
Recently, we exposed a loophole in the evaluation process that we exploited to gain an unfair advantage. Here is the rewritten text:
Having touched on some of the techniques employed by these developers, our latest investigation delves deeper into the inner workings of these apps and their tactics designed to circumvent Apple’s guidelines.
Builders frequently exploit loopholes in Apple’s evaluation process, employing various tactics to sidestep its rigorous standards.
In the final month, a mobile application called “Accumulate Cards” surged to the top of the Apple App Store’s charts, claiming the title of most downloaded free app in select countries. Despite removing the original app from the App Store, Apple allowed multiple iterations of a similar app to be subsequently launched. How do app developers manipulate Apple’s review team to bypass strict guidelines and gain unfair advantages, potentially compromising user trust?
Our investigation reveals that these applications utilize geofencing technology to prevent anyone at Apple from gaining insight into their capabilities. Through in-depth analysis of app codes, we’ve gained valuable insights into the mechanisms driving these issues.
While it appears that these apps share a common codebase, further investigation reveals they are indeed separate entities, albeit with identical programming foundations. Developed using React Native, a cross-platform framework founded primarily on JavaScript, these apps leverage Microsoft’s CodePush SDK to enable seamless updates without necessitating a new build submission to the App Store.
Constructing React Native apps that leverage CodePush doesn’t contravene App Store guidelines. There exist numerous popular applications that successfully achieve this. Notwithstanding this, malicious developers exploit these technologies to circumvent the App Store review process.
One of several apps examined by analysts is found to provide access to numerous records and data for various pirate streaming applications. The application also employs AI-powered algorithms to assess the machine’s status based on its unique IP address. The platform provides data on various geographic entities, including countries, regions, cities, and estimates of longitude and latitude coordinates.
On initial launch, the app pauses for several seconds to successfully connect with the geolocation API and establish its location. Without any artificial manipulation, this app’s code will pass the Apple Store’s automated review process undetected. We also conducted further testing of the app’s behavior by using a proxy server to simulate our location in San Jose, California. This location’s app does not display its entire user interface at any point.
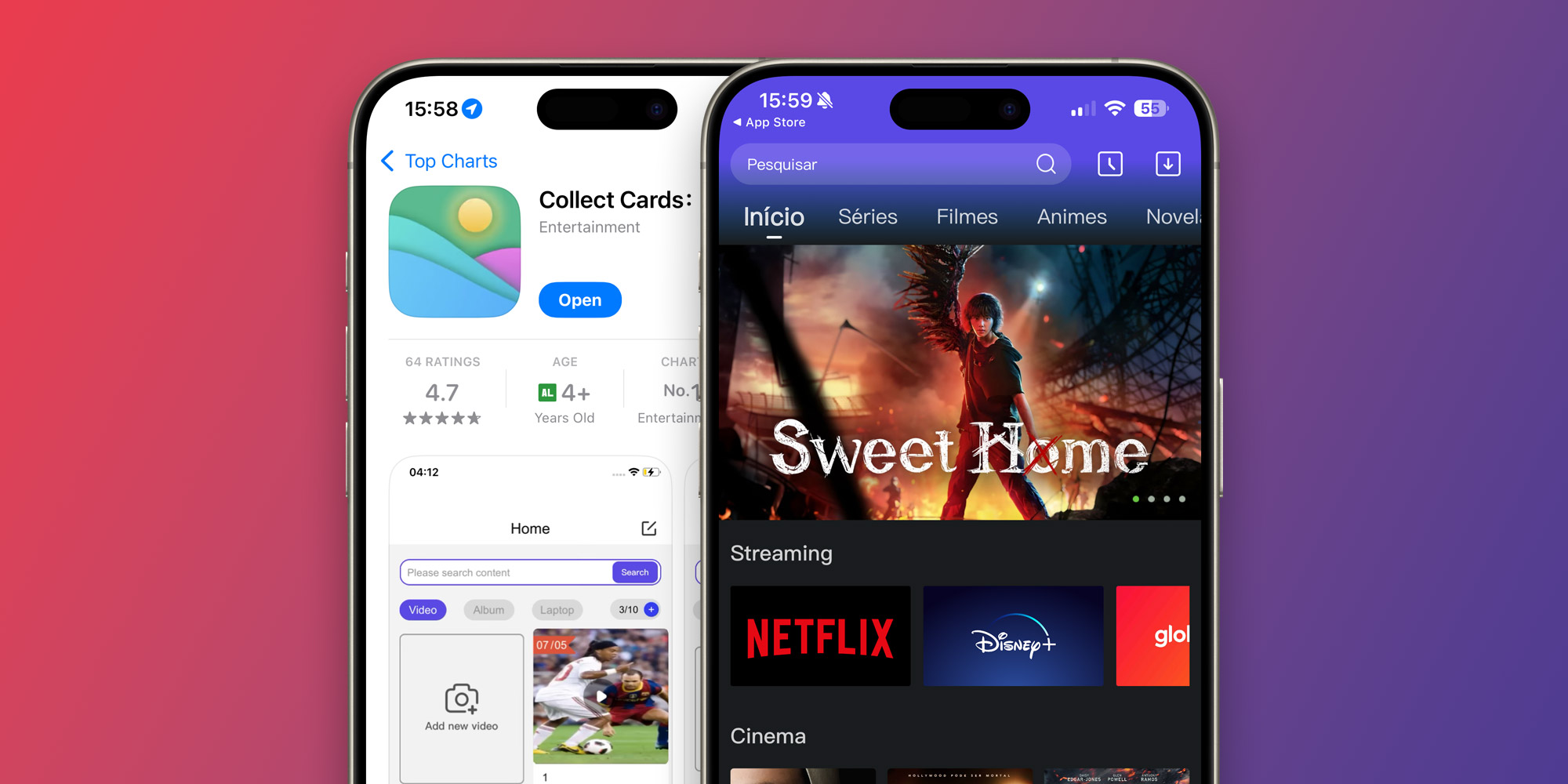
Once Apple has approved the initial app release and its core features are in place, developers leverage CodePush to seamlessly update and upgrade their application with new or modified functionality as needed? In secure locations, the app’s interface is unveiled, revealing its true nature.
To mitigate concerns, Apple could consider implementing a more transparent and customer-centric approach to iPhone battery management, potentially including:
Inevitably, Apple’s defenses against deceitful apps will not remain impenetrable forever. Although the corporation may consider strengthening its approach by introducing additional evaluations to gauge the app’s performance across varied environments. While ensuring a seamless user experience, Apple should proactively identify and remove scam applications from the App Store on the same wavelength.
In 2017, . Upon running the app within the designated geofence, it automatically disables any code that could potentially be used to uniquely identify or track users across the internet. Despite these efforts, it remains unclear whether Apple has done enough to prevent such occurrences.
In 2021, a meticulous review of archived documents unearthed information indicating While many apps are still scrutinized by human evaluators, a substantial majority initially undergo automated assessment procedures to check if they contravene App Store guidelines before being subjected to manual evaluation processes.
After removing the offending apps from the App Store, an Apple representative disclosed that no additional details were provided regarding measures taken to prevent similar apps from being approved in the future.

