ESET researchers have found a beforehand unknown vulnerability in WinRAR, being exploited within the wild by Russia-aligned group RomCom. That is at the least the third time that RomCom has been caught exploiting a major zero-day vulnerability within the wild. Earlier examples embody the abuse of CVE-2023-36884 through Microsoft Phrase in June 2023, and the mixed vulnerabilities assigned CVE‑2024‑9680 chained with one other beforehand unknown vulnerability in Home windows, CVE‑2024‑49039, focusing on weak variations of Firefox, Thunderbird, and the Tor Browser, resulting in arbitrary code execution within the context of the logged-in consumer in October 2024.
Key factors of this blogpost:
- In case you use WinRAR or different affected elements such because the Home windows variations of its command line utilities, UnRAR.dll, or the transportable UnRAR supply code, improve instantly to the most recent model.
- On July 18th, 2025, ESET researchers found a beforehand unknown zero-day vulnerability in WinRAR being exploited within the wild.
- Evaluation of the exploit led to the invention of the vulnerability, now assigned CVE-2025-8088: a path traversal vulnerability, made doable with the usage of alternate knowledge streams. After fast notification, WinRAR launched a patched model on July 30th, 2025.
- The vulnerability permits hiding malicious recordsdata in an archive, that are silently deployed when extracting.
- Profitable exploitation makes an attempt delivered varied backdoors utilized by the RomCom group, particularly a SnipBot variant, RustyClaw, and Mythic agent.
- This marketing campaign focused monetary, manufacturing, protection, and logistics corporations in Europe and Canada.
RomCom profile
RomCom (also referred to as Storm-0978, Tropical Scorpius, or UNC2596) is a Russia-aligned group that conducts each opportunistic campaigns towards chosen enterprise verticals and focused espionage operations. The group’s focus has shifted to incorporate espionage operations gathering intelligence, in parallel with its extra typical cybercrime operations. The backdoor generally utilized by the group is able to executing instructions and downloading further modules to the sufferer’s machine.
The invention of CVE-2025-8088
On July 18th, 2025, we noticed a malicious DLL named msedge.dll in a RAR archive containing uncommon paths that caught our consideration. Upon additional evaluation, we discovered that the attackers have been exploiting a beforehand unknown vulnerability affecting WinRAR, together with the then-current model, 7.12. On July 24th, 2025, we contacted the developer of WinRAR, and on the identical day, the vulnerability was mounted and WinRAR 7.13 beta 1 printed. WinRAR 7.13 was printed on July 30th, 2025. Customers of WinRAR are suggested to put in the most recent model as quickly as doable to mitigate the chance. Notice that software program options counting on publicly obtainable Home windows variations of UnRAR.dll or its corresponding supply code are affected as properly, particularly those who haven’t up to date their dependencies.
The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2025-8088, makes use of alternate knowledge streams (ADSes) for path traversal. Notice {that a} related path traversal vulnerability (CVE‑2025‑6218) affecting WinRAR was disclosed on June 19th, 2025, roughly a month earlier.
The attackers specifically crafted the archive to apparently comprise just one benign file (see Determine 1), whereas it comprises many malicious ADSes (there’s no indication of them from the consumer’s standpoint).
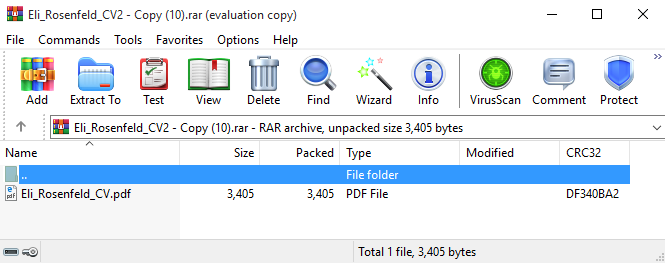
As soon as a sufferer opens this seemingly benign file, WinRAR unpacks it together with all its ADSes. For instance, for Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – Copy (10).rar, a malicious DLL is deployed into %TEMP%. Likewise, a malicious LNK file is deployed into the Home windows startup listing, thereby attaining persistence through execution on consumer login.
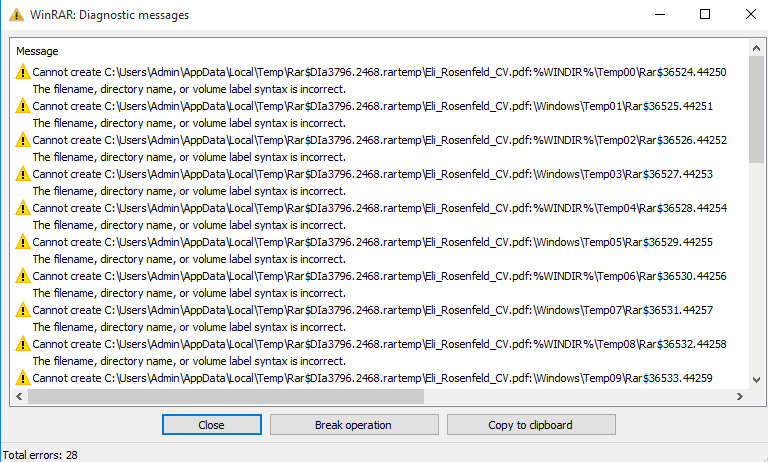
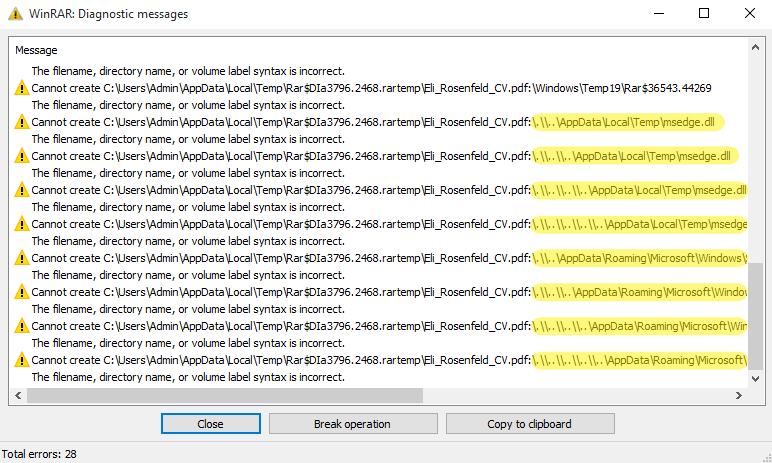
To make sure increased success, the attackers offered a number of ADSes with rising depths of mother or father listing relative path parts (..). Nonetheless, this introduces nonexistent paths that WinRAR visibly warns about. Curiously, the attackers added ADSes that comprise dummy knowledge and are anticipated to have invalid paths. We suspect that the attackers launched them in order that the sufferer doesn’t discover the suspicious DLL and LNK paths (see Determine 2). Solely when scrolling down within the WinRAR consumer interface are the suspicious paths revealed, as seen in Determine 3.
Compromise chain
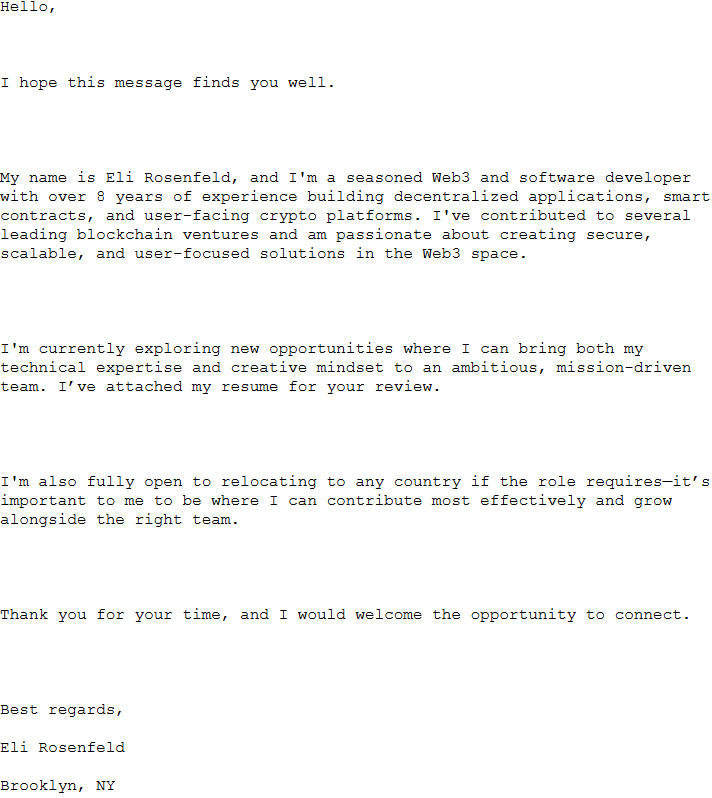
Based on ESET telemetry, such archives have been utilized in spearphishing campaigns from the 18th to 21st July, 2025, focusing on monetary, manufacturing, protection, and logistics corporations in Europe and Canada. Desk 1 comprises the spearphishing emails – sender, topic, and filename of the attachment – used within the campaigns, and Determine 4 exhibits the message we noticed in an e-mail. In all circumstances, the attackers despatched a CV hoping {that a} curious goal would open it. Based on ESET telemetry, not one of the targets have been compromised.
Desk 1. Spearphishing emails noticed in ESET telemetry
| Sender | Topic | Attachment |
| Simona | Skilled Web3 Developer – CV Connected for Consideration | Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – Copy (100) – Copy – Copy – Copy – Copy – Copy – Copy.rar |
| Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – Copy (100) – Copy – Copy – Copy – Copy – Copy.rar | ||
| Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – Copy (100) – Copy – Copy – Copy – Copy.rar | ||
| Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – Copy (10).rar | ||
| Marshall Rico | Motivated Applicant – Resume Enclosed | cv_submission.rar |
| Simona | ||
| Simona | ||
| Simona | ||
| Simona | ||
| Russell Martin | Job Software | Datos adjuntos sin título 00170.dat |
| Pepita Cordero | Software for Job Openings – Pepita Cordero | JobDocs_July2025.rar |
| Sacchetti Jami | Software for Job Openings – Sacchetti Jami | Recruitment_Dossier_July_2025.rar |
| Jennifer Hunt | Making use of for the Position | cv_submission.rar |
These RAR recordsdata all the time comprise two malicious recordsdata: a LNK file, unpacked to the Home windows startup listing, and a DLL or EXE, unpacked to both %TEMP% or %LOCALAPPDATA%. A number of the archives share the identical malware. We have now recognized three execution chains.
Mythic agent execution chain
Within the first execution chain, depicted in Determine 5, the malicious LNK file Updater.lnk provides the registry worth HKCUSOFTWAREClassesCLSID{1299CF18-C4F5-4B6A-BB0F-2299F0398E27}InprocServer32 and units it to %TEMPpercentmsedge.dll. That is used to set off execution of that DLL through COM hijacking. Particularly, the CLSID corresponds to the PSFactoryBuffer object current in npmproxy.dll. In consequence, any executable making an attempt to load it (e.g., Microsoft Edge) will set off code execution of the malicious DLL. This DLL is accountable for decrypting embedded shellcode through AES and subsequently executing it. Curiously, it retrieves the area identify for the present machine, which generally comprises the corporate identify, and compares it with a hardcoded worth, exiting if the 2 values don’t match. Because of this the attackers had performed reconnaissance beforehand, confirming that this e-mail was extremely focused.
The loaded shellcode seems to be a dynamichttp C2 profile for the Mythic agent having the next C&C server: https://srlaptop[.]com/s/0.7.8/readability.js.
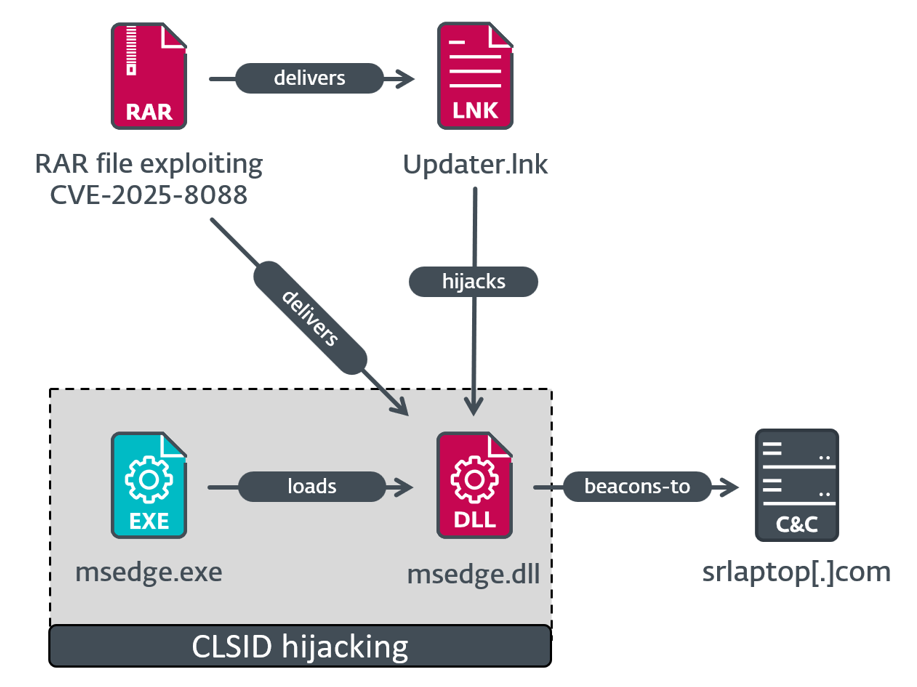
It comes with an ordinary configuration for the dynamichttp C2 profile and a customized one, which is displayed in Determine 6. Identical to within the earlier stage, this configuration comprises a hardcoded area identify of the goal.
{'disable_etw': '2', 'block_non_ms_dlls': '3', 'child_process': 'wmic.exe', 'use_winhttp': 1, 'inject_method': '1', 'dll_side': ['MsEdge', 'OneDrive'], 'area': '[REDACTED]'}Determine 6. Customized configuration within the Mythic execution chain
SnipBot variant execution chain
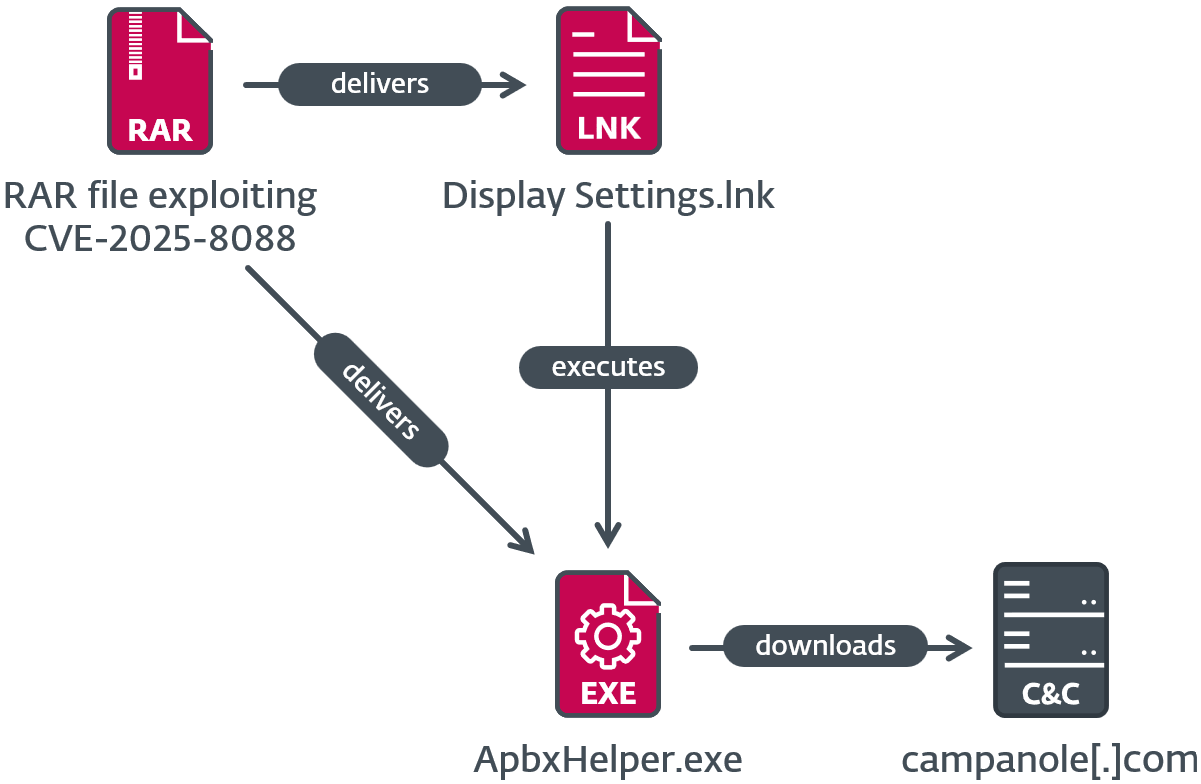
Within the second execution chain, which is depicted in Determine 7, the malicious LNK file Show Settings.lnk runs %LOCALAPPDATApercentApbxHelper.exe. It’s a modified model of PuTTY CAC, which is a fork of PuTTY, and is signed with an invalid code-signing certificates. The additional code makes use of the filename as a key for decrypting strings and the following stage, which is shellcode. The shellcode seems to be a variant of SnipBot, malware attributed to RomCom by UNIT 42. Execution of the shellcode solely proceeds if a selected registry worth (68 for this pattern) is current within the HKCUSOFTWAREMicrosoftWindowsCurrentVersionExplorerRecentDocs registry key (in different phrases, if at the least 69 paperwork have been just lately opened); that is an anti-analysis approach to stop execution in an empty digital machine or sandbox. If at the least 69 paperwork have been just lately opened, next-stage shellcode is decrypted utilizing the registry key identify (e.g., 68, however transformed from string to integer), and executed, downloading yet one more stage from https://campanole[.]com/TOfrPOseJKZ.
We additionally discovered an equivalent ApbxHelper.exe inside Adverse_Effect_Medical_Records_2025.rar, uploaded to VirusTotal from Germany. This archive additionally exploits the CVE-2025-8088 vulnerability.
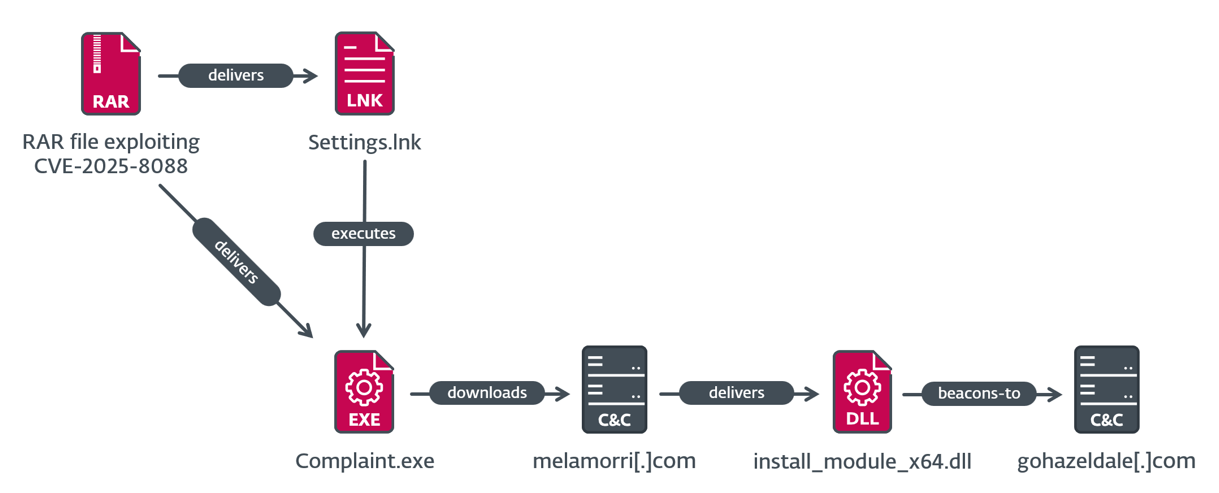
MeltingClaw execution chain
Within the third execution case, which is depicted in Determine 8, the malicious LNK file Settings.lnk runs %LOCALAPPDATApercentComplaint.exe, which is RustyClaw – a downloader written in Rust beforehand analyzed by Talos. This pattern is signed with an invalid code-signing certificates, which is totally different from the code-signing certificates used within the SnipBot variant. RustyClaw downloads and executes one other payload, from https://melamorri[.]com/iEZGPctehTZ. This payload (SHA-1: 01D32FE88ECDEA2B934A00805E138034BF85BF83), with inner identify install_module_x64.dll, partially matches the evaluation of MeltingClaw by Proofpoint, a special downloader attributed to RomCom. The C&C server of the MeltingClaw pattern that we noticed is https://gohazeldale[.]com.
Attribution
We attribute the noticed actions to RomCom with excessive confidence primarily based on the focused area, TTPs, and malware used.
This isn’t the primary time that RomCom has used exploits to compromise its victims. In June 2023, the group carried out a spearphishing marketing campaign focusing on protection and governmental entities in Europe, with lures associated to the Ukrainian World Congress. The Microsoft Phrase doc connected to the e-mail tried to use the CVE‑2023‑36884 vulnerability, as documented by the BlackBerry Menace Analysis and Intelligence group.
On October 8th, 2024, the group exploited a then-unknown vulnerability within the Firefox browser. The exploit focused a use-after-free vulnerability in Firefox Animation timelines, permitting an attacker to realize code execution in a content material course of, with the target of delivering the RomCom backdoor. The vulnerability identifier CVE‑2024‑9680 was assigned, as documented in our WeLiveSecurity blogpost.
Different actions
We’re conscious that this vulnerability has additionally been exploited by one other menace actor, and was independently found by the Russian cybersecurity firm BI.ZONE. Notably, this second menace actor started exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088 a couple of days after RomCom began doing so.
Conclusion
By exploiting a beforehand unknown zero-day vulnerability in WinRAR, the RomCom group has proven that it’s keen to speculate severe effort and sources into its cyberoperations. That is at the least the third time RomCom has used a zero-day vulnerability within the wild, highlighting its ongoing deal with buying and utilizing exploits for focused assaults. The found marketing campaign focused sectors that align with the everyday pursuits of Russian-aligned APT teams, suggesting a geopolitical motivation behind the operation.
We want to thank the WinRAR group for its cooperation and fast response, and acknowledge its effort in releasing a patch inside simply sooner or later.
Due to Peter Košinár for his help within the evaluation.
For any inquiries about our analysis printed on WeLiveSecurity, please contact us at threatintel@eset.com.ESET Analysis provides non-public APT intelligence studies and knowledge feeds. For any inquiries about this service, go to the ESET Menace Intelligence web page.
IoCs
A complete record of indicators of compromise (IoCs) and samples will be present in our GitHub repository.
Recordsdata
| SHA-1 | Filename | Detection | Description |
| 371A5B8BA86FBCAB80D4 | Adverse_Effect_Medi | LNK/Agent.AJN Win64/Agent.GPM | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088; discovered on VirusTotal. |
| D43F49E6A586658B5422 | cv_submission.rar | LNK/Agent.AJN July Win64/Agent.GPM | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088. |
| F77DBA76010A9988C9CE | Eli_Rosenfeld_CV2 – | Win64/Agent.GMQ | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088. |
| 676086860055F6591FED | Datos adjuntos sin | LNK/Agent.AJN Win64/Agent.GPM | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088. |
| 1F25E062E8E9A4F1792C | JobDocs_July2025.rar | LNK/Agent.AJN Win64/TrojanDownlo | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088. |
| C340625C779911165E39 | cv_submission.rar | LNK/Agent.AJN Win64/Agent.GPM | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088. |
| C94A6BD6EC88385E4E83 | Recruitment_Dossier | LNK/Agent.AJN Win64/TrojanDownlo | Archive exploiting CVE‑2025‑8088. |
| 01D32FE88ECDEA2B934A | install_module_x64 | Win64/Agent.GNV | MeltingClaw |
| AE687BEF963CB30A3788 | msedge.dll | Win64/Agent.GMQ | Mythic agent utilized by RomCom |
| AB79081D0E26EA278D3D | Grievance.exe | Win64/TrojanDownlo | RustyClaw |
| 1AEA26A2E2A7711F89D0 | ApbxHelper.exe | Win64/Agent.GPM | SnipBot variant |
Community
| IP | Area | Internet hosting supplier | First seen | Particulars |
| 162.19.175[.]44 | gohazeldale | OVH SAS | 2025‑06‑05 | MeltingClaw C&C server. |
| 194.36.209[.]127 | srlaptop[.]com | CGI GLOBAL LIMITED | 2025‑07‑09 | C&C server of the Mythic agent utilized by RomCom. |
| 85.158.108[.]62 | melamorri[.]com | HZ‑HOSTING‑LTD | 2025‑07‑07 | RustyClaw C&C server. |
| 185.173.235[.]134 | campanole[.]com | FiberXpress BV | 2025‑07‑18 | C&C server of the SnipBot variant. |
MITRE ATT&CK strategies
This desk was constructed utilizing model 17 of the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
| Tactic | ID | Identify | Description |
| Useful resource Improvement | T1583 | Purchase Infrastructure | RomCom units up VPSes and buys domains. |
| T1587.001 | Develop Capabilities: Malware | RomCom develops malware in a number of programming languages. | |
| T1587.004 | Develop Capabilities: Exploits | RomCom could develop exploits used for preliminary compromise. | |
| T1588.005 | Acquire Capabilities: Exploits | RomCom could purchase exploits used for preliminary compromise. | |
| T1588.006 | Acquire Capabilities: Vulnerabilities | RomCom could acquire details about vulnerabilities that it makes use of for focusing on victims. | |
| T1608 | Stage Capabilities | RomCom phases malware on a number of supply servers. | |
| Preliminary Entry | T1566.001 | Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment | RomCom compromises victims with a malicious RAR attachment despatched through spearphishing. |
| Execution | T1204.002 | Consumer Execution: Malicious File | RomCom lures victims into opening a weaponized RAR archive containing an exploit. |
| Persistence | T1547.001 | Boot or Logon Autostart Execution: Registry Run Keys / Startup Folder | For persistence, RomCom shops a LNK file within the Startup folder. |
| T1546.015 | Occasion Triggered Execution: Part Object Mannequin Hijacking | RomCom hijacks CLSIDs for persistence. | |
| Protection Evasion | T1497 | Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion | RomCom detects digital environments by checking for sufficient RecentDocs. |
| T1480 | Execution Guardrails | RomCom stops execution if operating in a digital atmosphere. It additionally checks for a hardcoded area identify earlier than executing. | |
| T1036.001 | Masquerading: Invalid Code Signature | RomCom tries to seem extra respectable to customers and safety instruments that improperly deal with digital signatures. | |
| T1027.007 | Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info: Dynamic API Decision | RomCom decrypts and resolves API dynamically. | |
| T1027.013 | Obfuscated Recordsdata or Info: Encrypted/Encoded File | RomCom decrypts shellcode primarily based on filename and machine artifacts. | |
| Credential Entry | T1555.003 | Credentials from Password Shops: Credentials from Internet Browsers | The RomCom backdoor collects passwords, cookies, and periods utilizing a browser stealer module. |
| T1552.001 | Unsecured Credentials: Credentials In Recordsdata | The RomCom backdoor collects passwords utilizing a file reconnaissance module. | |
| Discovery | T1087 | Account Discovery | The RomCom backdoor collects username, pc, and area knowledge. |
| T1518 | Software program Discovery | The RomCom backdoor collects details about put in software program and variations. | |
| Lateral Motion | T1021 | Distant Providers | The RomCom backdoor creates SSH tunnels to maneuver laterally inside compromised networks. |
| Assortment | T1560 | Archive Collected Information | The RomCom backdoor shops knowledge in a ZIP archive for exfiltration. |
| T1185 | Man within the Browser | The RomCom backdoor steals browser cookies, historical past, and saved passwords. | |
| T1005 | Information from Native System | The RomCom backdoor collects particular file varieties primarily based on file extensions. | |
| T1114.001 | E mail Assortment: Native E mail Assortment | The RomCom backdoor collects recordsdata with .msg, .eml, and .e-mail extensions. | |
| T1113 | Display Seize | The RomCom backdoor takes screenshots of the sufferer’s pc. | |
| Command and Management | T1071.001 | Software Layer Protocol: Internet Protocols | The RomCom backdoor makes use of HTTP or HTTPS as a C&C protocol. |
| T1573.002 | Encrypted Channel: Uneven Cryptography | The RomCom backdoor encrypts communication utilizing SSL certificates. | |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel | The RomCom backdoor exfiltrates knowledge utilizing the HTTPS C&C channel. |
| Affect | T1657 | Monetary Theft | RomCom compromises corporations for monetary curiosity. |


