Snowflake’s knowledge cloud allows corporations to retailer and share knowledge, then analyze this knowledge for enterprise intelligence. Though Snowflake is a superb software, generally querying huge quantities of information runs slower than your functions — and customers — require.
In our first article, What Do I Do When My Snowflake Question Is Gradual? Half 1: Analysis, we mentioned methods to diagnose sluggish Snowflake question efficiency. Now it’s time to deal with these points.
We’ll cowl Snowflake efficiency tuning, together with lowering queuing, utilizing consequence caching, tackling disk spilling, rectifying row explosion, and fixing insufficient pruning. We’ll additionally talk about options for real-time analytics that is likely to be what you’re in search of in case you are in want of higher real-time question efficiency.
Scale back Queuing
Snowflake strains up queries till sources can be found. It’s not good for queries to remain queued too lengthy, as they are going to be aborted. To forestall queries from ready too lengthy, you’ve two choices: set a timeout or modify concurrency.
Set a Timeout
Use STATEMENT_QUEUED_TIMEOUT_IN_SECONDS to outline how lengthy your question ought to keep queued earlier than aborting. With a default worth of 0, there isn’t a timeout.
Change this quantity to abort queries after a particular time to keep away from too many queries queuing up. As it is a session-level question, you may set this timeout for explicit classes.
Modify the Most Concurrency Stage
The entire load time depends upon the variety of queries your warehouse executes in parallel. The extra queries that run in parallel, the tougher it’s for the warehouse to maintain up, impacting Snowflake efficiency.
To rectify this, use Snowflake’s MAX_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL parameter. Its default worth is 8, however you may set the worth to the variety of sources you need to allocate.
Holding the MAX_CONCURRENCY_LEVEL low helps enhance execution pace, even for complicated queries, as Snowflake allocates extra sources.
Use Consequence Caching
Each time you execute a question, it caches, so Snowflake doesn’t must spend time retrieving the identical outcomes from cloud storage sooner or later.
One approach to retrieve outcomes straight from the cache is by RESULT_SCAN.
Fox instance:
choose * from desk(result_scan(last_query_id())) The LAST_QUERY_ID is the beforehand executed question. RESULT_SCAN brings the outcomes straight from the cache.
Deal with Disk Spilling
When knowledge spills to your native machine, your operations should use a small warehouse. Spilling to distant storage is even slower.
To deal with this difficulty, transfer to a extra in depth warehouse with sufficient reminiscence for code execution.
alter warehouse mywarehouse warehouse_size = XXLARGE auto_suspend = 300 auto_resume = TRUE; This code snippet allows you to scale up your warehouse and droop question execution routinely after 300 seconds. If one other question is in line for execution, this warehouse resumes routinely after resizing is full.
Prohibit the consequence show knowledge. Select the columns you need to show and keep away from the columns you don’t want.
choose last_name from employee_table the place employee_id = 101; choose first_name, last_name, country_code, telephone_number, user_id from employee_table the place employee_type like "%junior%"; The primary question above is restricted because it retrieves the final identify of a specific worker. The second question retrieves all of the rows for the employee_type of junior, with a number of different columns.
Rectify Row Explosion
Row explosion occurs when a JOIN question retrieves many extra rows than anticipated. This may happen when your be a part of by accident creates a cartesian product of all rows retrieved from all tables in your question.
Use the Distinct Clause
One approach to scale back row explosion is by utilizing the DISTINCT clause that neglects duplicates.
For instance:
SELECT DISTINCT a.FirstName, a.LastName, v.District FROM data a INNER JOIN sources v ON a.LastName = v.LastName ORDER BY a.FirstName; On this snippet, Snowflake solely retrieves the distinct values that fulfill the situation.
Use Momentary Tables
An alternative choice to cut back row explosion is by utilizing non permanent tables.
This instance exhibits methods to create a short lived desk for an current desk:
CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE tempList AS SELECT a,b,c,d FROM table1 INNER JOIN table2 USING (c); SELECT a,b FROM tempList INNER JOIN table3 USING (d); Momentary tables exist till the session ends. After that, the person can not retrieve the outcomes.
Verify Your Be a part of Order
An alternative choice to repair row explosion is by checking your be a part of order. Inside joins will not be a difficulty, however the desk entry order impacts the output for outer joins.
Snippet one:
orders LEFT JOIN merchandise ON merchandise.id = merchandise.id LEFT JOIN entries ON entries.id = orders.id AND entries.id = merchandise.id Snippet two:
orders LEFT JOIN entries ON entries.id = orders.id LEFT JOIN merchandise ON merchandise.id = orders.id AND merchandise.id = entries.id In idea, outer joins are neither associative nor commutative. Thus, snippet one and snippet two don’t return the identical outcomes. Pay attention to the be a part of sort you utilize and their order to save lots of time, retrieve the anticipated outcomes, and keep away from row explosion points.
Repair Insufficient Pruning
Whereas working a question, Snowflake prunes micro-partitions, then the remaining partitions’ columns. This makes scanning simple as a result of Snowflake now doesn’t need to undergo all of the partitions.
Nevertheless, pruning doesn’t occur completely on a regular basis. Right here is an instance:
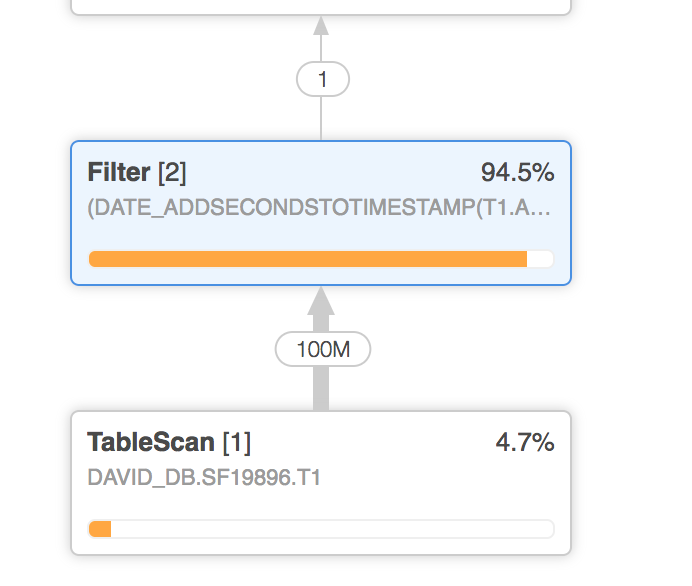
When executing the question, the filter removes about 94 % of the rows. Snowflake prunes the remaining partitions. Which means the question scanned solely a portion of the 4 % of the rows retrieved.
Knowledge clustering can considerably enhance this. You may cluster a desk whenever you create it or whenever you alter an current desk.
CREATE TABLE recordsTable (C1 INT, C2 INT) CLUSTER BY (C1, C2); ALTER TABLE recordsTable CLUSTER BY (C1, C2); Knowledge clustering has limitations. Tables will need to have a lot of data and shouldn’t change often. The correct time to cluster is when you understand the question is sluggish, and you understand you could improve it.
In 2020, Snowflake deprecated the handbook re-clustering function, so that isn’t an choice anymore.
Wrapping Up Snowflake Efficiency Points
We defined methods to use queuing parameters, effectively use Snowflake’s cache, and repair disk spilling and exploding rows. It’s simple to implement all these strategies to assist enhance your Snowflake question efficiency.
One other Technique for Enhancing Question Efficiency: Indexing
Snowflake is usually a good answer for enterprise intelligence, but it surely’s not at all times the optimum selection for each use case, for instance, scaling real-time analytics, which requires pace. For that, take into account supplementing Snowflake with a database like Rockset.
Excessive-performance real-time queries and low latency are Rockset’s core options. Rockset supplies lower than one second of information latency on massive knowledge units, making new knowledge prepared to question shortly. Rockset excels at knowledge indexing, which Snowflake doesn’t do, and it indexes all the fields, making it quicker on your software to scan by and supply real-time analytics. Rockset is way extra compute-efficient than Snowflake, delivering queries which are each quick and economical.
Rockset is a wonderful complement to your Snowflake knowledge warehouse. Enroll on your free Rockset trial to see how we will help drive your real-time analytics.
Rockset is the real-time analytics database within the cloud for contemporary knowledge groups. Get quicker analytics on more energizing knowledge, at decrease prices, by exploiting indexing over brute-force scanning.

