In my previous expertise designing conversational programs, I noticed firsthand the restrictions of conventional AI. The system I labored with might reliably detect entities, however its inflexible logic made scaling these options not possible. Conversations adopted preprogrammed paths: if the person stated X, reply with Y. Any deviation broke the movement, highlighting how rigid these programs had been.
Brokers, powered by basis fashions, change this.
They’re autonomous programs able to dealing with unpredictable situations and collaborating seamlessly. An agent can plan a visit, collect real-time knowledge, or handle a buyer account, adapting to adjustments on the fly.
Brokers aren’t simply customers of instruments; they’re instruments themselves. Like modular elements, they work independently or combine with others to unravel advanced issues. Predictive fashions introduced precision forecasting. Generative fashions redefined creativity. Now, Agentic AI takes intelligence into autonomous motion.
On this article, we’ll dissect the anatomy of brokers, discover their collaboration, and dive into the infrastructure wanted to scale them into highly effective, interconnected ecosystems.
What’s an Agent?
At its easiest, an agent has company, they don’t depend on static paths—they cause, use instruments, and adapt dynamically. Not like a scripted bot, brokers evolve their workflows in actual time, adapting to unpredictable inputs as they come up.
In synthetic intelligence, brokers have an extended historical past, from early theoretical issues by Alan Turing and John McCarthy to rule-based reasoning brokers within the Nineteen Sixties. These brokers had been designed to behave autonomously inside an outlined context, however their capabilities had been restricted by slim functions and inflexible logic.
At this time, the emergence of basis fashions has remodeled what’s doable.
These fashions present the reasoning and generalization wanted for brokers to adapt dynamically to advanced, unpredictable environments. An agent’s setting defines its scope, be it a chessboard, the online, or the highway, and its instruments decide what actions it could possibly take. Not like earlier programs, fashionable brokers mix highly effective reasoning with versatile instruments, unlocking functions that had been as soon as unimaginable.
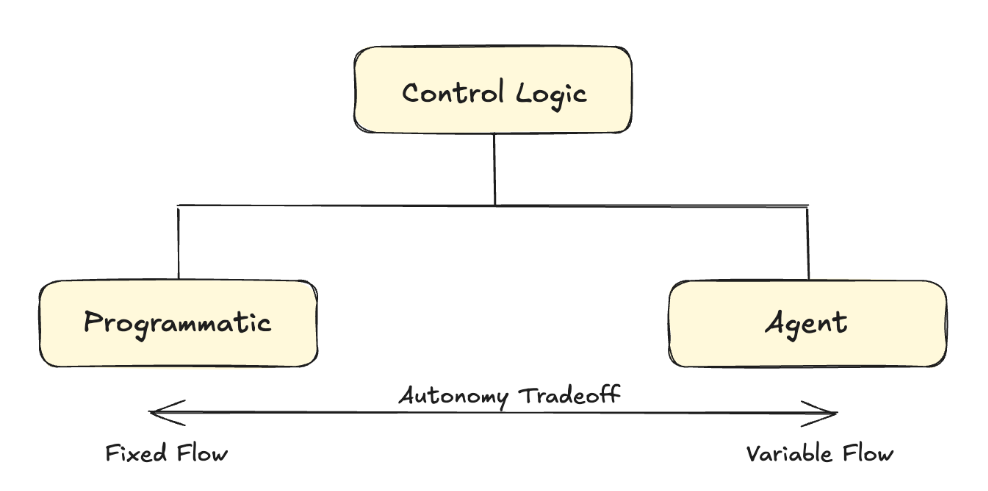

Management logic, programmatic versus agentic
Within the subsequent part, we’ll dissect their anatomy—how brokers understand, cause, act, and be taught.
Dissecting the Anatomy of an Agent
Similar to people, brokers clear up issues by combining their senses, reminiscence, reasoning, and skill to behave. However earlier than we dive into the mechanics of how they do that, there’s one foundational component that underpins every thing: their persona.
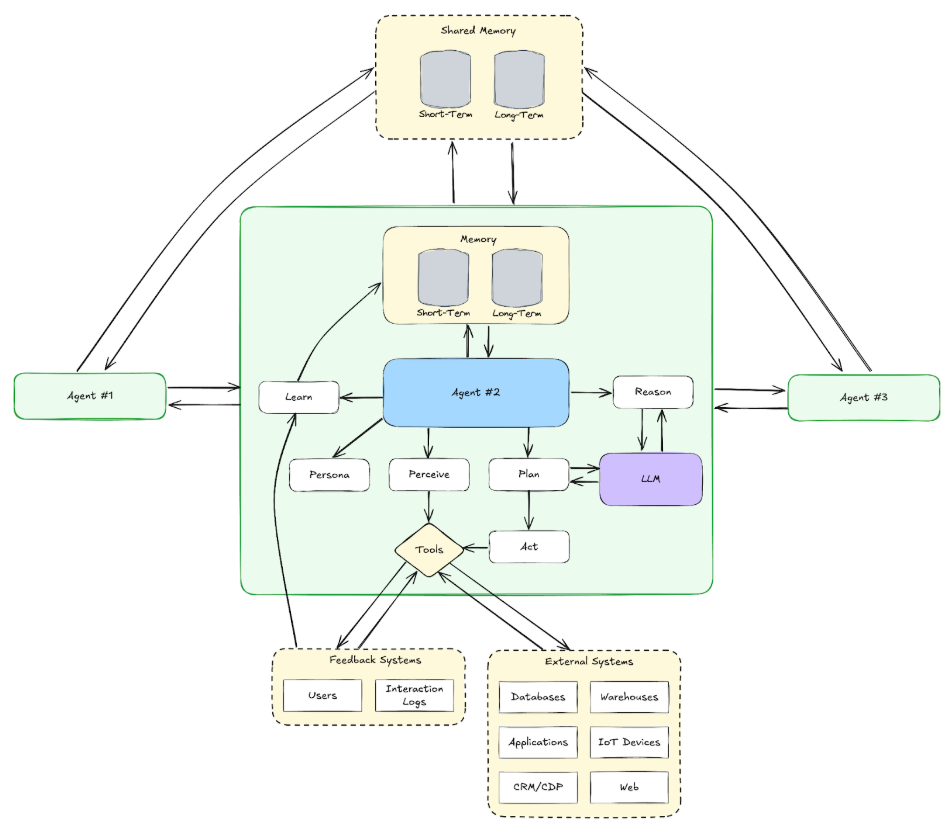

The Anatomy of a Multi-Agent System
Persona (Job Perform)
The persona of an agent defines its job operate and experience. It’s like an in depth job description embedded into the system immediate, shaping the agent’s habits and responses. The system immediate units expectations and influences the mannequin’s likelihood distribution over tokens to align outputs with the outlined position.
Instance System Immediate:


Notion (Sensing)
With a transparent position, step one to fixing any downside is knowing the setting. For brokers, notion is their sensory enter, that’s, how they collect knowledge from the world round them. People use eyes, ears, and contact; brokers use APIs, sensors, and person inputs.
- Instance: A logistics agent senses delays by pulling real-time knowledge from site visitors APIs and climate forecasts, very similar to a human driver checks site visitors experiences.
Reasoning and Resolution-Making
As soon as info is gathered, it must be processed and understood. Reasoning is the agent’s skill to investigate knowledge, derive insights, and resolve what to do subsequent. For people, this occurs within the mind. For brokers, it’s powered by fashions like LLMs, which dynamically adapt to inputs and contexts.
- Instance: A customer support agent would possibly analyze a person’s tone to determine frustration, cross-reference account historical past for unresolved points, and resolve to escalate the case.
Reminiscence
Reminiscence permits brokers to retain domain-specific info throughout interactions. It’s not about studying, which is a separate a part of the anatomy. People depend on each short-term reminiscence (like recalling the beginning of a dialog) and long-term reminiscence (like remembering a talent discovered years in the past). Brokers work the identical manner.
Quick-term reminiscence permits the agent to maintain observe of the quick context inside a dialog, which is likely to be saved quickly in reminiscence buffers in the course of the session. In the meantime, long-term reminiscence includes storing historic knowledge, reminiscent of person preferences or previous interactions. This may very well be a vector database or one other everlasting storage. A vector database permits semantic search, the place embeddings permit the agent to retrieve related info effectively.
- Instance: A gross sales assistant remembers previous interactions, like noting a consumer’s curiosity in a particular characteristic, and makes use of this to tailor follow-ups.
Planning
As soon as the agent is aware of what must be carried out, it devises a plan to realize its purpose. This step mirrors how people strategize: breaking an issue into smaller steps and prioritizing actions.
- Instance: A meal-planning agent organizes recipes for the week, accounting for dietary restrictions, obtainable components, and the person’s schedule.
Motion
Planning is nugatory with out execution. Motion is the place brokers work together with the world, whether or not by sending a message, controlling a tool, or updating a database.
- Instance: A buyer assist agent updates a ticket, points a refund, or sends an e mail to resolve a problem.
The agent’s execution handlers are accountable for guaranteeing these actions are carried out precisely and validating the outcomes.
Studying
People enhance by studying from errors and adapting to new info. Brokers do the identical, utilizing machine studying to refine their reasoning, enhance predictions, and optimize actions.
- Instance: A product advice engine tracks click-through charges and adjusts its ideas primarily based on what resonates with customers.
This course of might contain adjusting the agent’s context dynamically throughout immediate meeting, permitting it to refine its responses primarily based on situational suggestions with out making everlasting adjustments to the mannequin’s weights. Alternatively, studying may also happen by means of reinforcement studying, the place decision-making is optimized utilizing rewards or penalties tied to particular actions. In lots of instances, adapting context gives a versatile and environment friendly manner for brokers to enhance with out the overhead of fine-tuning.
Coordination and Collaboration
People hardly ever work alone—we collaborate, share data, and divide duties. In multi-agent programs, coordination permits brokers to do the identical, working collectively to realize shared targets.
- Instance: A CRM assistant updates a buyer’s contact particulars in Salesforce whereas notifying a billing assistant agent to regulate subscription data.
This collaboration is commonly powered by message brokers like Apache Kafka, which facilitate real-time communication and synchronization between brokers. The flexibility to share state and duties dynamically makes multi-agent programs considerably extra highly effective than standalone brokers.
Device Interface
People use instruments to amplify their capabilities, for instance, docs use stethoscopes, and programmers use built-in growth environments (IDEs). Brokers aren’t any totally different. The instrument interface is their bridge to specialised capabilities, permitting them to increase their attain and function successfully in the true world.
- Instance: A journey agent makes use of flight APIs to seek out tickets, climate APIs to plan routes, and monetary APIs to calculate prices.
These interfaces typically depend on modular API handlers or plugin architectures, permitting the agent to increase its performance dynamically and effectively.
The Takeaway
While you break it down, brokers clear up issues the identical manner people do: they sense their setting, course of info, recall related data, devise a plan, and take motion.
However what units brokers aside isn’t simply how they work—it’s their skill to scale.
A human might grasp one area, however an agent ecosystem can deliver collectively specialists from numerous fields, collaborating to deal with challenges no single system might deal with.
Within the subsequent part, we’ll discover how one can construct infrastructure that empowers these brokers to thrive—not as remoted instruments, however as a part of a dynamic, interconnected AI workforce.
Brokers as Instruments and Microservices
At their core, brokers are instruments with intelligence.
They will use APIs, exterior libraries, and even different brokers to get the job carried out. This modularity mirrors the rules of microservices structure, which has powered enterprise-grade programs for many years. By treating brokers as microservices, we will apply the identical classes: design them to be light-weight, specialised, and interoperable. This method lets us compose refined workflows by combining brokers like Lego blocks, scaling capabilities with out creating bloated, monolithic programs.
For instance, a advertising and marketing agent would possibly name a buyer segmentation agent to investigate person knowledge after which go the outcomes to a marketing campaign technique agent to optimize advert focusing on. By treating brokers as instruments inside a shared ecosystem, workflows might be stitched collectively dynamically, enabling unprecedented flexibility and scalability.
Why This Issues for Scalability
This microservices-like structure is crucial for constructing scalable agent ecosystems. As an alternative of making monolithic brokers that attempt to do every thing, we will design smaller, specialised brokers that work collectively. This method permits quicker growth, simpler upkeep, and the flexibility to scale particular person elements independently.
By standing on the shoulders of microservices structure, we will deliver enterprise-grade reliability, modularity, and efficiency to agent programs. The way forward for GenAI isn’t about constructing remoted brokers, it’s about creating collaborative ecosystems the place brokers operate like microservices, working collectively seamlessly to unravel advanced issues.
Within the subsequent part, we’ll discover how one can apply the teachings of scaling microservices to agent infrastructure, guaranteeing we’re able to assist the subsequent technology of GenAI programs.
Brokers Want Occasions
Drawing from the teachings of microservices, conventional request/response architectures merely don’t scale for brokers.
In these programs, each motion requires specific coordination, introducing delays, bottlenecks, and tightly coupled dependencies. It’s like needing written approval for each resolution in a company—purposeful in small setups however painfully gradual and inefficient as complexity grows.
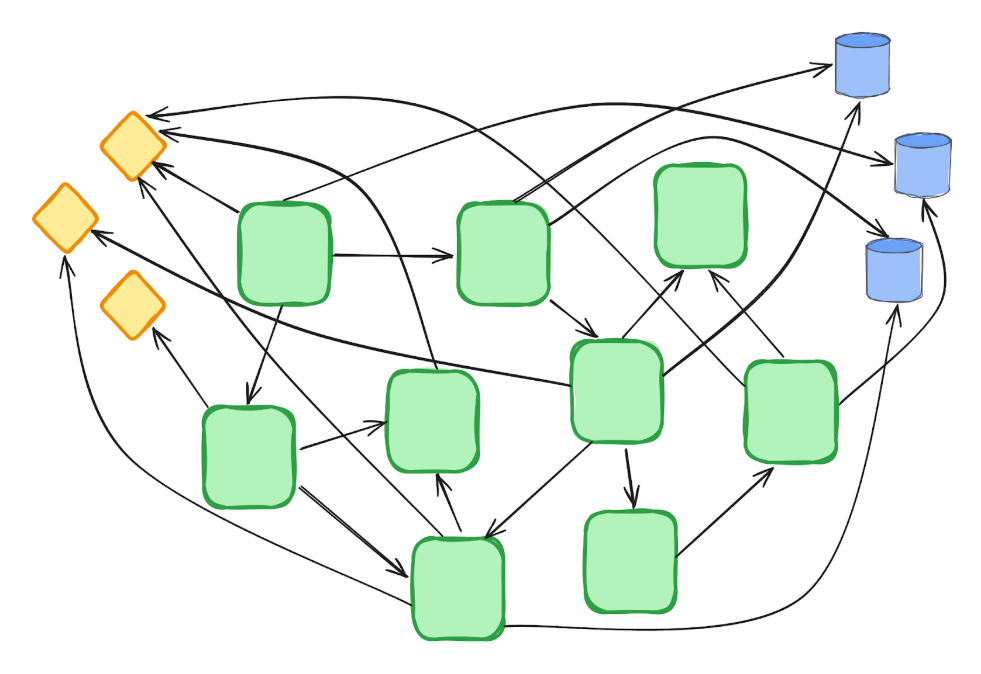

Multi-agent Techniques Result in a Labyrinth of Tightly Coupled Interdependencies
The shift to event-driven architectures marks a pivotal second in constructing scalable agent programs. As an alternative of ready for direct directions, brokers are designed to emit and hear for occasions autonomously. Occasions act as alerts that one thing has occurred—a change in knowledge, a triggered motion, or an necessary replace—permitting brokers to reply dynamically and independently.
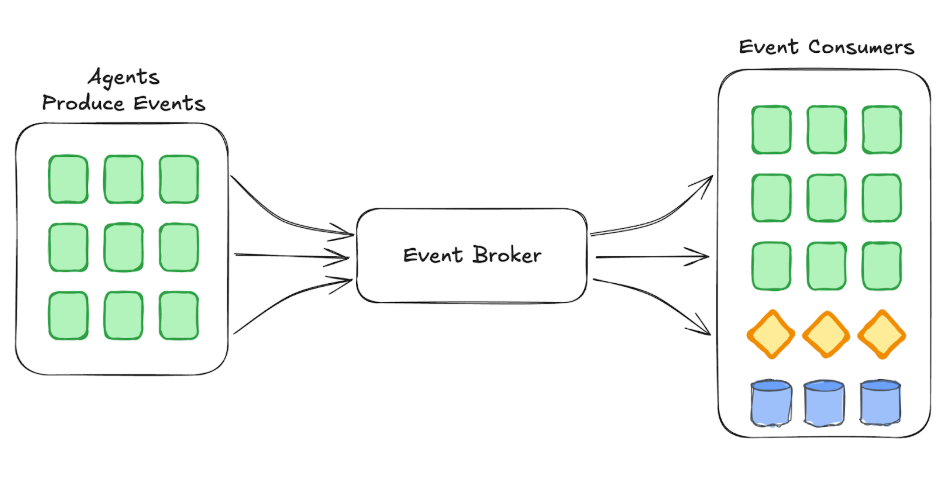

Occasion-Pushed Brokers: Brokers Emit and Pay attention for Occasions
The Anatomy of Occasion-Pushed Brokers
This structure straight impacts the elements of an agent’s anatomy:
- Notion: Brokers sense the world by means of occasions, which give structured, real-time inputs.
- Reasoning: Occasions drive the decision-making course of, with brokers dynamically deciphering alerts to find out subsequent steps.
- Reminiscence: Occasion persistence ensures that historic knowledge is all the time obtainable for contextual recall, decreasing the danger of misplaced or incomplete interactions.
- Motion: As an alternative of inflexible workflows, brokers act by emitting occasions, enabling downstream brokers or programs to choose up the place wanted.
Agent interfaces on this system are not outlined by inflexible APIs however by the occasions they emit and eat. These occasions are encapsulated in easy, standardized codecs like JSON payloads, which:
- Simplify how brokers perceive and react to adjustments.
- Promote reusability throughout totally different workflows and programs.
- Allow seamless integration in dynamic, evolving environments.
Constructing the Agent Ecosystem
“Going into 2025, there’s a higher must create infrastructure to handle a number of AI brokers and functions.” notes VentureBeat.
This isn’t only a forecast, it’s a name to motion.
The anatomy of brokers—notion, reasoning, reminiscence, motion, and collaboration—lays the inspiration for his or her capabilities, however with out the best infrastructure, these items can’t scale.
Platforms like Kafka and Flink are on the coronary heart of scaling microservices. By decoupling providers by means of occasions, these programs allow microservices—and now brokers—to work together seamlessly with out inflexible dependencies. For brokers as microservices, this implies they’ll emit and eat occasions autonomously, dynamically integrating into workflows whereas guaranteeing governance, consistency, and flexibility at scale.
The long run isn’t only one agent fixing one downside; it’s tons of of brokers working in live performance, seamlessly scaling and adapting to evolving challenges. To steer in 2025, we should focus not simply on constructing brokers however on creating the infrastructure to handle them at scale.

