Introduction
Have you ever found yourself staring at a desk cluttered with numbers – perhaps sales figures, customer demographics, or financial data – only to feel utterly overwhelmed by the sheer amount of information before you? You’re not alone! Deciphering unprocessed information can be a complex task, yet learning to identify crucial patterns can be a valuable skill, indeed. Despite this, with advanced knowledge visualization, all this unorganized information could potentially yield clear and actionable insights. Visualization techniques, such as heatmaps, play a crucial role in this process.
Heatmaps provide a valuable means of visualizing data density and highlighting patterns that may take significant time to emerge when relying solely on conventional statistical charts. Here’s the improved text:
Get clarity on creating custom heatmaps in Energy BI to enhance your data visualizations and gain insights. From leveraging built-in capabilities to tailored visualizations, this topic covers a wealth of information.

Overview
- Heatmaps effectively visualize knowledge density, uncover underlying trends, and transform raw data into meaningful takeaways, empowering informed decision-making.
- Explore the creation of heatmaps in Energy BI by leveraging built-in features such as conditional formatting and tailored visualizations.
- Heatmaps employ colour gradations to convey knowledge values, facilitating swift discovery of patterns and samples.
- Energy BI’s conditional formatting enables effortless heatmap generation through the modification of cell colors based on value ranges.
- Microsoft AppSource offers tailored visuals that enable precise geographical heatmaps within Energy Business Intelligence.
- Effective heatmaps necessitate deliberate design choices such as strategic color selection and informed data binning.
What are Heatmaps?
Heatmaps are visual depictions of data where values are represented using colors. Heatmaps are invaluable for illustrating the dispersion and profundity of data across a spatial domain or grid, providing a comprehensive overview of the patterns and trends present in the data. In PC-based imaginative and visual knowledge assessment, heatmaps employing color gradients effectively convey the emphasis or magnitude of specific values, such as pixel intensities, frequencies, or statistical metrics. Analysts and researchers are adept at quickly identifying patterns, characteristics, and anomalies in data. Heatmaps are versatile tools used across various disciplines, including biology, finance, and geology, with specific applications in image processing to visualize complexities such as activation regions in neural networks or statistical patterns throughout photographs.
To revitalize your learning curve in Energy BI, revisit and review this material.
Two methods to create a heatmap in Power BI?
Energy BI offers multiple approaches for crafting heatmaps, effectively addressing diverse knowledge visualization requirements:
- You’ll be able to apply conditional formatting to tables or matrices, allowing you to dynamically change cell colours based on their values and create a visually striking heatmap that highlights patterns and trends. This simple technique allows for rapid heatmap generation within a desk or matrix view.
- Customize map visuals from Microsoft AppSource marketplace to generate geospatial heatmaps. This technique proves particularly useful in mapping the dispersion of knowledge across disparate geographic regions.
Suggestions for Efficient Heatmaps
- Identify colours that exhibit distinctive contrasts and nuanced differences to effectively distinguish between diverse knowledge domains.
- In cases where measure values exhibit significant discrepancies, consider aggregating the data into distinct ranges to improve visual clarity and facilitate easier comprehension.
- Permit customers to explore specific knowledge factors through interactive tooltips, enabling them to delve deeper into the information for a more comprehensive understanding.
Creating a heatmap in Power BI provides a powerful way to visualize complex data and facilitate the interpretation of advanced knowledge units. By leveraging conditional formatting or bespoke visualizations, you can craft a heatmap that perfectly aligns with your specific needs and delivers valuable findings to your audience.
Let’s Create the Heatmap
Initially, we will craft it by leveraging Conditional Formatting.
Conditional Formatting
To create a heatmap in Power BI using conditional formatting, follow these steps.
1\. Open your Power BI report and navigate to the visualization you want to format as a heatmap.
2\. Click on the “Conditional Formatting” button located at the top of the visualization pane.
3\. Select “Heatmap” from the list of available formats.
4\. In the “Format Pane,” adjust the color palette, gradient direction, and other settings according to your preferences.
5\. You can also use the “Color Scale” dropdown menu to select different color options for your heatmap.
6\. To apply the formatting to a specific field or measure in your data model, click on the “Data Range” button and choose the desired field from the list.
7\. Adjust the aggregation type as needed (e.g., sum, average, count).
8\. Click “OK” to apply the heatmap format to your visualization.
Open Microsoft Power BI Desktop.
- Launch Energy BI Desktop and load your dataset by selecting “Get Data” and choosing a relevant data source.
- When using Python’s IDE, you can easily import modules by selecting the “Import knowledge” option from the top-level menu.
Import and Consolidate Your Data?
- Guarantee your knowledge is well-organized. We now possess detailed product revenue data.
- Click “Load” to load the information instantly, or click “Remodel” to organize the data before loading it.
What’s on your desktop?
What is your desired outcome? Are you looking to insert a matrix visualization within your data analysis process? If so, please clarify the type of matrix you wish to visualize (e.g., scatter plot, heatmap, etc.) and provide more context about your specific use case. This will enable me to better understand your requirements and assist you with inserting a suitable matrix visible.
Go to the Visualizations pane and select the Matrix visualization that is displayed beneath the Construct visualizer. Drag your data into the Rows and Columns sections, then position the Values part accordingly, following the demonstrated example structure.
Customise the Information
- We analyzed sales data across various columns within our dataset. Since Energy BI regularly supplies a date hierarchy, we ought to remove the predefined levels of Year, Semi-annual, Month, Quarter, and Date to customize our analysis.
- To aggregate values within the ‘Values’ discipline, select a suitable method such as “Sum” or modify it to suit your requirements by choosing options like “Average”, “Count”, or “Common”.
You are capable of performing all formatting tasks on this pane, encompassing filtering options, personalising your knowledge base, and various formatting features, as needed.
The view formats are set so that the formatting of a document is visible.
What cell parts would you like to add? Permit the “Background color” option and click the “” icon to personalize it.
With 95% complete, you’re almost there! The final 5% includes subtle tweaks to enhance visual appeal: background and font colours take centre stage, adding a professional touch to your near-finished project?
Background Coloration
We will formulate a background colour choice, grounded in a specific discipline, summarizing key findings and addressing diverse issues within it.
Font Coloration
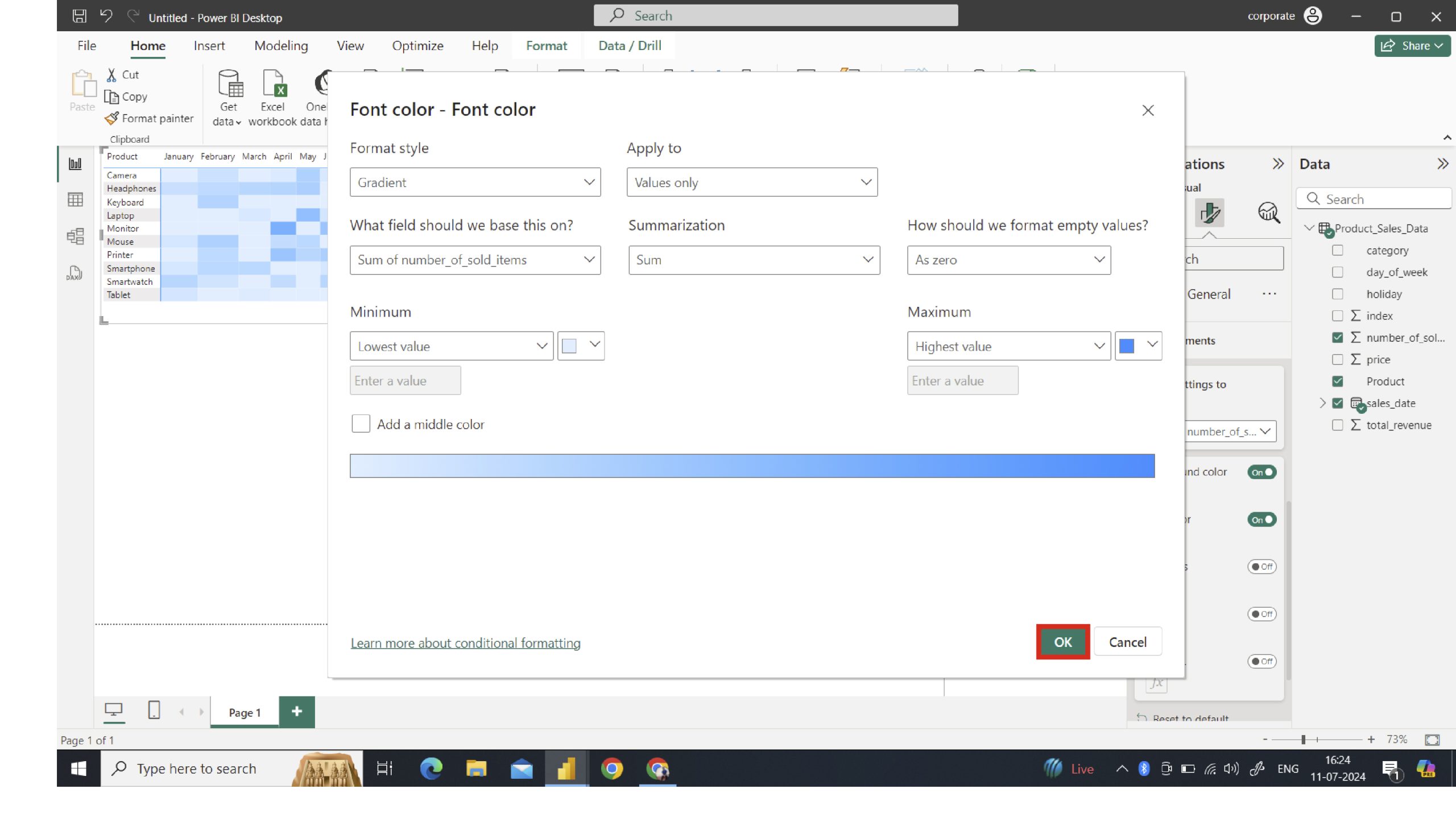
Select the desired font color by choosing from a range of options and clicking the “” button to customize it further. We will perform the identical process using font colours, format styling, summarisation, and various selections.
While this approach can transform text content and background color into identical copies, preserving the value remains unaffected, yielding a heatmap-like appearance.
Enhanced Visibility for Premium Power BI Subscribers
In the event that you possess a paid version of Energy BI, it is advisable to leverage this capability.
Customized visuals in Energy BI unlock numerous benefits, enhancing knowledge visualization through greater flexibility and performance beyond standard offerings.
The streamlined settings for a tailored visualization await – let us begin.
To set up a customizable heatmap in Energy BI, start by creating a new visualisation and selecting the ‘Heatmap’ option from the list of available visuals. Next, connect your data source and drag the relevant fields into the fields well.
You can adjust the colour palette to suit your needs, and add additional measures or dimensions as required. You can also use the ‘Customise Visuals’ button to further tailor the appearance of your heatmap. To access additional visualizations, navigate to the Visualizations pane and select the three-dot icon at the end of the list, then choose “Get more visuals” from the dropdown menu.
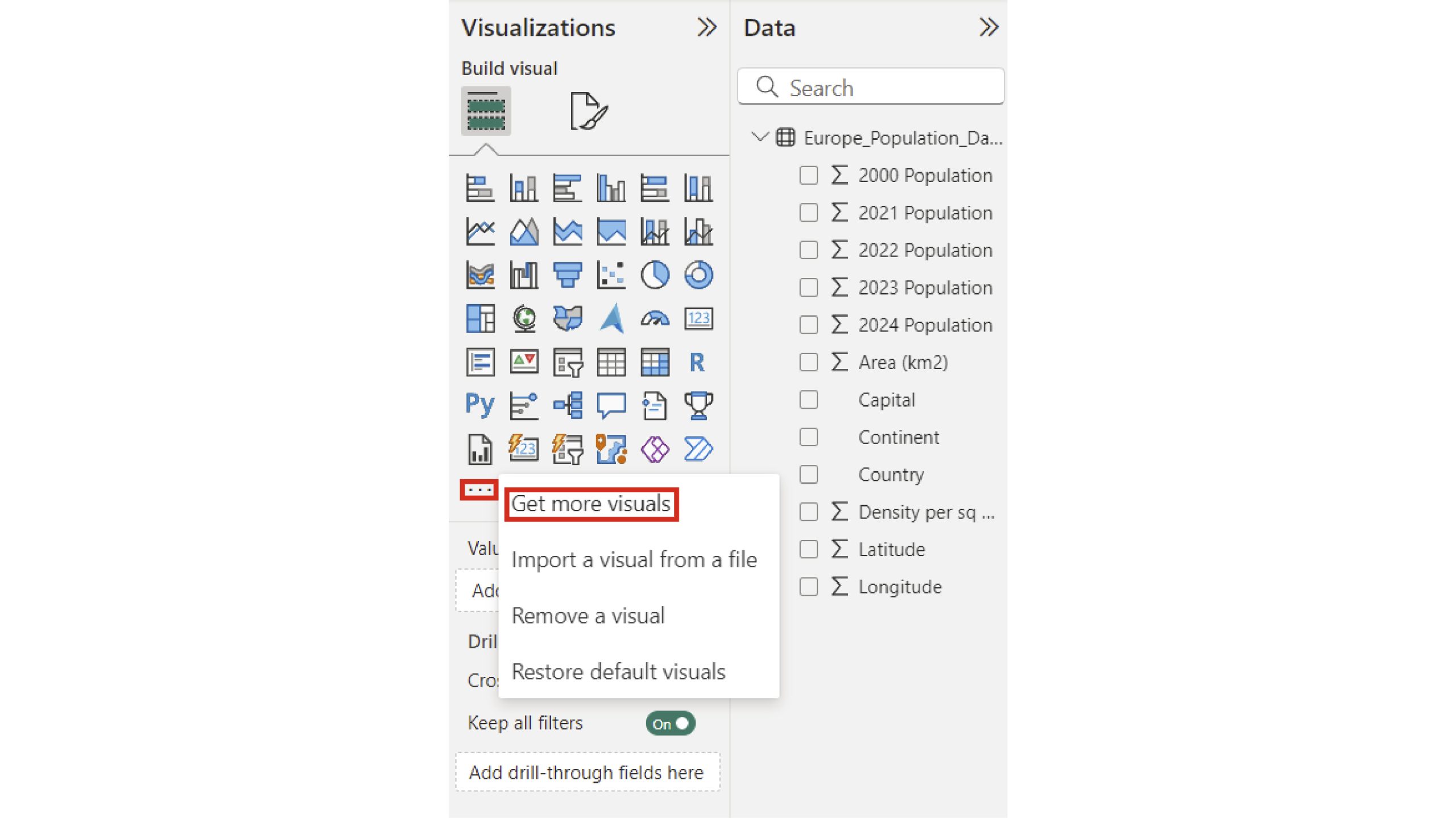
As you navigate through the data, identify areas that require attention by creating a heatmap. This visual representation will highlight trends and patterns, giving you a deeper understanding of your customers’ needs. The heatmap will showcase the correlation between different variables, helping you pinpoint the most effective strategies to engage your audience. By analyzing the heatmap, you’ll be able to optimize your content and target specific segments of your customer base.
After clicking, you are redirected to the Energy BI visuals dashboard where you can readily locate and explore the Heatmap visual. Please click on ‘Add’ to acquire the necessary visibility.
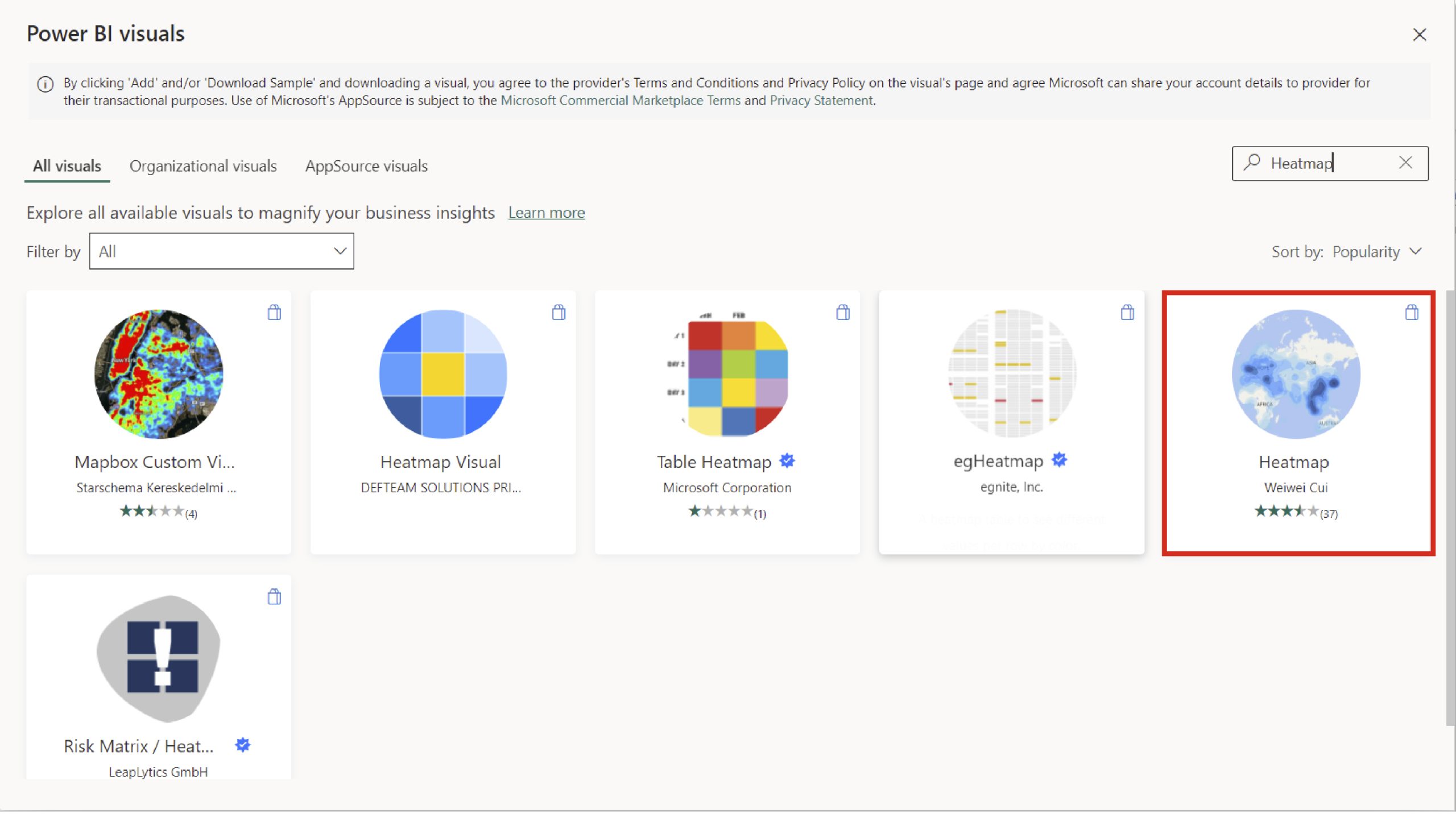
Here’s a revised version of the text in a different style:
Heatmap Visualizer: This comprehensive overview provides an insight into the intricacies of heatmap visualization.
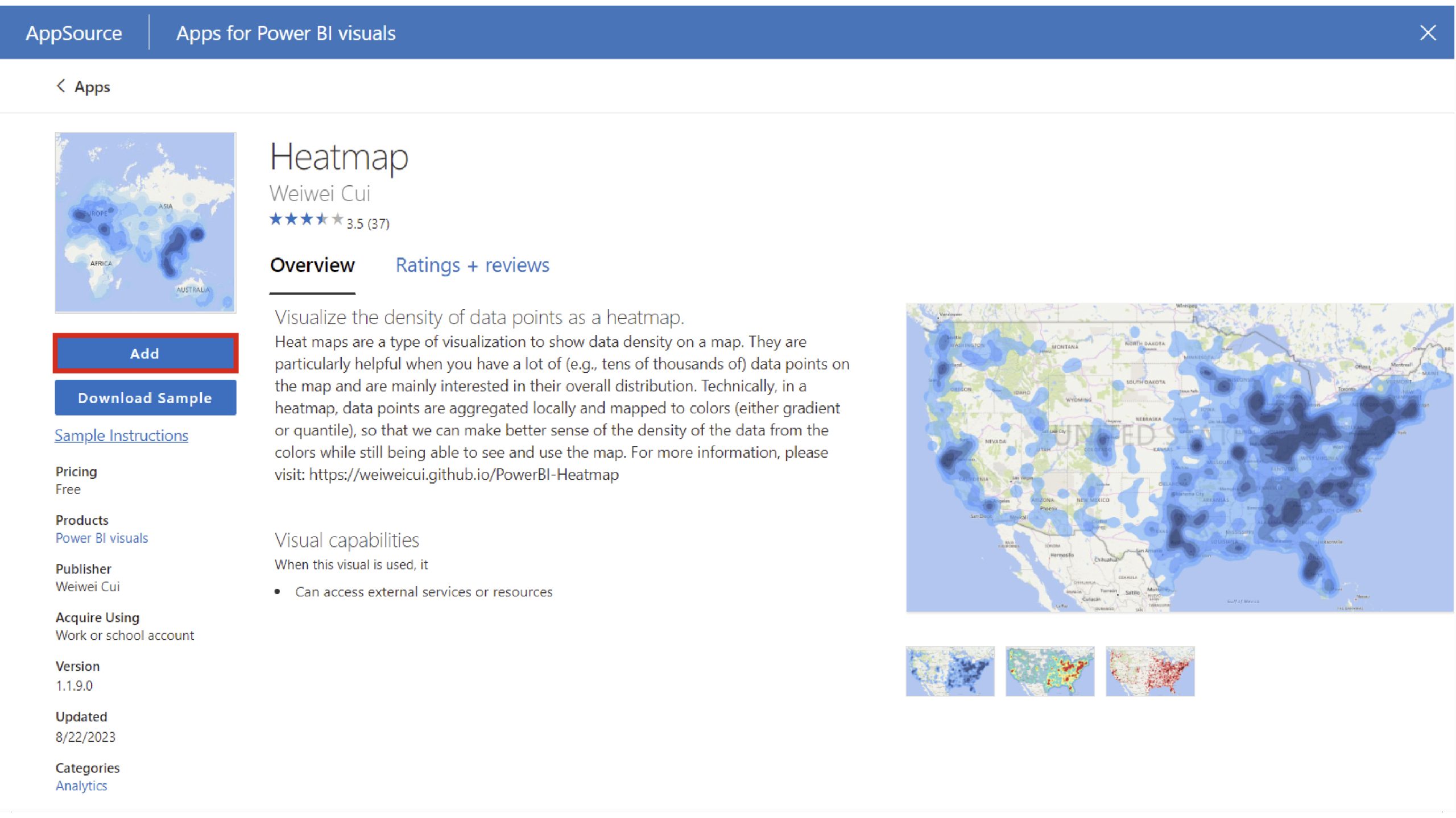
Regardless of the circumstances, we reiterate the process from acquiring knowledge to loading it, followed by identifying the distinct characteristics of the heatmap.
- :
- Find the report and navigate to its pane.
- :
- Click on the heatmap icon to easily add a professional-looking heatmap to your report.
- :
- Visualize the scenario by dragging and dropping columns denoting circumstances, geographic coordinates (latitude and longitude), and valuation metrics onto a heat map.
- Drag and drop the column representing the value or metric you wish to display (e.g. international population).
When working with datasets that include separate columns for longitude and latitude, it is advisable to utilize this information to define the location context instead of relying on a single “Location” column.
- :
- As the situation and worth fields are established, the heatmap is populated and becomes viewable within the report.
Conclusion
Creating heatmaps in Power BI is a powerful technique for transforming raw data into visually compelling insights. Rapidly identify patterns, trends, and anomalies with heatmaps, which can be further enhanced by incorporating conditional formatting or tailored visualizations. By following a structured approach, you can harness the power of Energy BI’s native capabilities or integrate custom-designed visualizations to craft dynamic and engaging heatmaps that effectively communicate complex data insights. By facilitating straightforward insights, this approach enables more informed and data-backed decision-making processes. By thoughtfully selecting design elements, harmonizing with suitable color palettes, and strategically organizing data bins, you can significantly enhance the legibility and visual impact of your heatmaps.
Regularly Requested Questions
Ans. A heatmap in Microsoft Power BI is a data visualization technique that utilizes color-coding to represent distinct values of various metrics, enabling users to quickly identify patterns and trends within their datasets. By visualizing data in a matrix structure, it enables identification of patterns, correlations, and anomalies within a dataset, utilizing distinct colors to represent individual data points.
Ans. To boost the legibility of your Power BI heatmap:
A. Utilize a straightforward and user-friendly color palette that minimizes visual overload, fostering effortless comprehension of the data visualization.
B. Knowledge levels are defined as Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced, and Expert.
Beginner: **What is a knowledge label?** A knowledge label is a tool used to provide extra context to users by offering definitions of key terms and phrases.
Intermediate: **Why use tooltips?** Tooltips are a form of interactive help that appears when a user hovers their cursor over a specific element, providing additional information or clarification on the topic at hand.
Advanced: **How do knowledge labels work?** Knowledge labels can be integrated into various formats such as text, images, and videos to offer users supplementary information without disrupting the main content flow. This approach helps users develop a deeper understanding of complex topics.
Expert: **What are the benefits of using knowledge labels?** By providing additional context through knowledge labels or tooltips, users can quickly grasp unfamiliar terms, reducing cognitive load and improving comprehension.
C. To prevent visual overload, utilize aggregated data ranges that group elements in a meaningful way, thereby maintaining a clean and readable heatmap.
D. By leveraging advanced filtering capabilities, customers can effortlessly zero in on specific segments of data that cater to their unique needs and preferences.
E. Ensure that your heatmap features a transparent title and axis labels to facilitate customer understanding of the data being presented.
Ans. The frequent use instances for heatmaps in Power BI encompass:
Temperature anomalies across various regions or facilities
Identifying trends and patterns within large datasets
Visualizing customer engagement metrics to inform marketing strategies
Analyzing product adoption rates and user behavior
Highlighting key performance indicators (KPIs) and areas of improvement
A. Examining cross-functional insights on gross sales trends across various domains and timeframes.
B. Analyzing underlying behavioral trends to better understand customer inclinations.
C. Tracking key performance indicators across diverse organizational entities?
D. Unraveling the intricacies of website visitor behavior and person-to-person interactions requires meticulous attention to detail.
E. Tracking patterns in financial literacy, correlated with income and expenses across varying periods of time.

