testing.T, buf bytes.Buffer) *goquery.Doc { assertWellFormedHtml(t, buf) doc, err := goquery.NewDocumentFromReader(bytes.NewReader(buf.Bytes())) if err != nil { // if parsing fails, we cease the take a look at right here with t.FatalF t.Fatalf("Error rendering template %s", err) } return doc } Java
non-public static Doc parseHtml(String html) { var parser = Parser.htmlParser().setTrackErrors(10); var doc = Jsoup.parse(html, "", parser); assertThat(parser.getErrors()).isEmpty(); return doc; } And with this, we are able to do away with the primary take a look at that we wrote, as we are actually testing for sound HTML on a regular basis.
The second take a look at
Now we’re in a very good place for testing extra rendering logic. The
second dynamic function in our record is “Record gadgets ought to get the category
accomplished when marked as accomplished”. We will write a take a look at for this:
Go
func Test_completedItemsGetCompletedClass(t *testing.T) { mannequin := todo.NewList() mannequin.Add("Foo") mannequin.AddCompleted("Bar") buf := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin) doc := parseHtml(t, buf) choice := doc.Discover("ul.todo-list li.accomplished") assert.Equal(t, 1, choice.Dimension()) assert.Equal(t, "Bar", textual content(choice.Nodes[0])) } Java
@Take a look at void completedItemsGetCompletedClass() { var mannequin = new TodoList(); mannequin.add("Foo"); mannequin.addCompleted("Bar"); var html = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin); Doc doc = Jsoup.parse(html, ""); var choice = doc.choose("ul.todo-list li.accomplished"); assertThat(choice).hasSize(1); assertThat(choice.textual content()).isEqualTo("Bar"); } And this take a look at might be made inexperienced by including this little bit of logic to the
template:
Go
<ul class="todo-list"> {{ vary .Objects }} <li class="{{ if .IsCompleted }}accomplished{{ finish }}"> <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label>{{ .Title }}</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> {{ finish }} </ul> Java – jmustache
<ul class="todo-list"> {{ #allItems }} <li class="{{ #isCompleted }}accomplished{{ /isCompleted }}"> <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label>{{ title }}</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> {{ /allItems }} </ul> So little by little, we are able to take a look at and add the assorted dynamic options
that our template ought to have.
Make it simple so as to add new checks
The primary of the 20 suggestions from the superb speak by Russ Cox on Go
Testing is “Make it simple so as to add new take a look at circumstances“. Certainly, in Go there
is an inclination to make most checks parameterized, for this very cause.
Then again, whereas Java has
good help
for parameterized checks with JUnit 5, they are not used as a lot.
Since our present two checks have the identical construction, we
might issue them right into a single parameterized take a look at.
A take a look at case for us will include:
- A reputation (in order that we are able to produce clear error messages when the take a look at
fails) - A mannequin (in our case a
todo.Record) - A CSS selector
- An inventory of textual content matches that we look forward to finding once we run the CSS
selector on the rendered HTML.
So that is the info construction for our take a look at circumstances:
Go
var testCases = []struct { title string mannequin *todo.Record selector string matches []string }{ { title: "all todo gadgets are proven", mannequin: todo.NewList(). Add("Foo"). Add("Bar"), selector: "ul.todo-list li", matches: []string{"Foo", "Bar"}, }, { title: "accomplished gadgets get the 'accomplished' class", mannequin: todo.NewList(). Add("Foo"). AddCompleted("Bar"), selector: "ul.todo-list li.accomplished", matches: []string{"Bar"}, }, } Java
report TestCase(String title, TodoList mannequin, String selector, Record<String> matches) { @Override public String toString() { return title; } } public static TestCase[] indexTestCases() { return new TestCase[]{ new TestCase( "all todo gadgets are proven", new TodoList() .add("Foo") .add("Bar"), "ul.todo-list li", Record.of("Foo", "Bar")), new TestCase( "accomplished gadgets get the 'accomplished' class", new TodoList() .add("Foo") .addCompleted("Bar"), "ul.todo-list li.accomplished", Record.of("Bar")), }; } And that is our parameterized take a look at:
Go
func Test_indexTemplate(t *testing.T) { for _, take a look at := vary testCases { t.Run(take a look at.title, func(t *testing.T) { buf := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", take a look at.mannequin) assertWellFormedHtml(t, buf) doc := parseHtml(t, buf) choice := doc.Discover(take a look at.selector) require.Equal(t, len(take a look at.matches), len(choice.Nodes), "sudden # of matches") for i, node := vary choice.Nodes { assert.Equal(t, take a look at.matches[i], textual content(node)) } }) } } Java
@ParameterizedTest @MethodSource("indexTestCases") void testIndexTemplate(TestCase take a look at) { var html = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", take a look at.mannequin); var doc = parseHtml(html); var choice = doc.choose(take a look at.selector); assertThat(choice).hasSize(take a look at.matches.dimension()); for (int i = 0; i < take a look at.matches.dimension(); i++) { assertThat(choice.get(i).textual content()).isEqualTo(take a look at.matches.get(i)); } } We will now run our parameterized take a look at and see it move:
Go
$ go take a look at -v === RUN Test_indexTemplate === RUN Test_indexTemplate/all_todo_items_are_shown === RUN Test_indexTemplate/completed_items_get_the_'accomplished'_class --- PASS: Test_indexTemplate (0.00s) --- PASS: Test_indexTemplate/all_todo_items_are_shown (0.00s) --- PASS: Test_indexTemplate/completed_items_get_the_'accomplished'_class (0.00s) PASS okay tdd-html-templates 0.608s
Java
$ ./gradlew take a look at > Process :take a look at IndexTemplateTest > testIndexTemplate(TestCase) > [1] all todo gadgets are proven PASSED IndexTemplateTest > testIndexTemplate(TestCase) > [2] accomplished gadgets get the 'accomplished' class PASSED
Word how, by giving a reputation to our take a look at circumstances, we get very readable take a look at output, each on the terminal and within the IDE:
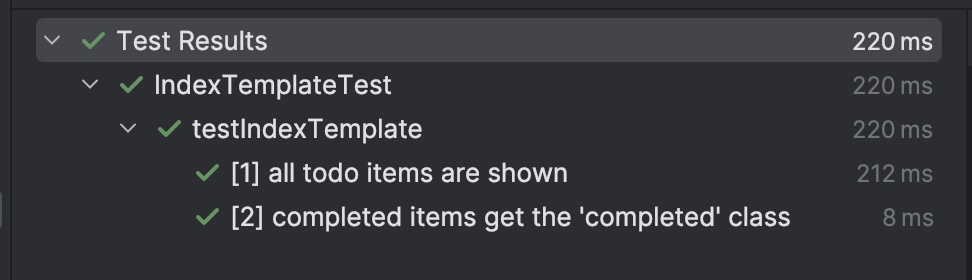
Having rewritten our two outdated checks in desk type, it is now tremendous simple so as to add
one other. That is the take a look at for the “x gadgets left” textual content:
Go
{ title: "gadgets left", mannequin: todo.NewList(). Add("One"). Add("Two"). AddCompleted("Three"), selector: "span.todo-count", matches: []string{"2 gadgets left"}, }, Java
new TestCase( "gadgets left", new TodoList() .add("One") .add("Two") .addCompleted("Three"), "span.todo-count", Record.of("2 gadgets left")), And the corresponding change within the html template is:
Go
<span class="todo-count"><robust>{{len .ActiveItems}}</robust> gadgets left</span> Java – jmustache
<span class="todo-count"><robust>{{activeItemsCount}}</robust> gadgets left</span> The above change within the template requires a supporting methodology within the mannequin:
Go
kind Merchandise struct { Title string IsCompleted bool } kind Record struct { Objects []*Merchandise } func (l *Record) ActiveItems() []*Merchandise { var consequence []*Merchandise for _, merchandise := vary l.Objects { if !merchandise.IsCompleted { consequence = append(consequence, merchandise) } } return consequence } Java
public class TodoList { non-public closing Record<TodoItem> gadgets = new ArrayList<>(); // ... public lengthy activeItemsCount() { return gadgets.stream().filter(TodoItem::isActive).rely(); } } We have invested slightly effort in our testing infrastructure, in order that including new
take a look at circumstances is less complicated. Within the subsequent part, we’ll see that the necessities
for the following take a look at circumstances will push us to refine our take a look at infrastructure additional.
Making the desk extra expressive, on the expense of the take a look at code
We are going to now take a look at the “All”, “Energetic” and “Accomplished” navigation hyperlinks at
the underside of the UI (see the image above),
and these depend upon which url we’re visiting, which is
one thing that our template has no technique to discover out.
Presently, all we move to our template is our mannequin, which is a todo-list.
It is not right so as to add the at present visited url to the mannequin, as a result of that’s
person navigation state, not utility state.
So we have to move extra info to the template past the mannequin. A straightforward manner
is to move a map, which we assemble in our
renderTemplate operate:
Go
func renderTemplate(mannequin *todo.Record, path string) bytes.Buffer { templ := template.Should(template.ParseFiles("index.tmpl")) var buf bytes.Buffer information := map[string]any{ "mannequin": mannequin, "path": path, } err := templ.Execute(&buf, information) if err != nil { panic(err) } return buf } Java
non-public String renderTemplate(String templateName, TodoList mannequin, String path) { var template = Mustache.compiler().compile( new InputStreamReader( getClass().getResourceAsStream(templateName))); var information = Map.of( "mannequin", mannequin, "path", path ); return template.execute(information); } And correspondingly our take a look at circumstances desk has yet one more area:
Go
var testCases = []struct { title string mannequin *todo.Record path string selector string matches []string }{ { title: "all todo gadgets are proven", mannequin: todo.NewList(). Add("Foo"). Add("Bar"), selector: "ul.todo-list li", matches: []string{"Foo", "Bar"}, }, // ... the opposite circumstances { title: "highlighted navigation hyperlink: All", path: "/", selector: "ul.filters a.chosen", matches: []string{"All"}, }, { title: "highlighted navigation hyperlink: Energetic", path: "/lively", selector: "ul.filters a.chosen", matches: []string{"Energetic"}, }, { title: "highlighted navigation hyperlink: Accomplished", path: "/accomplished", selector: "ul.filters a.chosen", matches: []string{"Accomplished"}, }, } Java
report TestCase(String title, TodoList mannequin, String path, String selector, Record<String> matches) { @Override public String toString() { return title; } } public static TestCase[] indexTestCases() { return new TestCase[]{ new TestCase( "all todo gadgets are proven", new TodoList() .add("Foo") .add("Bar"), "/", "ul.todo-list li", Record.of("Foo", "Bar")), // ... the earlier circumstances new TestCase( "highlighted navigation hyperlink: All", new TodoList(), "/", "ul.filters a.chosen", Record.of("All")), new TestCase( "highlighted navigation hyperlink: Energetic", new TodoList(), "/lively", "ul.filters a.chosen", Record.of("Energetic")), new TestCase( "highlighted navigation hyperlink: Accomplished", new TodoList(), "/accomplished", "ul.filters a.chosen", Record.of("Accomplished")), }; }
We discover that for the three new circumstances, the mannequin is irrelevant;
whereas for the earlier circumstances, the trail is irrelevant. The Go syntax permits us
to initialize a struct with simply the fields we’re taken with, however Java doesn’t have
an analogous function, so we’re pushed to move additional info, and this makes the take a look at circumstances
desk more durable to grasp.
A developer would possibly take a look at the primary take a look at case and marvel if the anticipated habits relies upon
on the trail being set to "/", and may be tempted so as to add extra circumstances with
a special path. In the identical manner, when studying the
highlighted navigation hyperlink take a look at circumstances, the developer would possibly marvel if the
anticipated habits will depend on the mannequin being set to an empty todo record. In that case, one would possibly
be led so as to add irrelevant take a look at circumstances for the highlighted hyperlink with non-empty todo-lists.
We wish to optimize for the time of the builders, so it is worthwhile to keep away from including irrelevant
information to our take a look at case. In Java we would move null for the
irrelevant fields, however there’s a greater manner: we are able to use
the builder sample,
popularized by Joshua Bloch.
We will shortly write one for the Java TestCase report this manner:
Java
report TestCase(String title, TodoList mannequin, String path, String selector, Record<String> matches) { @Override public String toString() { return title; } public static closing class Builder { String title; TodoList mannequin; String path; String selector; Record<String> matches; public Builder title(String title) { this.title = title; return this; } public Builder mannequin(TodoList mannequin) { this.mannequin = mannequin; return this; } public Builder path(String path) { this.path = path; return this; } public Builder selector(String selector) { this.selector = selector; return this; } public Builder matches(String ... matches) { this.matches = Arrays.asList(matches); return this; } public TestCase construct() { return new TestCase(title, mannequin, path, selector, matches); } } } Hand-coding builders is slightly tedious, however doable, although there are
automated methods to jot down them.
Now we are able to rewrite our Java take a look at circumstances with the Builder, to
obtain larger readability:
Java
public static TestCase[] indexTestCases() { return new TestCase[]{ new TestCase.Builder() .title("all todo gadgets are proven") .mannequin(new TodoList() .add("Foo") .add("Bar")) .selector("ul.todo-list li") .matches("Foo", "Bar") .construct(), // ... different circumstances new TestCase.Builder() .title("highlighted navigation hyperlink: Accomplished") .path("/accomplished") .selector("ul.filters a.chosen") .matches("Accomplished") .construct(), }; } So, the place are we with our checks? At current, they fail for the flawed cause: null-pointer exceptions
as a result of lacking mannequin and path values.
As a way to get our new take a look at circumstances to fail for the fitting cause, particularly that the template does
not but have logic to focus on the proper hyperlink, we should
present default values for mannequin and path. In Go, we are able to do that
within the take a look at methodology:
Go
func Test_indexTemplate(t *testing.T) { for _, take a look at := vary testCases { t.Run(take a look at.title, func(t *testing.T) { if take a look at.mannequin == nil { take a look at.mannequin = todo.NewList() } buf := renderTemplate(take a look at.mannequin, take a look at.path) // ... identical as earlier than }) } } In Java, we are able to present default values within the builder:
Java
public static closing class Builder { String title; TodoList mannequin = new TodoList(); String path = "/"; String selector; Record<String> matches; // ... } With these modifications, we see that the final two take a look at circumstances, those for the highlighted hyperlink Energetic
and Accomplished fail, for the anticipated cause that the highlighted hyperlink doesn’t change:
Go
=== RUN Test_indexTemplate/highlighted_navigation_link:_Active index_template_test.go:82: Error Hint: .../tdd-templates/go/index_template_test.go:82 Error: Not equal: anticipated: "Energetic" precise : "All" === RUN Test_indexTemplate/highlighted_navigation_link:_Completed index_template_test.go:82: Error Hint: .../tdd-templates/go/index_template_test.go:82 Error: Not equal: anticipated: "Accomplished" precise : "All"
Java
IndexTemplateTest > testIndexTemplate(TestCase) > [5] highlighted navigation hyperlink: Energetic FAILED org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError: Anticipating: <"All"> to be equal to: <"Energetic"> however was not. IndexTemplateTest > testIndexTemplate(TestCase) > [6] highlighted navigation hyperlink: Accomplished FAILED org.opentest4j.AssertionFailedError: Anticipating: <"All"> to be equal to: <"Accomplished"> however was not.
To make the checks move, we make these modifications to the template:
Go
<ul class="filters"> <li> <a class="{{ if eq .path "/" }}chosen{{ finish }}" href="#/">All</a> </li> <li> <a class="{{ if eq .path "/lively" }}chosen{{ finish }}" href="#/lively">Energetic</a> </li> <li> <a class="{{ if eq .path "/accomplished" }}chosen{{ finish }}" href="#/accomplished">Accomplished</a> </li> </ul>
Java – jmustache
<ul class="filters"> <li> <a class="{{ #pathRoot }}chosen{{ /pathRoot }}" href="#/">All</a> </li> <li> <a class="{{ #pathActive }}chosen{{ /pathActive }}" href="#/lively">Energetic</a> </li> <li> <a class="{{ #pathCompleted }}chosen{{ /pathCompleted }}" href="#/accomplished">Accomplished</a> </li> </ul>
Because the Mustache template language doesn’t enable for equality testing, we should change the
information handed to the template in order that we execute the equality checks earlier than rendering the template:
Java
non-public String renderTemplate(String templateName, TodoList mannequin, String path) { var template = Mustache.compiler().compile( new InputStreamReader( getClass().getResourceAsStream(templateName))); var information = Map.of( "mannequin", mannequin, "pathRoot", path.equals("/"), "pathActive", path.equals("/lively"), "pathCompleted", path.equals("/accomplished") ); return template.execute(information); } And with these modifications, all of our checks now move.
To recap this part, we made the take a look at code slightly bit extra difficult, in order that the take a look at
circumstances are clearer: this can be a superb tradeoff!
Degree 3: testing HTML behaviour
Within the story thus far, we examined the behaviour of the HTML
templates, by checking the construction of the generated HTML.
That is good, however what if we needed to check the behaviour of the HTML
itself, plus any CSS and JavaScript it might use?
The behaviour of HTML by itself is often fairly apparent, as a result of
there’s not a lot of it. The one parts that may work together with the
person are the anchor (<a>), <type> and
<enter> parts, however the image modifications utterly when
we add CSS, that may conceal, present, transfer round issues and plenty extra, and
with JavaScript, that may add any behaviour to a web page.
In an utility that’s primarily rendered server-side, we anticipate
that almost all behaviour is carried out by returning new HTML with a
round-trip to the person, and this may be examined adequately with the
methods we have seen thus far, however what if we needed to hurry up the
utility behaviour with a library corresponding to HTMX? This library works by means of particular
attributes which can be added to parts so as to add Ajax behaviour. These
attributes are in impact a DSL that we would wish to
take a look at.
How can we take a look at the mixture of HTML, CSS and JavaScript in
a unit take a look at?
Testing HTML, CSS and JavaScript requires one thing that is ready to
interpret and execute their behaviours; in different phrases, we’d like a
browser! It’s customary to make use of headless browsers in end-to-end checks;
can we use them for unitary checks as a substitute? I feel that is potential,
utilizing the next methods, though I need to admit I’ve but to strive
this on an actual undertaking.
We are going to use the Playwright
library, that’s out there for each Go and
Java. The checks we
are going to jot down can be slower, as a result of we should wait a number of
seconds for the headless browser to start out, however will retain a few of the
necessary traits of unit checks, primarily that we’re testing
simply the HTML (and any related CSS and JavaScript), in isolation from
every other server-side logic.
Persevering with with the TodoMVC
instance, the following factor we would wish to take a look at is what occurs when the
person clicks on the checkbox of a todo merchandise. What we would prefer to occur is
that:
- A POST name to the server is made, in order that the applying is aware of
that the state of a todo merchandise has modified - The server returns new HTML for the dynamic a part of the web page,
particularly all the part with class “todoapp”, in order that we are able to present the
new state of the applying together with the rely of remaining “lively”
gadgets (see the template above) - The web page replaces the outdated contents of the “todoapp” part with
the brand new ones.
Loading the web page within the Playwright browser
We begin with a take a look at that can simply load the preliminary HTML. The take a look at
is slightly concerned, so I present the whole code right here, after which I’ll
remark it little by little.
Go
func Test_toggleTodoItem(t *testing.T) { // render the preliminary HTML mannequin := todo.NewList(). Add("One"). Add("Two") initialHtml := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin, "/") // open the browser web page with Playwright web page := openPage() defer web page.Shut() logActivity(web page) // stub community calls err := web page.Route("**", func(route playwright.Route) { if route.Request().URL() == "http://localhost:4567/index.html" { // serve the preliminary HTML stubResponse(route, initialHtml.String(), "textual content/html") } else { // keep away from sudden requests panic("sudden request: " + route.Request().URL()) } }) if err != nil { t.Deadly(err) } // load preliminary HTML within the web page response, err := web page.Goto("http://localhost:4567/index.html") if err != nil { t.Deadly(err) } if response.Standing() != 200 { t.Fatalf("sudden standing: %d", response.Standing()) } } Java
public class IndexBehaviourTest { static Playwright playwright; static Browser browser; @BeforeAll static void launchBrowser() { playwright = Playwright.create(); browser = playwright.chromium().launch(); } @AfterAll static void closeBrowser() { playwright.shut(); } @Take a look at void toggleTodoItem() { // Render the preliminary html TodoList mannequin = new TodoList() .add("One") .add("Two"); String initialHtml = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin, "/"); strive (Web page web page = browser.newPage()) { logActivity(web page); // stub community calls web page.route("**", route -> { if (route.request().url().equals("http://localhost:4567/index.html")) { // serve the preliminary HTML route.fulfill(new Route.FulfillOptions() .setContentType("textual content/html") .setBody(initialHtml)); } else { // we do not need sudden calls fail(String.format("Surprising request: %s %s", route.request().methodology(), route.request().url())); } }); // load preliminary html web page.navigate("http://localhost:4567/index.html"); } } } Firstly of the take a look at, we initialize the mannequin with two todo
gadgets “One” and “Two”, then we render the template as earlier than:
Go
mannequin := todo.NewList(). Add("One"). Add("Two") initialHtml := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin, "/") Java
TodoList mannequin = new TodoList() .add("One") .add("Two"); String initialHtml = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin, "/"); Then we open the Playwright “web page”, which can begin a headless
browser
Go
web page := openPage() defer web page.Shut() logActivity(web page)
Java
strive (Web page web page = browser.newPage()) { logActivity(web page); The openPage operate in Go returns a Playwright
Web page object,
Go
func openPage() playwright.Web page { pw, err := playwright.Run() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("couldn't begin playwright: %v", err) } browser, err := pw.Chromium.Launch() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("couldn't launch browser: %v", err) } web page, err := browser.NewPage() if err != nil { log.Fatalf("couldn't create web page: %v", err) } return web page } and the logActivity operate gives suggestions on what
the web page is doing
Go
func logActivity(web page playwright.Web page) { web page.OnRequest(func(request playwright.Request) { log.Printf(">> %s %sn", request.Methodology(), request.URL()) }) web page.OnResponse(func(response playwright.Response) { log.Printf("<< %d %sn", response.Standing(), response.URL()) }) web page.OnLoad(func(web page playwright.Web page) { log.Println("Loaded: " + web page.URL()) }) web page.OnConsole(func(message playwright.ConsoleMessage) { log.Println("! " + message.Textual content()) }) } Java
non-public void logActivity(Web page web page) { web page.onRequest(request -> System.out.printf(">> %s %spercentn", request.methodology(), request.url())); web page.onResponse(response -> System.out.printf("<< %s %spercentn", response.standing(), response.url())); web page.onLoad(page1 -> System.out.println("Loaded: " + page1.url())); web page.onConsoleMessage(consoleMessage -> System.out.println("! " + consoleMessage.textual content())); } Then we stub all community exercise that the web page would possibly attempt to do
Go
err := web page.Route("**", func(route playwright.Route) { if route.Request().URL() == "http://localhost:4567/index.html" { // serve the preliminary HTML stubResponse(route, initialHtml.String(), "textual content/html") } else { // keep away from sudden requests panic("sudden request: " + route.Request().URL()) } }) Java
// stub community calls web page.route("**", route -> { if (route.request().url().equals("http://localhost:4567/index.html")) { // serve the preliminary HTML route.fulfill(new Route.FulfillOptions() .setContentType("textual content/html") .setBody(initialHtml)); } else { // we do not need sudden calls fail(String.format("Surprising request: %s %s", route.request().methodology(), route.request().url())); } }); and we ask the web page to load the preliminary HTML
Go
response, err := web page.Goto("http://localhost:4567/index.html") Java
web page.navigate("http://localhost:4567/index.html"); With all this equipment in place, we run the take a look at; it succeeds and
it logs the stubbed community exercise on customary output:
Go
=== RUN Test_toggleTodoItem >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html --- PASS: Test_toggleTodoItem (0.89s)
Java
IndexBehaviourTest > toggleTodoItem() STANDARD_OUT >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html IndexBehaviourTest > toggleTodoItem() PASSED
So with this take a look at we are actually in a position to load arbitrary HTML in a
headless browser. Within the subsequent sections we’ll see learn how to simulate person
interplay with parts of the web page, and observe the web page’s
behaviour. However first we have to remedy an issue with the shortage of
identifiers in our area mannequin.
Figuring out todo gadgets
Now we wish to click on on the “One” checkbox. The issue we now have is
that at current, we now have no technique to establish particular person todo gadgets, so
we introduce an Id area within the todo merchandise:
Go – up to date mannequin with Id
kind Merchandise struct { Id int Title string IsCompleted bool } func (l *Record) AddWithId(id int, title string) *Record { merchandise := Merchandise{ Id: id, Title: title, } l.Objects = append(l.Objects, &merchandise) return l } // Add creates a brand new todo.Merchandise with a random Id func (l *Record) Add(title string) *Record { merchandise := Merchandise{ Id: generateRandomId(), Title: title, } l.Objects = append(l.Objects, &merchandise) return l } func generateRandomId() int { return abs(rand.Int()) } Java – up to date mannequin with Id
public class TodoList { non-public closing Record<TodoItem> gadgets = new ArrayList<>(); public TodoList add(String title) { gadgets.add(new TodoItem(generateRandomId(), title, false)); return this; } public TodoList addCompleted(String title) { gadgets.add(new TodoItem(generateRandomId(), title, true)); return this; } public TodoList add(int id, String title) { gadgets.add(new TodoItem(id, title, false)); return this; } non-public static int generateRandomId() { return new Random().nextInt(0, Integer.MAX_VALUE); } } public report TodoItem(int id, String title, boolean isCompleted) { public boolean isActive() { return !isCompleted; } } And we replace the mannequin in our take a look at so as to add express Ids
Go – including Id within the take a look at information
func Test_toggleTodoItem(t *testing.T) { // render the preliminary HTML mannequin := todo.NewList(). AddWithId(101, "One"). AddWithId(102, "Two") initialHtml := renderTemplate("index.tmpl", mannequin, "/") // ... } Java – including Id within the take a look at information
@Take a look at void toggleTodoItem() { // Render the preliminary html TodoList mannequin = new TodoList() .add(101, "One") .add(102, "Two"); String initialHtml = renderTemplate("/index.tmpl", mannequin, "/"); } We are actually prepared to check person interplay with the web page.
Clicking on a todo merchandise
We wish to simulate person interplay with the HTML web page. It may be
tempting to proceed to make use of CSS selectors to establish the precise
checkbox that we wish to click on, however there’s a greater manner: there’s a
consensus amongst front-end builders that one of the simplest ways to check
interplay with a web page is to make use of it
the identical manner that customers do. As an example, you do not search for a
button by means of a CSS locator corresponding to button.purchase; as a substitute,
you search for one thing clickable with the label “Purchase”. In observe,
this implies figuring out elements of the web page by means of their
ARIA roles.
To this finish, we add code to our take a look at to search for a checkbox labelled
“One”:
Go
func Test_toggleTodoItem(t *testing.T) { // ... // click on on the "One" checkbox checkbox := web page.GetByRole(*playwright.AriaRoleCheckbox, playwright.PageGetByRoleOptions{Identify: "One"}) if err := checkbox.Click on(); err != nil { t.Deadly(err) } } Java
@Take a look at void toggleTodoItem() { // ... // click on on the "One" checkbox var checkbox = web page.getByRole(AriaRole.CHECKBOX, new Web page.GetByRoleOptions().setName("One")); checkbox.click on(); } } We run the take a look at, and it fails:
Go
>> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html --- FAIL: Test_toggleTodoItem (32.74s) index_behaviour_test.go:50: playwright: timeout: Timeout 30000ms exceeded. Java
IndexBehaviourTest > toggleTodoItem() STANDARD_OUT >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html IndexBehaviourTest > toggleTodoItem() FAILED com.microsoft.playwright.TimeoutError: Error { message="hyperlink the label to the checkbox correctly: generated HTML with dangerous accessibility
<li> <div class="view"> <enter class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label>One</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> We repair it by utilizing the for attribute within the
template,
index.tmpl – Go
<li> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-{{.Id}}" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-{{.Id}}">{{.Title}}</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li>
index.tmpl – Java
<li> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-{{ id }}" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-{{ id }}">{{ title }}</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li>
In order that it generates correct, accessible HTML:
generated HTML with higher accessibility
<li> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-101" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-101">One</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li>
We run once more the take a look at, and it passes.
On this part we noticed how testing the HTML in the identical was as customers
work together with it led us to make use of ARIA roles, which led to bettering
accessibility of our generated HTML. Within the subsequent part, we are going to see
learn how to take a look at that the clicking on a todo merchandise triggers a distant name to the
server, that ought to end in swapping part of the present HTML with
the HTML returned by the XHR name.
Spherical-trip to the server
Now we are going to lengthen our take a look at. We inform the take a look at that if name to
POST /toggle/101 is obtained, it ought to return some
stubbed HTML.
Go
} else if route.Request().URL() == "http://localhost:4567/toggle/101" && route.Request().Methodology() == "POST" { // we anticipate {that a} POST /toggle/101 request is made once we click on on the "One" checkbox const stubbedHtml = ` <part class="todoapp"> <p>Stubbed html</p> </part>` stubResponse(route, stubbedHtml, "textual content/html")
Java
} else if (route.request().url().equals("http://localhost:4567/toggle/101") && route.request().methodology().equals("POST")) { // we anticipate {that a} POST /toggle/101 request is made once we click on on the "One" checkbox String stubbedHtml = """ <part class="todoapp"> <p>Stubbed html</p> </part> """; route.fulfill(new Route.FulfillOptions() .setContentType("textual content/html") .setBody(stubbedHtml));
And we stub the loading of the HTMX library, which we load from a
native file:
Go
} else if route.Request().URL() == "https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12" { // serve the htmx library stubResponse(route, readFile("testdata/htmx.min.js"), "utility/javascript") Go
} else if (route.request().url().equals("https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12")) { // serve the htmx library route.fulfill(new Route.FulfillOptions() .setContentType("textual content/html") .setBody(readFile("/htmx.min.js"))); Lastly, we add the expectation that, after we click on the checkbox,
the part of the HTML that incorporates a lot of the utility is
reloaded.
Go
// click on on the "One" checkbox checkbox := web page.GetByRole(*playwright.AriaRoleCheckbox, playwright.PageGetByRoleOptions{Identify: "One"}) if err := checkbox.Click on(); err != nil { t.Deadly(err) } // verify that the web page has been up to date doc := parseHtml(t, content material(t, web page)) parts := doc.Discover("physique > part.todoapp > p") assert.Equal(t, "Stubbed html", parts.Textual content(), should(web page.Content material())) java
// click on on the "One" checkbox var checkbox = web page.getByRole(AriaRole.CHECKBOX, new Web page.GetByRoleOptions().setName("One")); checkbox.click on(); // verify that the web page has been up to date var doc = parseHtml(web page.content material()); var parts = doc.choose("physique > part.todoapp > p"); assertThat(parts.textual content()) .describedAs(web page.content material()) .isEqualTo("Stubbed html"); We run the take a look at, and it fails, as anticipated. As a way to perceive
why precisely it fails, we add to the error message the entire HTML
doc.
Go
assert.Equal(t, "Stubbed html", parts.Textual content(), should(web page.Content material())) Java
assertThat(parts.textual content()) .describedAs(web page.content material()) .isEqualTo("Stubbed html"); The error message could be very verbose, however we see that the explanation it
fails is that we do not see the stubbed HTML within the output. This implies
that the web page didn’t make the anticipated XHR name.
Go – Java is analogous
--- FAIL: Test_toggleTodoItem (2.75s) === RUN Test_toggleTodoItem >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html index_behaviour_test.go:67: Error Hint: .../index_behaviour_test.go:67 Error: Not equal: anticipated: "Stubbed html" precise : "" ... Take a look at: Test_toggleTodoItem Messages: <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta title="viewport" content material="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Template • TodoMVC</title> <script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12"></script> <physique> <part class="todoapp"> ... <li class=""> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-101" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-101">One</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> ...
We will make this take a look at move by altering the HTML template to make use of HTMX
to make an XHR name again to the server. First we load the HTMX
library:
index.tmpl
<title>Template • TodoMVC</title> <script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12"></script> Then we add the HTMX attributes to the checkboxes:
index.tmpl
<enter data-hx-post="/toggle/{{.Id}}" data-hx-target="part.todoapp" id="checkbox-{{.Id}}" class="toggle" kind="checkbox">
The data-hx-post annotation will make HTMX do a POST
name to the required url. The data-hx-target tells HTMX
to repeat the HTML returned by the decision, to the aspect specified by the
part.todoapp CSS locator.
We run once more the take a look at, and it nonetheless fails!
Go – Java is analogous
--- FAIL: Test_toggleTodoItem (2.40s) === RUN Test_toggleTodoItem >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html >> GET https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12 << 200 https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12 Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html >> POST http://localhost:4567/toggle/101 << 200 http://localhost:4567/toggle/101 index_behaviour_test.go:67: Error Hint: .../index_behaviour_test.go:67 Error: Not equal: anticipated: "Stubbed html" precise : "" ... Take a look at: Test_toggleTodoItem Messages: <!DOCTYPE html><html lang="en"><head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta title="viewport" content material="width=device-width, initial-scale=1"> <title>Template • TodoMVC</title> <script src="https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12"></script> ... <physique> <part class="todoapp"><part class="todoapp"> <p>Stubbed html</p> </part></part> ... </physique></html>
The log traces present that the POST name occurred as anticipated, however
examination of the error message reveals that the HTML construction we
anticipated just isn’t there: we now have a part.todoapp nested
inside one other. Which means that we aren’t utilizing the HTMX annotations
accurately, and reveals why this sort of take a look at might be useful. We add the
lacking annotation
index.tmpl
<enter data-hx-post="/toggle/{{.Id}}" data-hx-target="part.todoapp" data-hx-swap="outerHTML" id="checkbox-{{.Id}}" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> The default behaviour of HTMX is to interchange the inside HTML of the
goal aspect. The data-hx-swap="outerHTML" annotation
tells HTMX to interchange the outer HTML as a substitute.
and we take a look at once more, and this time it passes!
Go
=== RUN Test_toggleTodoItem >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html >> GET https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12 << 200 https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12 Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html >> POST http://localhost:4567/toggle/101 << 200 http://localhost:4567/toggle/101 --- PASS: Test_toggleTodoItem (1.39s)
Java
IndexBehaviourTest > toggleTodoItem() STANDARD_OUT >> GET http://localhost:4567/index.html << 200 http://localhost:4567/index.html >> GET https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12 << 200 https://unpkg.com/htmx.org@1.9.12 Loaded: http://localhost:4567/index.html >> POST http://localhost:4567/toggle/101 << 200 http://localhost:4567/toggle/101 IndexBehaviourTest > toggleTodoItem() PASSED
On this part we noticed learn how to write a take a look at for the behaviour of our
HTML that, whereas utilizing the difficult equipment of a headless browser,
nonetheless feels extra like a unit take a look at than an integration take a look at. It’s in
truth testing simply an HTML web page with any related CSS and JavaScript,
in isolation from different elements of the applying corresponding to controllers,
companies or repositories.
The take a look at prices 2-3 seconds of ready time for the headless browser to return up, which is often an excessive amount of for a unit take a look at; nonetheless, like a unit take a look at, it is rather steady, as it isn’t flaky, and its failures are documented with a comparatively clear error message.
See the ultimate model of the take a look at in Go and in Java.
Bonus degree: Stringly asserted
Esko Luontola, TDD professional and writer of the net course tdd.mooc.fi, instructed another to testing HTML with CSS selectors: the thought is to remodel HTML right into a human-readable canonical type.
Let’s take for instance this snippet of generated HTML:
<ul class="todo-list"> <li class=""> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-100" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-100">One</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> <li class=""> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-200" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-200">Two</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> <li class="accomplished"> <div class="view"> <enter id="checkbox-300" class="toggle" kind="checkbox"> <label for="checkbox-300">Three</label> <button class="destroy"></button> </div> </li> </ul>
We might visualize the above HTML by:
- deleting all HTML tags
- decreasing each sequence of whitespace characters to a single clean
to reach at:
One Two Three
This, nonetheless, removes an excessive amount of of the HTML construction to be helpful. As an example, it doesn’t allow us to distinguish between lively and accomplished gadgets. Some HTML aspect symbolize seen content material: as an illustration
<enter worth="foo" />
reveals a textual content field with the phrase “foo” that is a vital a part of the manner we understand HTML. To visualise these parts, Esko suggests so as to add a data-test-icon attribute that provides some textual content for use instead of the aspect when visualizing it for testing. With this,
<enter worth="foo" data-test-icon="[foo]" />
the enter aspect is visualized as [foo], with the sq. brackets hinting that the phrase “foo” sits inside an editable textual content field. Now if we add test-icons to our HTML template,
Go — Java is analogous
<ul class="todo-list"> {{ vary .mannequin.AllItems }} <li class="{{ if .IsCompleted }}accomplished{{ finish }}"> <div class="view"> <enter data-hx-post="/toggle/{{ .Id }}" data-hx-target="part.todoapp" data-hx-swap="outerHTML" id="checkbox-{{ .Id }}" class="toggle" kind="checkbox" data-test-icon="{{ if .IsCompleted }}✅{{ else }}⬜{{ finish }}"> <label for="checkbox-{{ .Id }}">{{ .Title }}</label> <button class="destroy" data-test-icon="❌️"></button> </div> </li> {{ finish }} </ul> we are able to assert towards its canonical visible illustration like this:
Go
func Test_visualize_html_example(t *testing.T) { mannequin := todo.NewList(). Add("One"). Add("Two"). AddCompleted("Three") buf := renderTemplate("todo-list.tmpl", mannequin, "/") anticipated := ` ⬜ One ❌️ ⬜ Two ❌️ ✅ Three ❌️ ` assert.Equal(t, normalizeWhitespace(anticipated), visualizeHtml(buf.String())) } Java
@Take a look at void visualize_html_example() { var mannequin = new TodoList() .add("One") .add("Two") .addCompleted("Three"); var html = renderTemplate("/todo-list.tmpl", mannequin, "/"); assertThat(visualizeHtml(html)) .isEqualTo(normalizeWhitespace(""" ⬜ One ❌️ ⬜ Two ❌️ ✅ Three ❌️ """)); } Right here is Esko Luontola’s Java implementation of the 2 features that make this potential, and my translation to Go of his code.
Go
func visualizeHtml(html string) string em func normalizeWhitespace(s string) string { return strings.TrimSpace(replaceAll(s, "s+", " ")) } func replaceAll(src, regex, repl string) string { re := regexp.MustCompile(regex) return re.ReplaceAllString(src, repl) } Java
public static String visualizeHtml(String html) robust public static String normalizeWhitespace(String s) { return s.replaceAll("s+", " ").trim(); } On this part, we now have seen a method for asserting HTML content material that’s a substitute for the CSS selector-based method utilized in the remainder of the article. Esko Luontola has reported nice success with it, and I hope readers have success with it too!
This method of asserting towards massive, difficult information constructions corresponding to HTML pages by decreasing them to a canonical string model has no title that I do know of. Martin Fowler instructed “stringly asserted”, and from his suggestion comes the title of this part.












 Assemblage of seven properties in Analysis Triangle Park owned by Apple
Assemblage of seven properties in Analysis Triangle Park owned by Apple








