The annual clock of the seasons—winter, spring, summer time, autumn—is commonly taken as a given. However our new research in Nature, utilizing a brand new strategy for observing seasonal progress cycles from satellites, exhibits that this notion is much too easy.
My colleagues and I current an unprecedented and intimate portrait of the seasonal cycles of Earth’s land-based ecosystems. This reveals “hotspots” of seasonal asynchrony all over the world—areas the place the timing of seasonal cycles will be out of sync between close by areas.
We then present these variations in timing can have stunning ecological, evolutionary, and even financial penalties.
Watching the Seasons From House
The seasons set the rhythm of life. Dwelling issues, together with people, alter the timing of their annual actions to take advantage of sources and situations that fluctuate via the yr.
The research of this timing, often called phenology, is an age-old type of human statement of nature. However as we speak, we are able to additionally watch phenology from area.
With decades-long archives of satellite tv for pc imagery, we are able to use computing to raised perceive seasonal cycles of plant progress. Nevertheless, strategies for doing this are sometimes based mostly on the assumption of easy seasonal cycles and distinct rising seasons.
This works effectively in a lot of Europe, North America, and different high-latitude locations with sturdy winters. Nevertheless, this technique can battle within the tropics and in arid areas. Right here, satellite-based estimates of plant progress can fluctuate subtly all year long, with out clear-cut rising seasons.
Stunning Patterns
By making use of a brand new evaluation to twenty years of satellite tv for pc imagery, we made a greater map of the timing of plant progress cycles across the globe. Alongside anticipated patterns, corresponding to delayed spring at larger latitudes and altitudes, we noticed extra stunning ones too.
One stunning sample occurs throughout Earth’s 5 Mediterranean local weather areas, the place winters are delicate and moist and summers are scorching and dry. These embody California, Chile, South Africa, southern Australia, and the Mediterranean itself.
These areas all share a “double peak” seasonal sample, beforehand documented in California, as a result of forest progress cycles are likely to peak roughly two months later than different ecosystems. Additionally they present stark variations within the timing of plant progress from their neighboring drylands, the place summer time precipitation is extra widespread.
Recognizing Hotspots
This advanced mixture of seasonal exercise patterns explains one main discovering of our work: The Mediterranean climates and their neighboring drylands are hotspots of out-of-sync seasonal exercise. In different phrases, they’re areas the place the seasonal cycles of close by locations can have dramatically completely different timing.
Contemplate, for instance, the marked distinction between Phoenix, Arizona (which has comparable quantities of winter and summer time rainfall) and Tucson solely 160 kilometers away (the place most rainfall comes from the summer time monsoon).
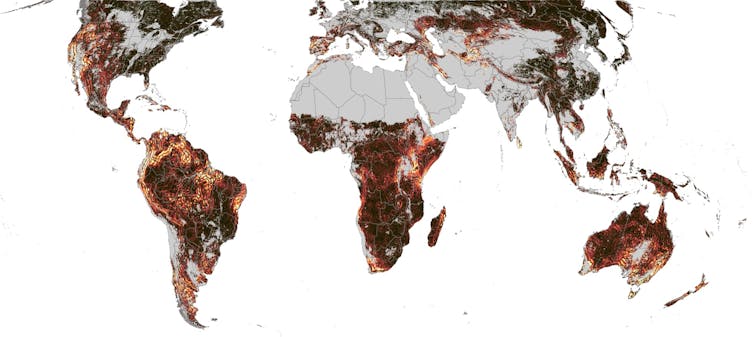
Hotspots of seasonal asynchrony: brighter colours present areas the place the timing of seasonal exercise varies quite a bit over brief distances. Picture Credit score: Terasaki Hart et al. / Nature
Different world hotspots happen largely in tropical mountains. The intricate patterns of out-of-sync seasons we observe there could relate to the advanced methods during which mountains can affect airflow, dictating native patterns of seasonal rainfall and cloud. These phenomena are nonetheless poorly understood, however could also be basic to the distribution of species in these areas of outstanding biodiversity.
Seasonality and Biodiversity
Figuring out world areas the place seasonal patterns are out of sync was the unique motivation for our work. And our discovering that they overlap with lots of Earth’s biodiversity hotspots—locations with giant numbers of plant and animal species—might not be a coincidence.
In these areas, as a result of seasonal cycles of plant progress will be out of sync between close by locations, the seasonal availability of sources could also be out of sync, too. This is able to have an effect on the seasonal reproductive cycles of many species, and the ecological and evolutionary penalties could possibly be profound.
One such consequence is that populations with out-of-sync reproductive cycles could be much less prone to interbreed. In consequence, these populations could be anticipated to diverge genetically and, maybe, ultimately even break up into completely different species.
If this occurred to even a small proportion of species at any given time, then over the lengthy haul these areas would produce giant quantities of biodiversity.
Again Right down to Earth
We don’t but know whether or not this has actually been taking place. However our work takes the primary steps in direction of discovering out.
We present that, for a variety of plant and animal species, our satellite-based map predicts stark on-ground variations within the timing of plant flowering and in genetic relatedness between close by populations.
Our map even predicts the advanced geography of espresso harvests in Colombia. Right here, espresso farms separated by a day’s drive over the mountains can have reproductive cycles as out of sync as in the event that they have been a hemisphere aside.
Understanding seasonal patterns in area and time isn’t simply necessary for evolutionary biology. Additionally it is basic to understanding the ecology of animal motion, the results of local weather change for species and ecosystems, and even the geography of agriculture and different types of human exercise.
Need to know extra? You possibly can discover our leads to extra element with this interactive on-line map.
This text is republished from The Dialog underneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the authentic article.

