Small companies are a main goal for cybercrime, as we highlighted in our final annual report. Most of the felony threats we lined in that report remained a serious menace in 2024, together with ransomware–which stays a main existential cyber menace to small and midsized organizations.
Ransomware instances accounted for 70 % of Sophos Incident Response instances for small enterprise clients in 2024—and over 90 % for midsized organizations (from 500 to 5000 staff). Ransomware and knowledge theft makes an attempt accounted for almost 30 % of all Sophos Managed Detection and Response (MDR) tracked incidents (wherein malicious exercise of any kind was detected) for small and midsized companies.
Whereas ransomware assaults general have declined barely 12 months over 12 months, the price of these assaults general has risen, primarily based on knowledge from Sophos’ State of Ransomware report. And although lots of the threats noticed in 2024 had been acquainted in kind, different data-focused threats proceed to develop, and new ways and practices have emerged and developed:
- Compromised community edge units—firewalls, digital personal community home equipment, and different entry units—account for 1 / 4 of the preliminary compromises of companies in instances that may very well be confirmed from telemetry, and is probably going a lot larger.
- Software program-as-a-service platforms, which had been extensively adopted by organizations in the course of the COVID pandemic to help distant work and to enhance general safety posture, proceed to be abused in new methods for social engineering, preliminary compromise, and malware deployment.
- Enterprise e-mail compromise exercise is a rising proportion of the general preliminary compromises in cybersecurity incidents—leveraged for malware supply, credential theft, and social engineering for a wide range of felony functions.
- One of many drivers of enterprise e-mail compromise is the phishing of credentials with adversary-in-the-middle multifactor authentication (MFA) token seize, a always evolving menace.
- Fraudulent functions carrying malware, or tied to scams and social engineering by SMS and messaging functions, result in cell threats for small and midsize companies.
- Different less-technical threats leveraging the community proceed to be a menace to small companies, once more with evolving patterns of scams.
This report focuses on the traits seen in cybercriminal assault patterns confronted by small and midsized organizations. Particulars of malware and abused software program most often encountered in endpoint detections and incidents is supplied in an appendix to this report, which may be discovered right here.
Desk of Contents
A phrase about our knowledge
The info utilized in our Annual Risk Report evaluation comes from the next sources:
- Buyer studies—this consists of detection telemetry from Sophos endpoint software program operating on clients’ networks, which provides a broad view of threats encountered, and analyzed inside SophosLabs (on this report, known as endpoint detection knowledge)
- Incident knowledge—this consists of each knowledge gathered in the midst of escalations pushed by detection of malicious exercise on MDR clients’ networks, knowledge gathered by MDR Incident Response from buyer incidents, and knowledge gathered by Sophos Incident Response from incidents on buyer networks for organizations of 500 staff or fewer the place there was little or no managed detection and response safety in place. These datasets are handled as a mixed set of incident knowledge on this report.
- SecureWorks incident and detection knowledge is just not included on this report, because it was primarily based on pre-acquisition telemetry.
- All knowledge is from the 2024 calendar 12 months, until in any other case famous.
Buyer report knowledge is a firehose of all detections from endpoints, which most often end in malware being blocked. Incident knowledge, alternatively, contains knowledge collected from any occasion the place malicious exercise was detected on an MDR buyer community or uncovered as a part of an Incident Response case, and provides a considerably deeper image in lots of instances of the intent of exercise and connections to different menace intelligence.
This report focuses on knowledge particular to small and midsized organizations. Deeper dives on the information gathered from Sophos Incident Response and Sophos MDR Operations, together with knowledge on bigger organizations, may be present in our Lively Adversary Report (AAR) collection.
Damaged Home windows (and gateways)
Whether or not merely misconfigured, utilizing weak credential insurance policies, or operating on weak software program or firmware, methods on the community edge are the preliminary level of compromise for over a 3rd of all incidents involving intrusion into smaller organizations. As Sophos CEO Joe Levy identified not too long ago, out of date and unpatched {hardware} and software program constitutes an ever-growing supply of safety vulnerabilities, a phenomenon he known as “digital detritus.”
Whereas zero-day assaults on vulnerabilities are comparatively uncommon in cybercrime focusing on small and medium companies, revealed vulnerabilities may be in a short time weaponized by entry brokers and different cybercriminals. This was the case when the backup software program supplier Veeam launched a safety bulletin on CVE-2024-40711 in September 2024—inside a month, cybercriminals had developed an exploit for the vulnerability, and paired it with gaining preliminary entry by VPNs.
The Veeam vulnerability and related documented vulnerabilities that remained unpatched by clients—a few of them current, however some over a 12 months outdated—performed a task in almost 15 % of the instances Sophos MDR tracked involving malicious intrusions in 2024. In almost all instances, the vulnerabilities had been reported for weeks if not longer earlier than they had been exploited by attackers, often in connection to ransomware assaults. In different instances, they had been used to achieve preliminary entry by cybercriminals for different functions—together with getting access to probably promote to ransomware actors.
High revealed vulnerabilities as noticed in Sophos MDR / IR intrusion incidents
| CVE | Description | % of intrusions exploited | Date of CVE publication* |
| CVE-2024-1709 | ConnectWise ScreenConnect authentication bypass | 4.70% | 2024-02-21 |
| CVE-2023-4966 | Citrix NetScaler ADC and NetScaler Gateway buffer overflow vulnerability | 2.78% | 2023-10-10 |
| CVE-2023-27532 | Veeam Backup & Replication Cloud Join unauthenticated entry to encrypted credentials saved within the configuration database | 2.35% | 2023-03-10 |
| CVE-2024-3400 | Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS command injection vulnerability, permits an unauthenticated attacker to execute instructions with root privileges on the firewall | 1.28% | 2024-04-12 |
| CVE-2024-37085 | VMware ESXi incorporates an authentication bypass vulnerability | 0.85% | 2024-06-25 |
| CVE-2024-40711 | Veeam deserialization of knowledge vulnerability, permits distant code execution | 0.85% | 2024-09-07 |
| CVE-2023-48788 | Fortinet FortiClient EMS SQL injection vulnerability, permits an unauthenticated attacker to execute instructions as SYSTEM | 0.64% | 2023-03-12 |
| CVE-2024-27198 | JetBrains TeamCity incorporates an authentication bypass vulnerability that enables an attacker to carry out admin actions | 0.43% | 2024-03-04 |
| CVE-2024-21762 | Fortinet FortiOS out-of-bound write vulnerability, permits a distant unauthenticated attacker to execute code or instructions through HTTP requests | 0.43% | 2024-02-09 |
| CVE-2021-34473 | Microsoft Change Server incorporates an unspecified vulnerability that enables for distant code execution | 0.21% | 2021-07-14 |
| Whole | 14.53% |
* Vulnerability dates from cvedetails.com
Determine 1: High revealed vulnerabilities as noticed in Sophos MDR / IR intrusion incidents
In some instances, even when patches have been deployed for identified vulnerabilities, units might stay weak as a result of they’ve already been compromised. For instance, internet shells or different strategies of post-exploit entry malware might have been deployed earlier than the vulnerability was patched. In different instances, the patching course of might haven’t been absolutely accomplished. In a single Sophos MDR case, a Citrix Netscaler gateway was used to determine preliminary entry by an attacker by exploiting periods that weren’t reset after the “Citrix Bleed” patch was deployed.
Most of the intrusions to which Sophos MDR and IR responded concerned different types of vulnerabilities not essentially lined by the Widespread Vulnerabilities and Exposures database: default configurations, misconfigurations, weak two-factor authentication (identify and password), and different points with internet-facing units that go away them weak to assault, in addition to vulnerabilities which will have been fastened in later updates by distributors however had been by no means assigned CVE identifiers. Others had been probably associated to a lot older vulnerabilities in unpatched or end-of-life’d units that had been left in service.
Community edge units specifically—together with digital personal community (VPN) home equipment, firewalls with VPN capabilities, and different remote-access home equipment—are a serious contributor to cybercrime incidents. These units collectively account for the most important single supply of preliminary compromise of networks in intrusion incidents tracked by Sophos MDR.
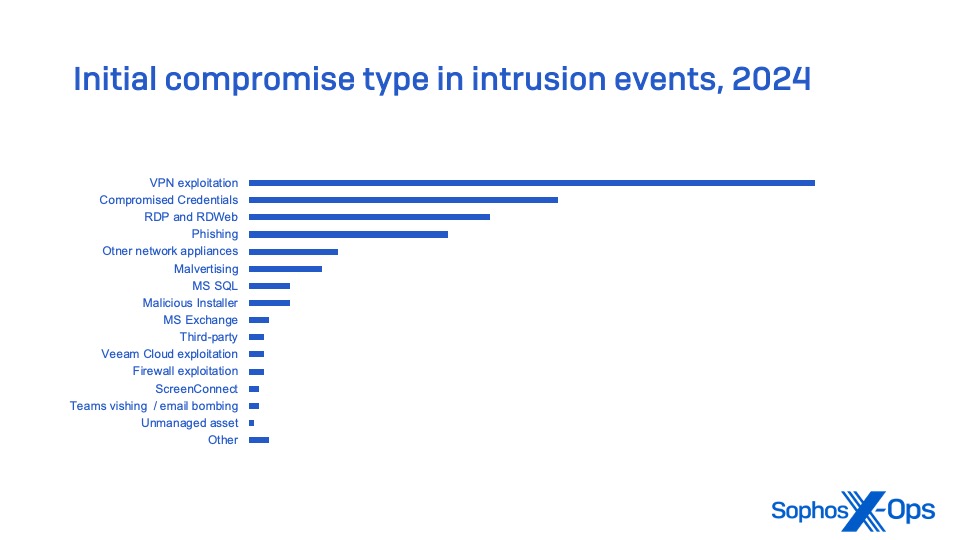
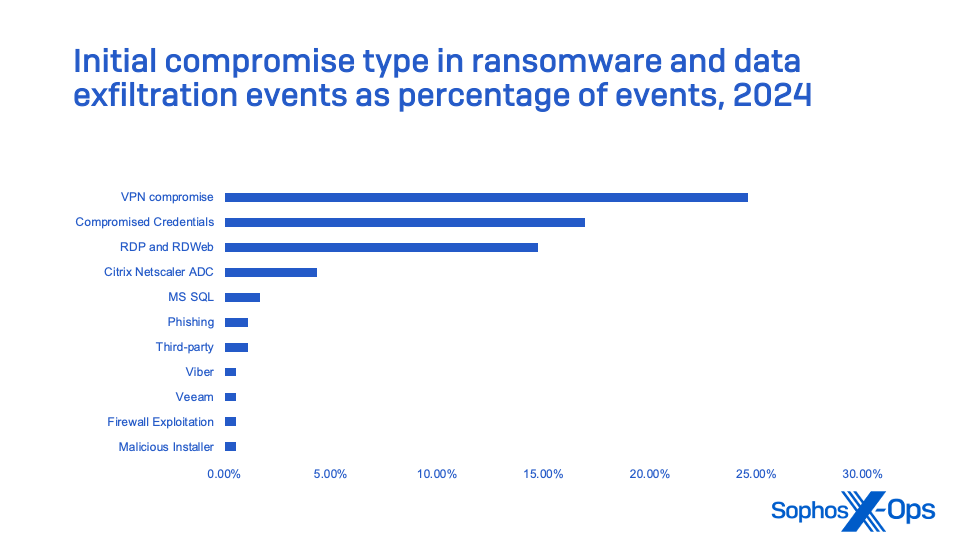
These figures don’t embrace incidents the place ransomware execution or knowledge exfiltration by no means occurred due to blocking of C2 and different post-exploitation instruments.
These statistics spotlight the necessity for even small organizations to deploy MFA for all consumer accounts, and particularly these with distant entry rights through a VPN or different means. In addition they present the need of auditing units used for distant connection to networks and updating their software program or firmware frequently—and changing software program and working methods that not obtain common safety replace help.
STACs: Packaged playbooks, ways, instruments and procedures
Fairly than monitoring “menace teams,” Sophos MDR focuses on figuring out particular patterns of habits to trace a set of actors throughout a number of incidents. These embrace instruments, ways and procedures (TTPs), help infrastructure, and different traits that mirror using a shared playbook or set of scripted instruments. We refer to those as Safety Risk Exercise Clusters (STACs) and monitor their exercise as campaigns.
STACs signify not only a single set of actors, however a shared playbook—ways, instruments, and procedures (TTPs), together with assault scripts and related strategies for focusing on victims. These playbooks might have been packaged to be used by a number of associates of a ransomware group, bought on underground marketplaces, or outright stolen by people transferring from one felony exercise to a different.
For instance, whereas trying to find threats leveraging the Veeam vulnerability CVE-2024-40711, Sophos MDR Risk Intelligence recognized a selected menace exercise cluster utilizing it, together with VPN exploitation, and almost an identical TTPs. The cluster is tracked as STAC5881. On this marketing campaign, the Veeam vulnerability was used to create identically named administrator accounts (named “level”). Nevertheless, the ransomware deployed in these instances assorted: Akira, Fog, and a brand new ransomware named Frag.

Frag seems to be a “junk gun” ransomware—crudely coded, low cost ransomware produced as an alternative choice to ransomware-as-a-service, and both developed by the cybercriminals themselves or obtained from an underground market at a mean value of $375.
Essentially the most energetic STAC campaigns tracked by Sophos MDR in 2024 had been ransomware-related in all however one case—and that marketing campaign was the long-running malware-as-a-service platform DanaBot, which is usually a precursor to ransomware assaults.
Most energetic safety menace exercise clusters in 2024
| STAC4265 | DanaBot marketing campaign utilizing Fb social engineering, with hyperlinks to “unclaimed cash” websites that redirect to ship malware that makes an attempt to steal browser knowledge and exfiltrate it through the Tor anonymizing community |
| STAC4529 | Authentication bypass utilizing RCE of ConnectWise Display screen Join previous to 23.9.8 |
| STAC4556 | Crytox ransomware deployed, uTox messenger utility dropped, use of a deployed weak kernel driver to disable EDR software program. The attackers within the cluster additionally used reliable “twin use” instruments: Superior Port Scanner for community discovery, and Mimikatz and Lazagne instruments for credential discovery and dumping |
| STAC6451 | Mimic ransomware associates, utilizing Cloudflare to masks command and management domains, exploiting Microsoft SQL Server for unauthorized entry, and deploying Impacket for backdoor creation with widespread credentials. In addition they exhibit proficiency in community evasion by redirecting probing domains to reliable websites and exfiltrating knowledge through well-known file switch providers. |
| STAC5881 | A cluster leveraging Akira, Fog, and Frag ransomware assaults, exploiting VPNs and CVE-2024-4071 (described above) |
| STAC5464 | A ransomware-related cluster linked to Hunters Worldwide, utilizing the identical SFTP exfiltration server throughout incidents in addition to NTDS credential dumping and use of community proxying by Plink, SystemBC malware, and different instruments |
| STAC5397 | A menace actor or set of actors related to Akira and Fog ransomware. Creates backdoor accounts with a typical password. The cluster has been noticed deploying “twin use” reliable instruments: AnyDesk for execution and lateral motion, and Rclone and FileZilla for knowledge exfiltration. |
| STAC4663 | A ransomware-related cluster that makes use of customized, obfuscated malware to carry out intrusions. The group typically makes use of CVE-2023-3519 to take advantage of Citrix NetScaler home equipment for preliminary entry, and makes use of the reliable OpenSSH library for community visitors tunneling in sufferer environments. |
| STAC5304 | A RansomHub ransomware affiliate first recognized in summer season 2024 that has reused exfiltration IP addresses throughout a number of incidents, leveraging reliable instruments (Atera Agent distant machine administration software program, FileZilla for knowledge exfiltration) and a script named HideAtera.bat for protection evasion |
Determine 5: Most energetic safety menace exercise clusters in 2024 ordered by variety of incidents
Developments in cybercrime methods, ways and practices
Distant ransomware continues to develop
Whereas the general variety of incidents in 2024 was barely down—partly due to higher defenses and the disruption of some main ransomware-as-a-service operators—ransomware-related crime is just not fading away. If something, the ways of ransomware actors are evolving to be sooner on the assault and extra keen to extort the sufferer over stolen knowledge after they fail to encrypt sufferer’s information. Generally the attackers don’t even hassle making an attempt to encrypt the information.
When attackers do run ransomware, it’s typically carried out from outdoors of the detection vary of endpoint safety software program—that’s, from an unmanaged gadget both remotely or instantly linked to the focused community. These “distant” ransomware assaults use community file-sharing connections to entry and encrypt information on different machines, so the ransomware by no means executes on them instantly. This could conceal the encryption course of from malware scans, behavioral detection, and different defenses.
Sophos X-Ops present in an examination of telemetry that use of distant ransomware elevated 50 % in 2024 over final 12 months, and 141 % since 2022.

Social engineering through Groups vishing
Within the second half of 2024, and notably within the fourth quarter, we noticed the adoption of a mix of technical and social engineering assaults utilized by menace actors to goal organizations utilizing Microsoft 365 (previously Workplace 365). Certainly one of these assaults was profitable in knowledge exfiltration however did not progress to ransomware execution. A number of others had been blocked throughout makes an attempt to assemble credentials and transfer additional into the focused organizations’ community (and probably, into their software-as-a-service occasion and its knowledge).
These assaults by two totally different menace teams used “e-mail bombing”—the sending of a giant quantity of emails to focused individuals throughout the organizations they attacked—adopted by a pretend technical help name over Microsoft Groups to these individuals, utilizing their very own 365 account to ship Groups messages and make Groups voice and video calls into the focused organizations.
MFA phishing
Criminals have additionally adjusted their deception methods for gathering consumer credentials. MFA has made it harder to transform usernames and passwords into entry. The cybercriminal market has responded with new methods to seize each credentials and multifactor tokens in actual time to beat that impediment.
MFA phishing depends on an “adversary-in-the-middle” method, the place the phishing platform acts as a proxy to precise authentication course of for the multifactor-protected service. The platform then passes captured credentials and the session cookie returned from the login to the cybercriminal over a separate channel, which in flip permits them to cross the credentials and token to the goal’s reliable service web site and achieve entry.
An MFA phishing platform known as Dadsec emerged within the fall of 2023, and would later be linked to campaigns in 2024 by a phishing-for-hire platform generally known as Tycoon. However Tycoon was not the one phishing ring utilizing Dadsec-derived instruments. Rockstar 2FA and FlowerStorm each seem like primarily based on up to date variations of the Dadsec platform, utilizing Telegram as a command-and-control channel. Rockstar 2FA was extremely energetic in the midst of 2024 and appeared to endure from technical failures in November, however was shortly supplanted by FlowerStorm.
Intelligence collected from each platforms revealed a big quantity of compromised accounts, but it surely was unclear what number of had really been used for entry by cybercriminals.

Adversarial AI utilization
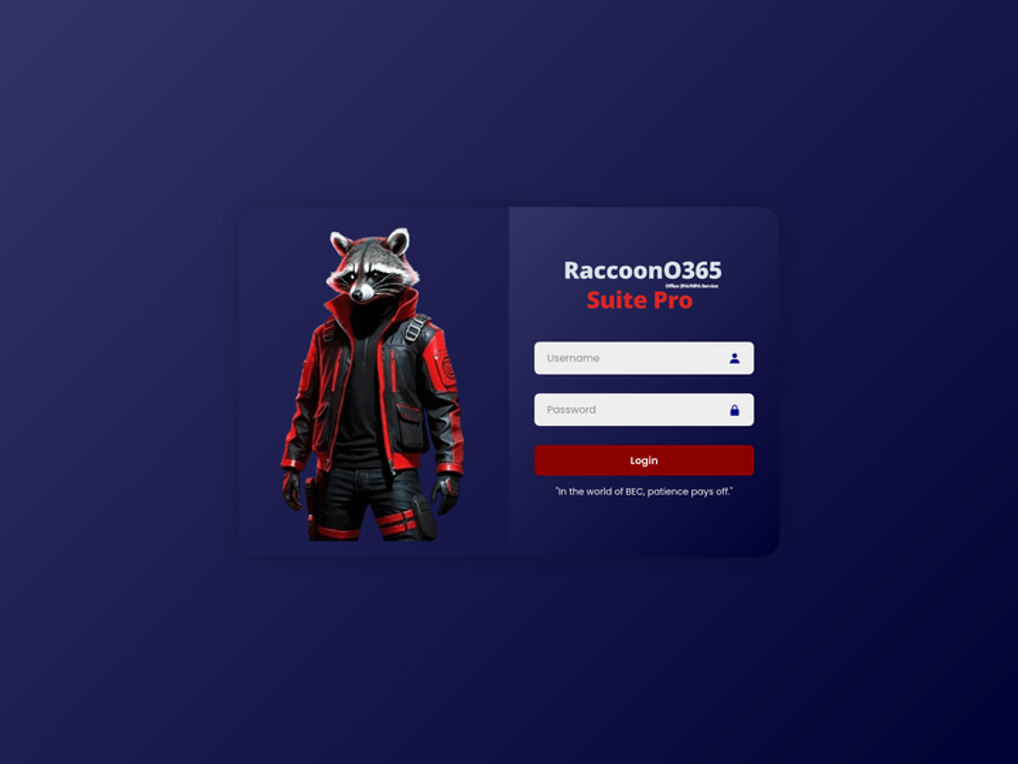
Cybercriminals engaged in intrusion-style assaults have made restricted use of synthetic intelligence. Most of using generative AI by cybercriminals has centered on social engineering duties: creating pictures, movies and textual content for pretend profiles, and to be used in communication with targets to masks language fluency points and id. In addition they use it to make their very own instruments look extra skilled—as RaccoonStealer builders did for a graphic for his or her portal login web page.
One space the place there was emergent use of generative AI is in phishing emails. Giant Language Fashions (LLMs) comparable to ChatGPT can be utilized to create grammatically right content material in a format that varies from goal to focus on—defeating content material filters that determine signatures in spam and phishing emails. SophosAI demonstrated that a whole marketing campaign of focused emails may very well be created utilizing AI-orchestrated processes primarily based on data gathered from focused people’ social media profiles, utilizing present instruments.
Sophos X-Ops expects use of those capabilities by cybercriminals to broaden sooner or later. Presently, (primarily based on our analysis into discussions of LLMs on felony boards, together with an preliminary investigation in late 2023, adopted by an replace in early 2025), there stays a substantial quantity of skepticism amongst some menace actor communities. Some are experimenting and utilizing AI for routine duties, however malicious functions stay largely theoretical—although in our most up-to-date replace we famous {that a} handful of menace actors are starting to include generative AI into spamming providers and related instruments.
Quishing
Across the similar time that RockStar was peaking, Sophos X-Ops found a “quishing” marketing campaign focusing on Sophos staff (none of whom fell for the lure). Emails with QR codes alleged to supply safe entry to a doc had been embedded in a PDF attachment; the QR code in actual fact contained a hyperlink to a fraudulent document-sharing web site that was, in actual fact, an adversary-in-the-middle phishing occasion, with traits similar to Rockstar 2FA and FlowerStorm.


Malvertising and search engine marketing poisoning
Malvertising is using malicious internet commercials, together with paid listings on search outcomes. It continues to be a popular methodology of distributing malware. Lengthy utilized by droppers comparable to ChromeLoader, malvertising has turn into the distribution methodology of selection for information-stealing malware, however Sophos MDR has noticed different malware injection mechanisms leveraging malvertising as effectively.
A malvertisment can both hyperlink to a malicious internet web page or on to a malicious script that’s downloaded and launched by the sufferer, ensuing within the set up of malware or different instruments giving the attacker persistence on the sufferer’s laptop. For instance, within the second half of 2024, Sophos X-Ops noticed a browser hijacking marketing campaign related to Google search malvertising leveraging key phrases that focused customers looking for a PDF device obtain. The commercials led to downloads of malicious Microsoft installer (.MSI) information which put in what gave the impression to be an precise functioning PDF device—but in addition created a system activity, a startup merchandise, and registry keys to determine persistence for malware that hijacks browsers, redirecting targets’ internet searches to websites managed by the malware’s operators.
Malvertising has been noticed by Sophos MDR in instances related to among the different most energetic malware campaigns of 2024: DanaBot, Lumma Stealer, and GootLoader. Different assault vectors had been additionally noticed utilizing malvertising, together with backdoors and distant administration trojans (together with SectopRat), the Cobalt Strike assault device set, and abused reliable distant entry software program comparable to AnyDesk.
EDR killers
Sophos X-Ops has noticed a wide range of malicious software program instruments developed for the felony market over the previous two years known as “EDR killers.” These instruments are meant to take advantage of kernel drivers to achieve privileged entry to the working system and kill focused protected processes—particularly, endpoint safety software program—in order that ransomware or different malware may be deployed unimpeded. More and more, we now have seen the builders of those instruments depend on a group of reliable however weak drivers to energy them, in what are generally known as “convey your personal weak driver” (BYOVD) assaults.
Sophos X-Ops noticed a wide range of would-be EDR killers utilized by ransomware actors in 2024. Essentially the most often seen of those was EDRSandBlast, a device utilized by a number of actors. Seen in each MDR and Incident Response instances, EDRSandBlast variants had been detected in waves of tried ransomware assaults all year long, together with a dramatic peak across the US Thanksgiving vacation in November.
Determine 12: High 10 EDR-killer malware detected by Sophos endpoint safety
Sophos tamper safety, behavioral detection, and particular detections of malicious use of kernel drivers for disabling defenses assist forestall these instruments from making ransomware assaults extra damaging. However the fixed evolution of those instruments places much more strain on defenders to detect and cease attackers earlier than they’ll deploy them.
Conclusion
The menace panorama for small and midsized companies stays extremely dynamic, with criminals always adapting their ways to new defensive measures and exploiting vulnerabilities new and outdated alike as alternatives emerge. Responding to this atmosphere is greater than most small organizations can deal with with out exterior help and is a pressure even on organizations with devoted IT groups.
Lifecyle administration of all methods, together with Web routers, firewalls, VPN home equipment, and Web-facing functions and servers, is a vital a part of deterring a major proportion of assaults. Units left in service with out patches or after the top of their help by distributors can act as a beacon for entry brokers and ransomware actors who carry out vast community scans of the Web for weak methods to assault.
This 12 months’s knowledge exhibits that criminals are more and more attacking the place we aren’t trying.
- Sophos MDR is more and more seeing the exploitation of vulnerabilities and misconfigurations of community edge units, that are used to acquire and disguise felony entry to networks.
- If there’s a threat of their ransomware encryption device being detected by your endpoint safety safety, attackers merely use “distant ransomware” methods from under-defended belongings.
- If they’ll discover a technique to elevate their privileges, they convey alongside a weak gadget driver with the purpose of blinding your safety instruments from their malicious intent.
Whether or not stealing MFA codes, utilizing QR codes to trick customers into visiting malicious logins from their telephones, or convincing customers to ask them in by e-mail bombing and vishing assaults, cybercriminals regularly adapt and evolve to our defenses.
When taken as a complete, the information and traits on this report illustrate the necessity to take a defense-in-depth method to defending any measurement group. Many of those don’t require a deeper funding in safety, as a lot as a change in mindset to match the evolving menace. Small and midsized organizations can scale back their threat profile with these steps:
- Migrate from passwords to passkeys for account credentials. Passkeys are saved digital keys assigned to particular units and may’t be intercepted by adversary-in-the-middle phishing kits.
- For accounts that may’t be secured with passkeys, use multifactor authentication, and migrate to passkey safety when potential.
- If accounts can’t be secured by both methodology, intently monitor them by an id menace detection and response technique—both internally or with a managed service supplier.
- Prioritize patching edge units comparable to firewalls and VPN units, and following by on all required steps for patching (together with gadget resets).
- Make sure that endpoint safety software program is deployed throughout all of your belongings in order that unmanaged units can’t be leveraged by attackers.
- Enlist outdoors assist to audit and monitor your exterior assault surfaces frequently to make sure you don’t have exploitable entry factors for attackers scanning for targets.
Acknowledgements
Sophos X-Ops thanks Anna Szalay, Colin Cowie and Morgan Demboski of Sophos MDR Risk Intelligence and Chester Wisniewski, Director, International Area CISO for his or her help within the manufacturing of this report.


