In the event of a catastrophe, having a reliable backup and restoration strategy in place is vital to ensure business continuity and minimize disruption to a company’s entire Google Cloud account. The existence of an impenetrable, physically isolated model offers a degree of confidence in the integrity of high-consequence information.
On Sept. Google Cloud has bolstered its backup and disaster recovery capabilities by introducing an immutable vault.
The service is currently in preview mode, with a planned rollout to Google Cloud customers expected within the next few months, according to the company’s announcement.
The new backup and restoration service is securely isolated from any potential cyber threats, with no network connectivity to prevent unauthorized access.
The distinctive characteristic of a backup vault lies in its immutability, ensuring information cannot be altered or modified, as well as its indelibility, which guarantees that data cannot be deleted once stored. Data is seamlessly transmitted to the secure backup vault through the Backup and Disaster Recovery (DR) service, safeguarding against potential cyber threats or catastrophic errors with robust data protection. Customers within the parent group cannot access the backup vault either.
Directors can configure a retention interval during which the vault cannot be modified.
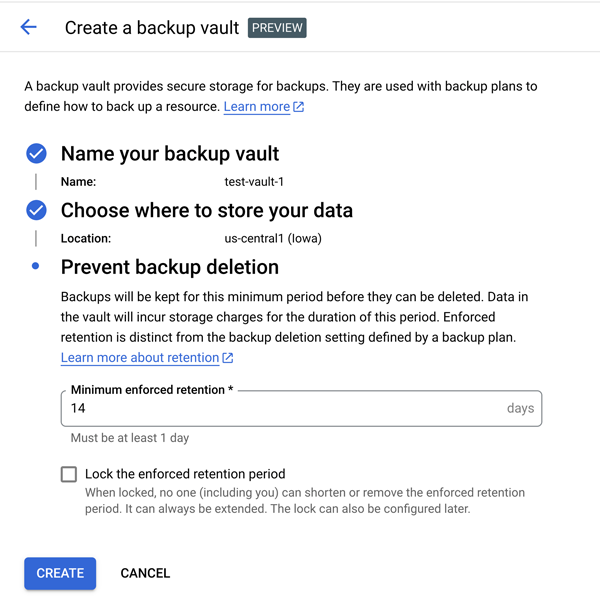
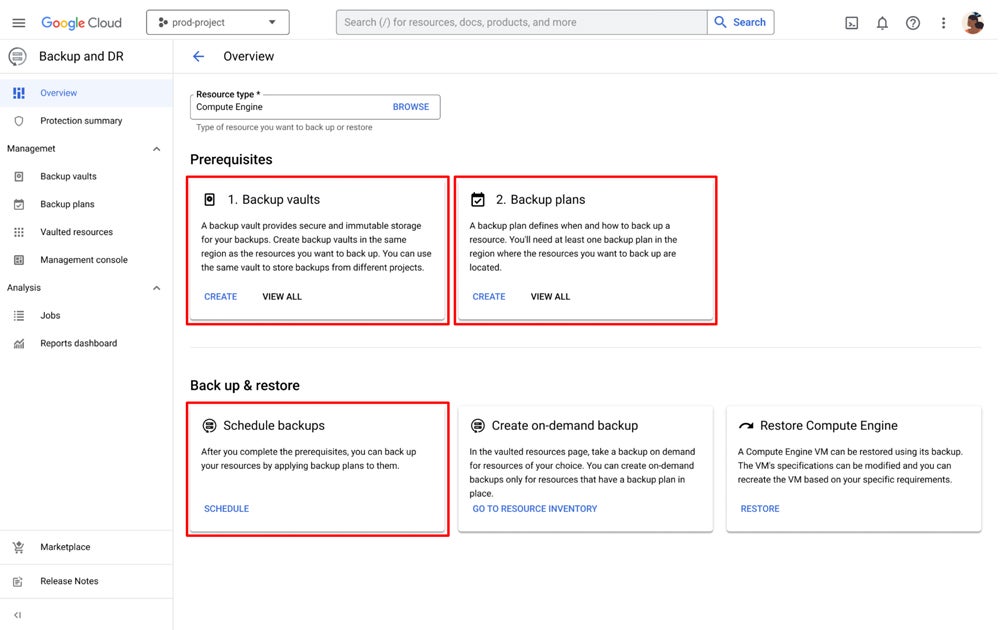
Organizations leveraging Google’s Compute Engine virtual machines (VMs) can now securely store their data in a dedicated vault. The vaults are unrelated to the supply undertaking and can be primarily situated within Compute Engine VMs, VMware ESXi hosts, Oracle relational databases, or Microsoft SQL Server databases.
Computing Engine VM backups can commence at the moment of creation, seamlessly integrating with the VM provisioning process. The process adheres to Google Cloud’s guidelines for identification and entry management, ensuring a seamless and secure setup that meets Google’s standards.
Create and manage scalable and highly available virtual machines on Google Cloud with Compute Engine. Use the Google Cloud Console, command-line tool, or API to create a customised VM that meets your application’s specific needs. With support for Linux, Windows, and Chrome OS, you can run a wide range of workloads, from web servers to databases and more?
Administrators and application developers have the ability to manually inspect and validate scheduled backup and restoration processes, uncover insights from unsuccessful or bypassed operations, and receive timely notifications for pivotal events related to data protection. To ensure reliable data preservation, administrators should systematically develop a comprehensive backup strategy within the Google Cloud environment.
In lieu of relying solely on Google Cloud backups, considering a multi-cloud strategy can provide benefits, as witnessed in recent instances where companies have encountered issues due to inadequate Google Cloud account backups last year.

