With the pace of technological advancements and shifting employee expectations, recruitment practices have undergone a seismic transformation. By 2024, one of the most significant advancements in expertise acquisition is likely to be generative AI. While recruitment is not a novel concept, the emergence of generative AI capable of crafting human-like text, automating communications, and tailoring candidate interactions to unprecedented levels introduces a profound paradigm shift in the industry. At the forefront of this revolution is a push for diversity-powered hiring, a transformative initiative that empowers companies to build more equitable and inclusive workplaces.
While range, fairness, and diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) initiatives have long been core components of effective recruitment strategies, traditional hiring approaches often struggle to adequately eliminate unconscious biases. With its suite of cutting-edge options, AIRecruit aims to tackle the issue of biased hiring practices head-on by crafting innovative tools that foster a more inclusive and equitable job search process.
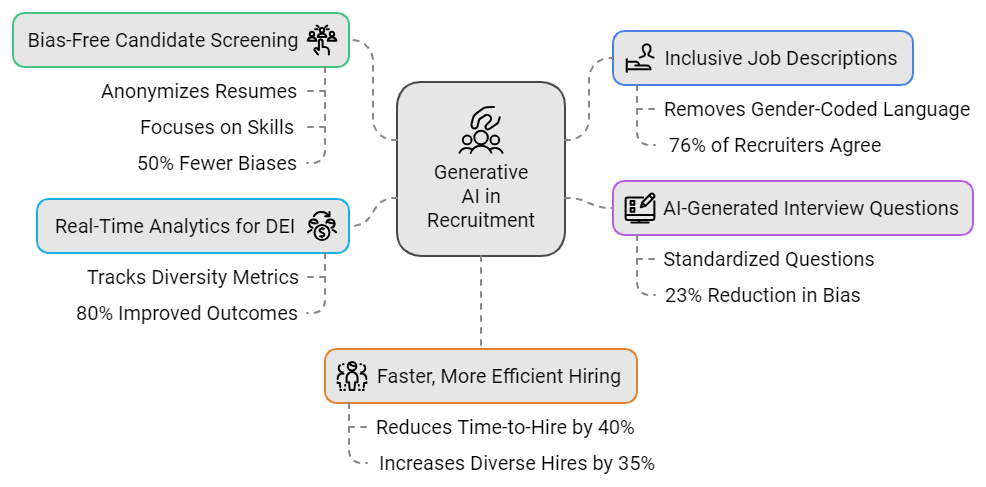
In 2023, the company introduced advanced generative capabilities within its HR software suite, aimed at revolutionizing diversity hiring processes. Powered by AI technology, these innovative tools focus on multiple stages of the recruitment process, encompassing job posting, candidate assessment, and interview procedures. Through anonymization of candidate profiles, removal of gendered language from job descriptions, and the application of data-driven insights to identify potential biases, a paradigm shift towards more inclusive hiring practices is being pioneered.
Despite concerted efforts to promote inclusivity, unconscious bias continues to plague the hiring process, perpetuating inequality and hindering diversity. Studies conducted by the Harvard Enterprise Assessment have revealed that job applicants with “ethnically distinct” names tend to receive significantly fewer interview callbacks compared to those with more traditionally “Anglo-Saxon” sounding names, with differences ranging from in certain studies. Despite growing recognition among organizations that unconscious bias significantly influences their recruitment decisions, they continue to struggle with a smaller, less diverse workforce and higher employee turnover rates.
Generating presents an answer by providing data-driven objectivity to the recruitment process. Algorithms can anonymize resumes by eliminating identifiable information, such as names, genders, and academic backgrounds. By removing human judgment from the initial evaluation process, this innovative approach allows recruiters to concentrate exclusively on the candidate’s skills and qualifications, significantly reducing the likelihood of unconscious bias.
Job descriptions often contain biased language that can discourage a wide range of qualified candidates from applying? According to a study by Textio, job postings containing phrases such as “aggressive” or “rockstar”-style descriptions are more likely to attract male applicants, while those using more neutral language tend to receive a broader range of responses? Instruments, such as Textio’s predictive writing tools, proactively eliminate gender-coded language and suggest alternative options that foster greater inclusivity.
Generative AI can revolutionize job descriptions, transforming phrases like “powerful chief” into “capable leader,” thereby broadening the applicant pool by eliminating gender-biased terminology.
Driven screening instruments analyze resumes at scale, matching candidates primarily based on qualifications and expertise rather than demographic factors. This automated process improves effectiveness and minimizes the potential for bias during the initial stages of recruitment. According to studies, companies leveraging AI-powered tools in their recruitment processes have observed a significant reduction in time-to-hire and a noticeable enhancement in candidate quality.
Driven screening instruments not only analyze resumes, but also provide insight into the likelihood of a candidate succeeding in the role. Predictive analytics is leveraged to forecast candidate success by analyzing the background profiles of current employees and identifying correlations with job performance.
Additionally, generative AI boosts transparency by offering real-time analytics that provide valuable insights into the hiring process and its underlying characteristics. A cutting-edge recruitment software program can create narratives that analyze the diversity of a company’s candidate pool and workforce. This perception enables companies to gauge their standing regarding DEI targets and adjust their hiring strategies accordingly.
Through a strategic partnership with Eightfold, organisations can bridge the disparity in their talent pipelines by pinpointing knowledge gaps and taking measurable actions to address them effectively. Such organizations excel when they have multiple divisions, as companies with more extensive portfolios outperform their smaller counterparts by up to 15% in terms of financial performance, according to McKinsey’s 2020 report.
During interviewing, unconscious biases can often unintentionally influence hiring decisions. Generating AI-powered interview tools can produce standardized, skills-based questions that objectively evaluate a candidate’s competencies, rather than relying on subjective factors. Powered instruments, leveraging AI-driven insights, can analyze candidate responses in real-time and offer personalized recommendations on suitability for specific roles based on objective criteria rather than individual opinions.
According to a case study by HireVue, companies that leveraged technology to conduct interviews witnessed a significant reduction in bias, with a corresponding acceleration of the hiring process. Powered by these insights, organizations can conduct more effective goal-oriented analyses of candidates, thereby better aligning their hiring processes with targeted diversity, equity, and inclusion initiatives.
In 2023, the tech giant made waves by announcing the integration of cutting-edge generative tools within its comprehensive HR software ecosystem. These solutions aim to help companies streamline crucial aspects of their recruitment process while fostering a culture of diversity and inclusion. The corporation’s partnership with OpenAI leverages cutting-edge technologies such as GPT-4 to boost personalized candidate interactions and provide actionable predictive insights.
Recently, the company has introduced a groundbreaking Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion (DEI)-specific model, harnessing the power of sentiment analysis to comprehensively assess candidate skills throughout the entire hiring process in 2024.
This AI-driven solution pinpoints bias-prone areas and streamlines the candidate experience to ensure that individuals from traditionally marginalized groups are not inadvertently excluded from the hiring process due to unfair biases.
- Data-driven recruitment tools yield a significant boost in diversity hiring results, according to a recent study published by the Society for Human Resource Management (SHRM).
- According to a survey conducted by Glassdoor, job seekers are more likely to apply to companies that demonstrate a genuine commitment to diversity.
- Powered recruitment platforms have demonstrated a notable ability to reduce time-to-hire by an average of __%, while simultaneously yielding a significant increase in the number of qualified candidates being considered, according to LinkedIn’s 2024 Recruiting Trends report.
As generative technology rapidly transforms the landscape of expertise acquisition, innovative tools empowered by this revolution are spearheading the change. By addressing biases, amplifying Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion initiatives, and streamlining recruitment strategies, organizations gain a unique opportunity to build more diverse and inclusive teams. As knowledge advances, companies that seize these opportunities will pave the way for creating more equitable, sustainable, and diverse workspaces.
The article was first published on.

