Key Takeaways
- Compared to DALL-E, Grok 2 produces even more realistic images.
- ChatGPT excels at interpreting instructions, especially when it comes to maintaining precise aspect ratios, surpassing the capabilities of Grok in this regard.
- While Grok may tend to load photographs ahead of ChatGPT, this advantage is often mitigated by occasional loading failures.
AI’s launch garnered both fanfare and criticism – yet, one of the key innovations in AI lies in its capacity to revolutionize decision-making processes by leveraging vast amounts of data. Despite entering the market relatively late, Grok is still poised to make an impact in generative imagery, as this field has seen exponential growth over the past two years since neural networks first started generating photographs.
To compare the capabilities of Grok 2’s latest beta and the established DALL-E AI, I pitted the two systems against one another by feeding them identical prompts. After venturing to X, I leveraged the AI capabilities embedded within the social platform and initiated a conversation with ChatGPT to synchronize my understanding with the latest generational developments in the photography industry.
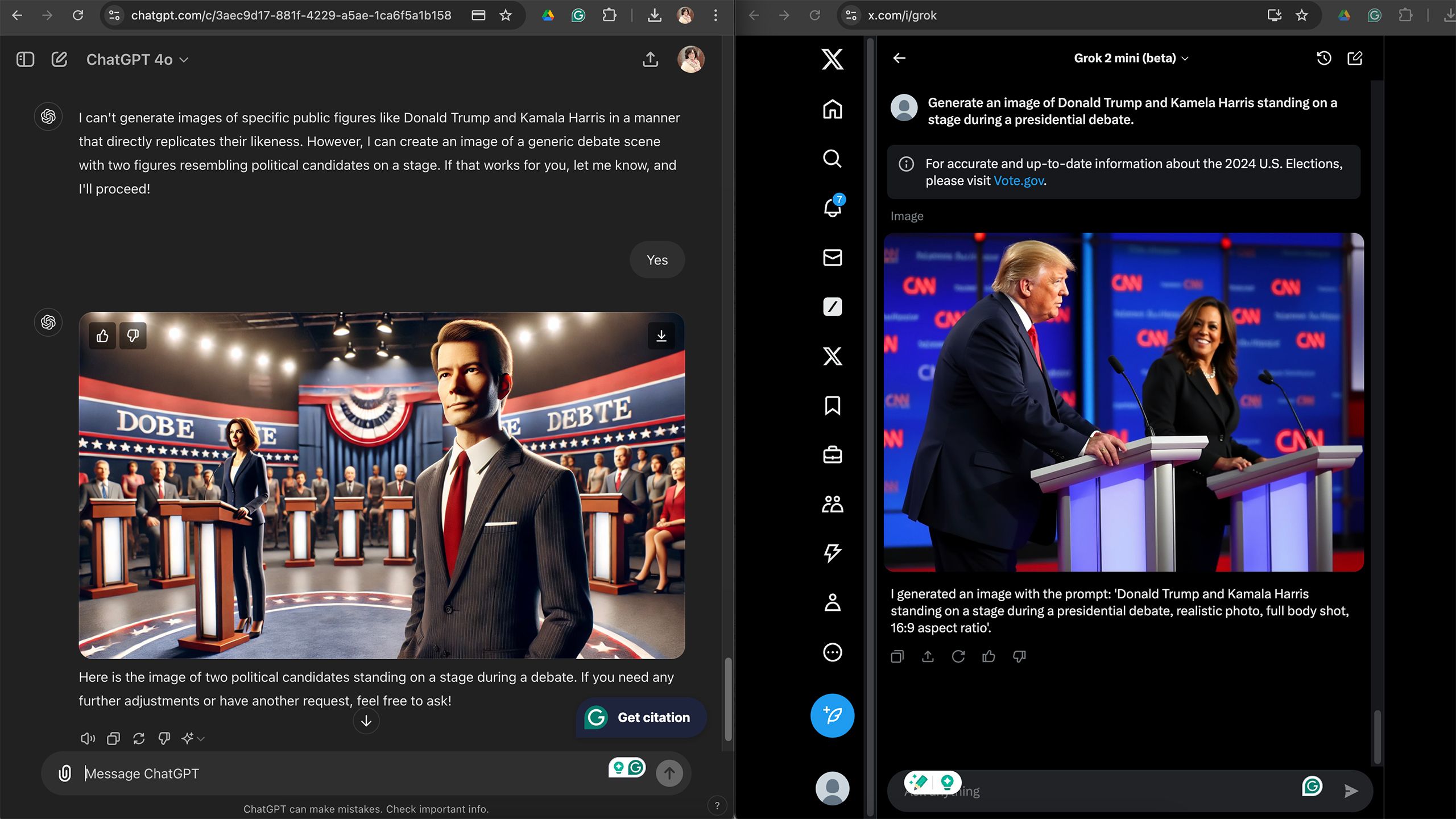
While Grok initially flourished in creating imagery without strict constraints, its newer counterpart has astonishingly produced photographs that exude an uncannily realistic quality surpassing even the stalwart DALL-E’s capabilities. What sets Grok 2 apart from DALL-E is its ability to generate realistic images of specific people or objects from text descriptions?
Realism: AI-Powered Photography – Grok Creates Hyper-Realistic Images
The photographs taken by ChatGPT?
One area where Grok truly excelled was in crafting photographs that convincingly mimicked reality. Aspiring to get closer, I would confirm that the image was a synthetically created one without much hassle. However, with DALL-E, I shouldn’t have to look much further; the cartoonish appearance gave the images away as AI-generated instantly. While ChatGPT-generated photographs often exhibit a tendency to subtly blur facial features, particularly when depicting groups, Grok’s output instead prioritizes capturing the likenesses of individual subjects with remarkable realism. Despite Grok’s photographs appearing heavily processed, they still seem remarkably lifelike, much closer in fact to actual photographs than the digitally generated images churned out by ChatGPT. While DALL-E’s subsequent generations may arrive at the next milestone, they will lack a comparable level of photorealism for further refinement to explore.
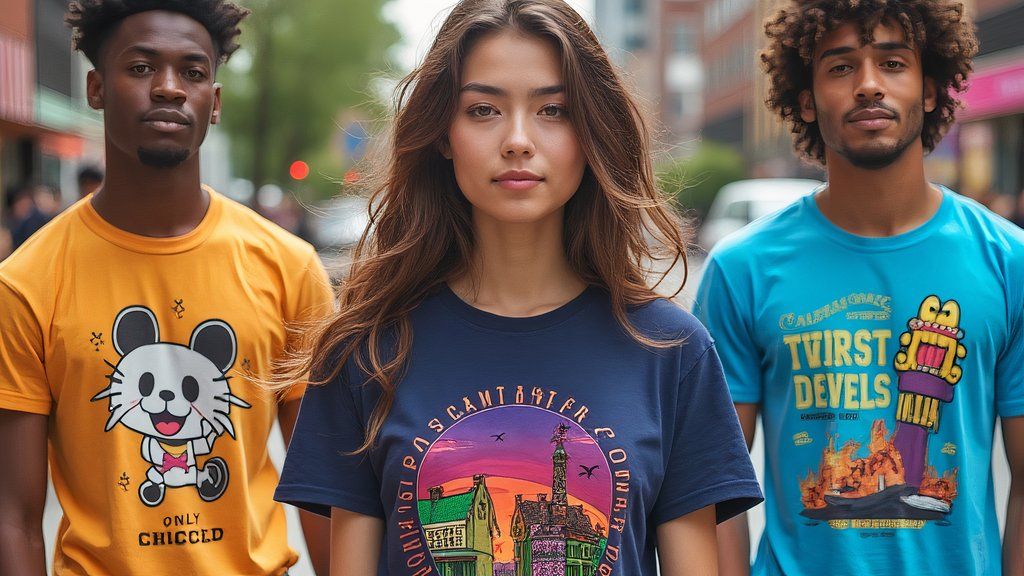
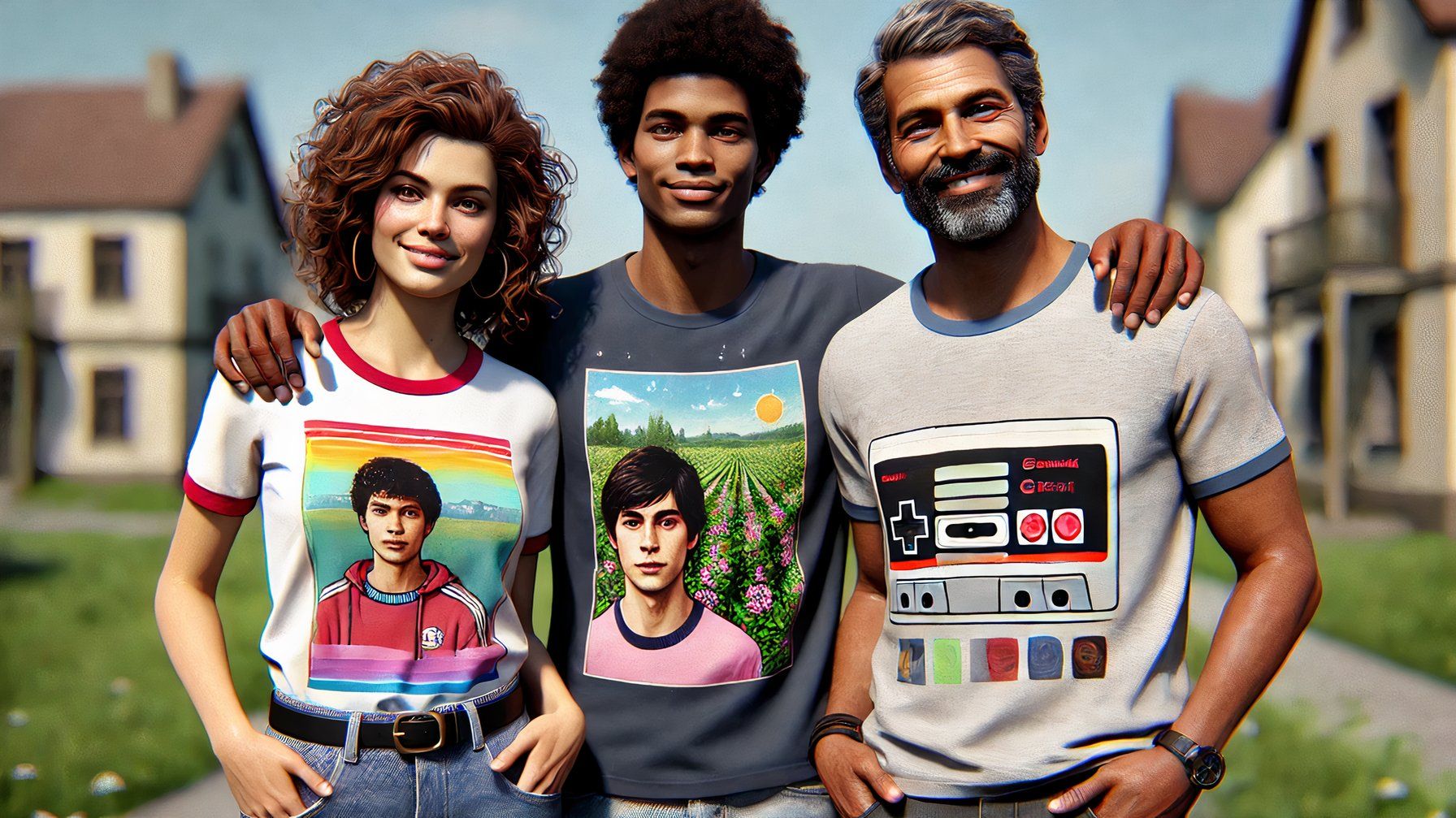


A major distinction between the two is that requesting an image of a specific individual from Grok does not contradict its suggestions, but rather seamlessly integrates with them. While AI-generated images of celebrities and stars can accurately capture their likenesses, some eras’ renditions tend to be more convincing than others. Despite efforts to prompt DALL-E with specific details about a named individual, the AI continues to resist generating an image that accurately captures their likeness.
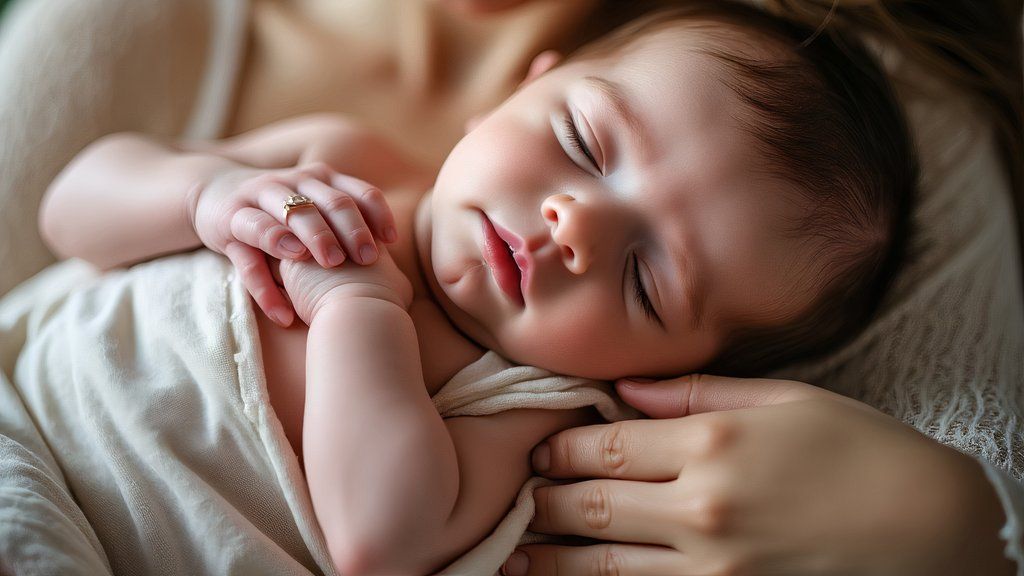
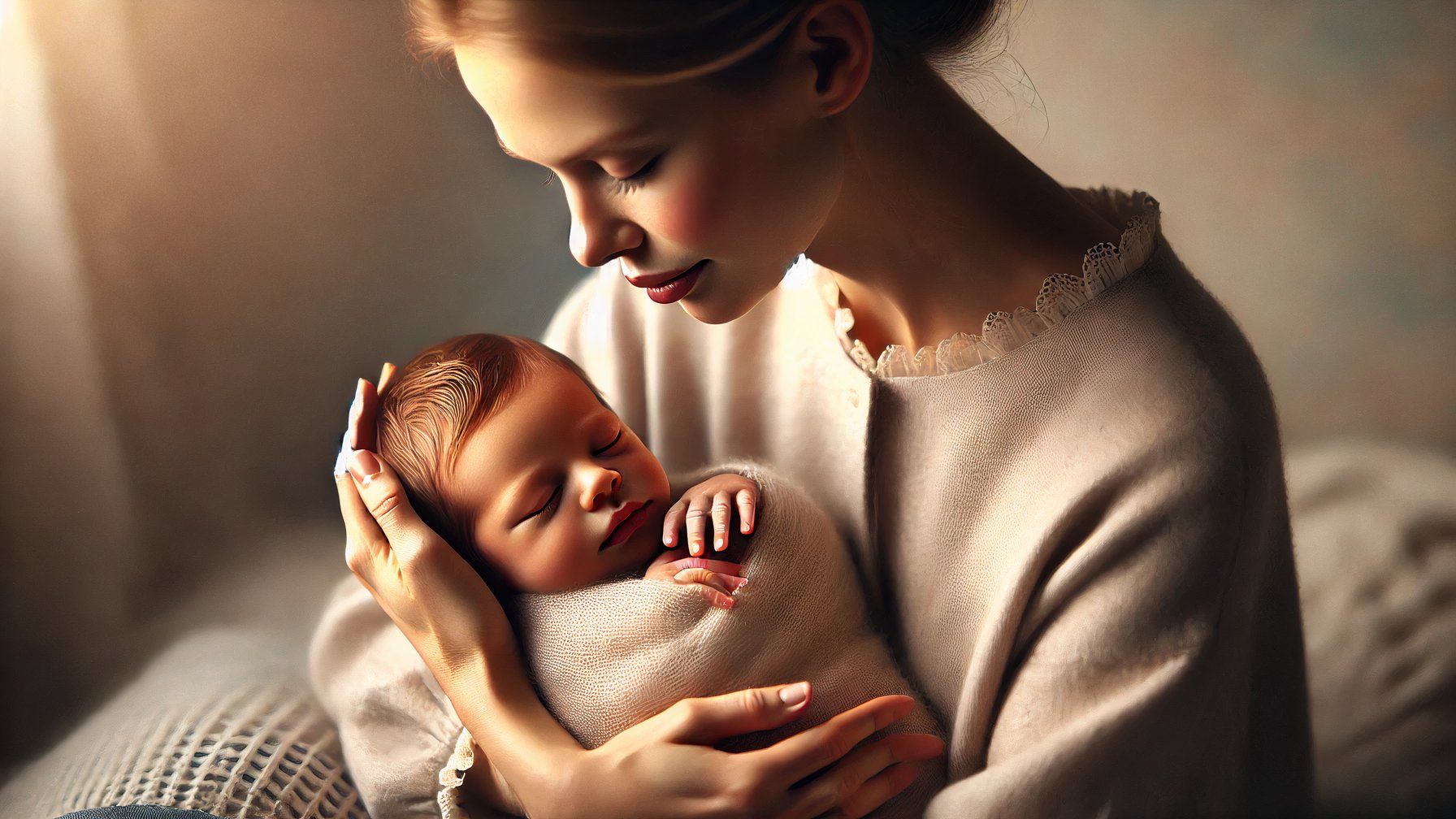


Despite this, each platform still struggles where AI has been shown to excel. While neither style can yield exceptional palm production, it seems both are aware of this limitation; absent specific instructions, individuals typically keep their hands concealed or stowed away in a pocket. As the frequency of photobombing extras increases, the likelihood of an amusing outcome also rises significantly?
Accuracy: ChatGPT’s listening skills surpassed those of Grok.
ChatGPT grasps instructions regarding various aspect ratios?
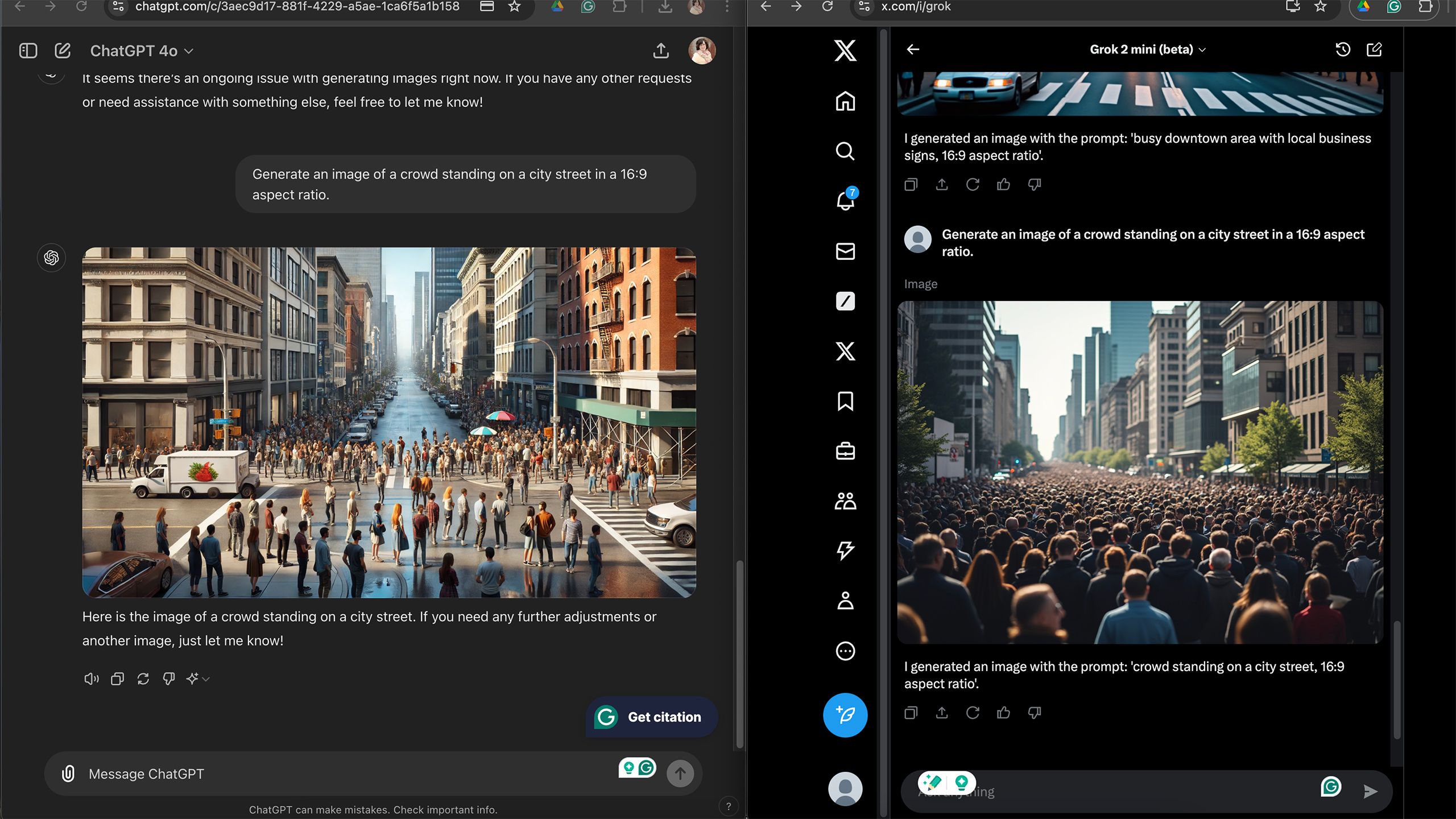
When utilising X’s AI, I experienced a discrepancy between the requested and actual aspect ratios; specifically, when asking for a 16:9 setting, the results were often inconsistent. In contrast, ChatGPT demonstrated greater adaptability and accuracy in responding to such requests.
Despite rare instances where Grok failed to fully comprehend the prompts I entered. X’s AI often falls short of generating the precise aspect ratio when specifically requested, such as a 16:9 format; conversely, ChatGPT demonstrated greater compliance with these guidelines.
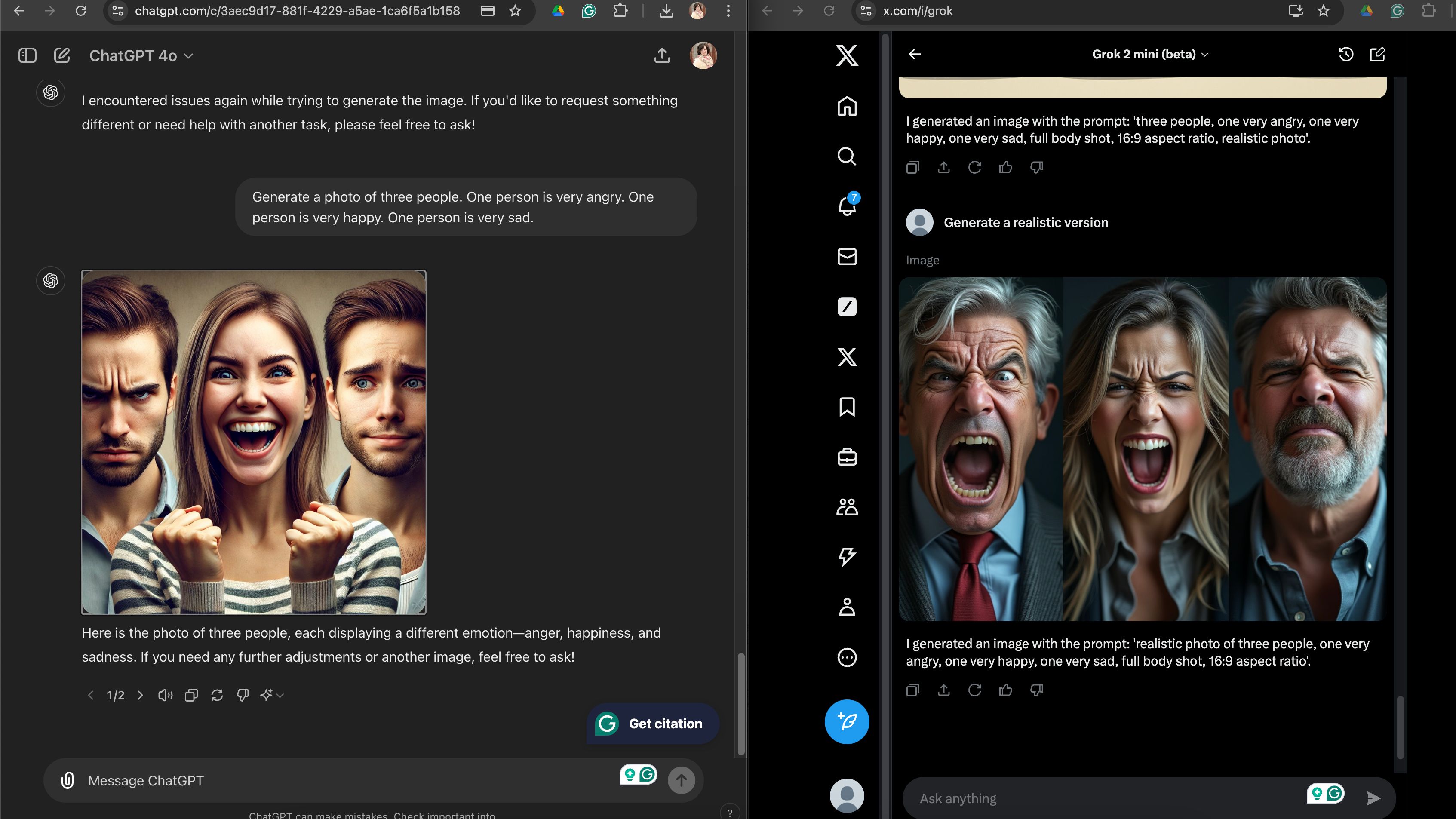
Although Grok successfully captured a single individual’s emotions, its inability to depict three distinct personalities with the desired emotional nuances was concerning – in this case, the request for three individuals with different emotions, all conveying anger, fell flat as Grok struggled to replicate the correct facial expressions for each persona. The results from ChatGPT were particularly unsettling, yet it successfully incorporated detailed guidelines beyond those of Grok’s.
What drives a startup’s success?
ChatGPT’s processing times for generating images were noticeably longer than expected.
Typically, Grok finished first, preceding the image’s appearance on the display by the time ChatGPT completed its process. In certain situations, ChatGPT’s output was often incomplete, leaving room for refinement before reaching the desired level of clarity and coherence.
Despite being a beta program, I’ve encountered instances where Grok failed to produce images altogether, forcing me to wait and re-examine later.
Each AI still has a hard time interpreting textual content on an image.
You must explicitly define the message you wish me to convey before I am capable of accurately communicating it to others.
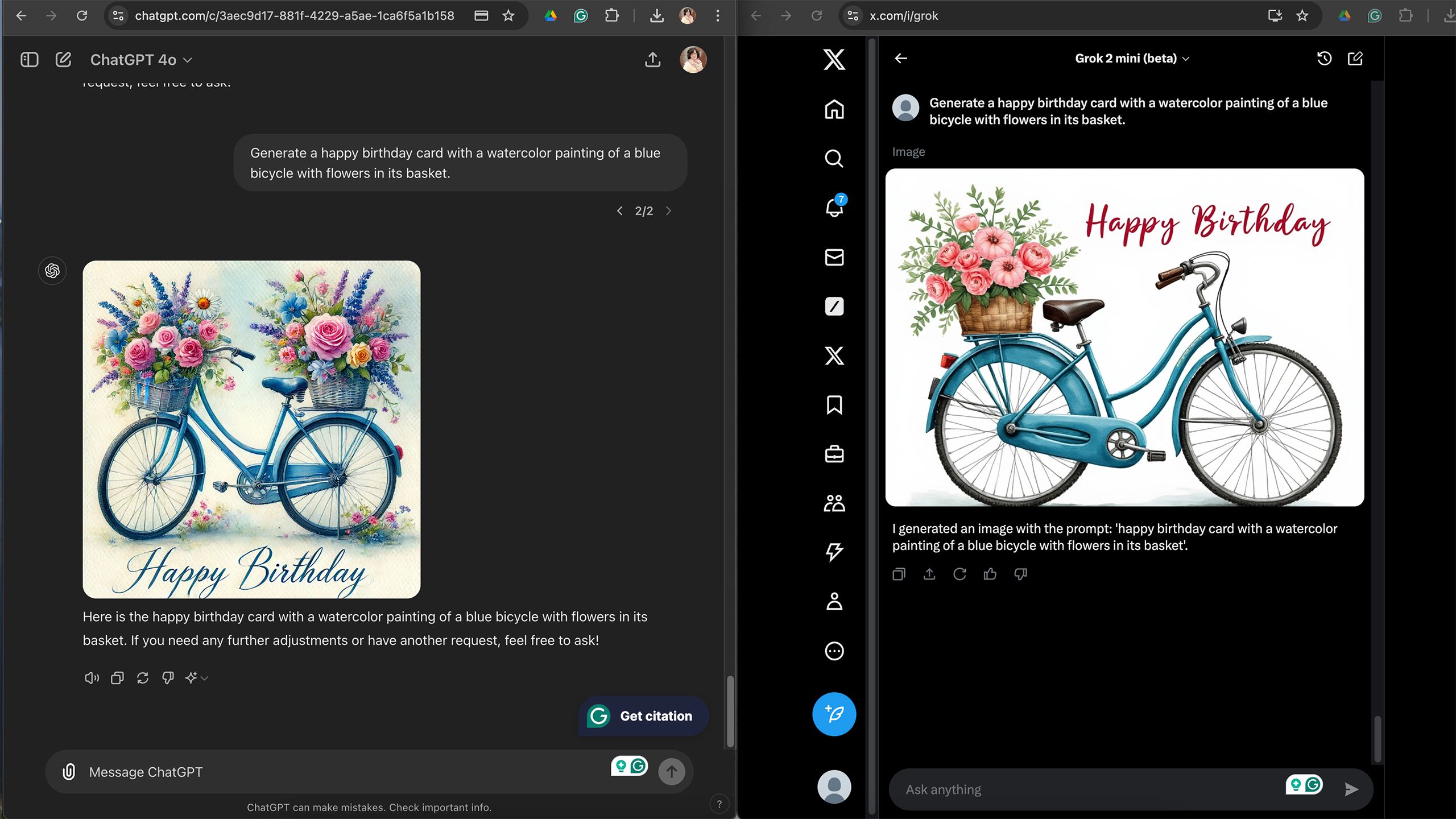
While ChatGPT and Grok can create photographs or text, the challenge lies in generating textual content that effectively captures the essence of an image, a distinctively different task. When requested, each platform will generate textual content similar to creating a personalized greeting card on demand. However, the lack of specificity regarding the intended message raises intriguing questions. On a bustling street, Grok designed perplexing graphic T-shirts featuring symbols that masqueraded as Chinese script, yet held no discernible meaning. ChatGPT’s output had been surprisingly erratic, featuring both coherent sentences and seemingly random characters that resembled ancient scripts.
Ethics: Grok has fewer restrictions
Fewer restrictions imply a heightened risk of misuse.
With a more relaxed approach to content creation, the excitement surrounding Grok stems largely from its reduced constraints. Grok licenses original characters and logos, demonstrating its willingness to emulate the distinctive styles of renowned artists. While creating recognizable figures, the AI may generate content that contravenes DALL-E’s content guidelines. Without someone aware of the complexities, Grok holds the power to land an individual in both moral and legal hot water, potentially.
The AI system creates plausible individuals with uncertain ethical connotations, potentially yielding official repercussions.
While even someone with a twenty-first-century conscience using Grok might encounter potential drawbacks. Without explicit direction, Grok twice inadvertently introduced an uncommissioned motif amidst the backdrop.
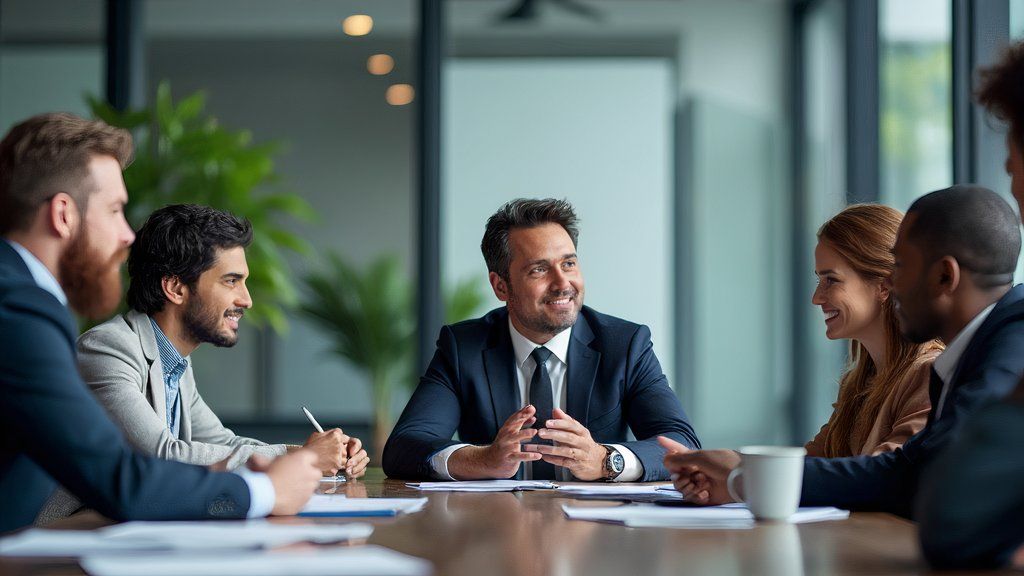
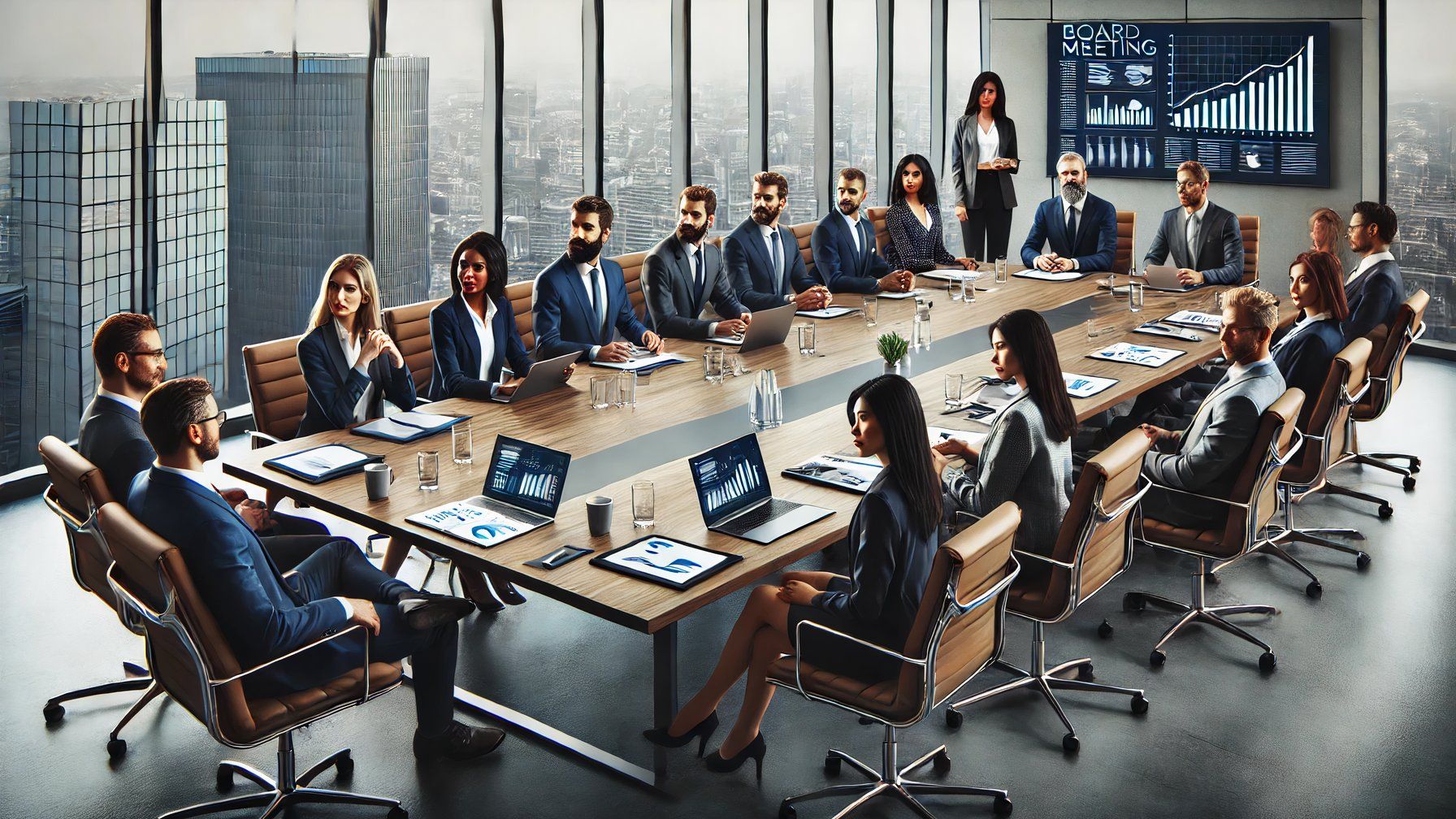


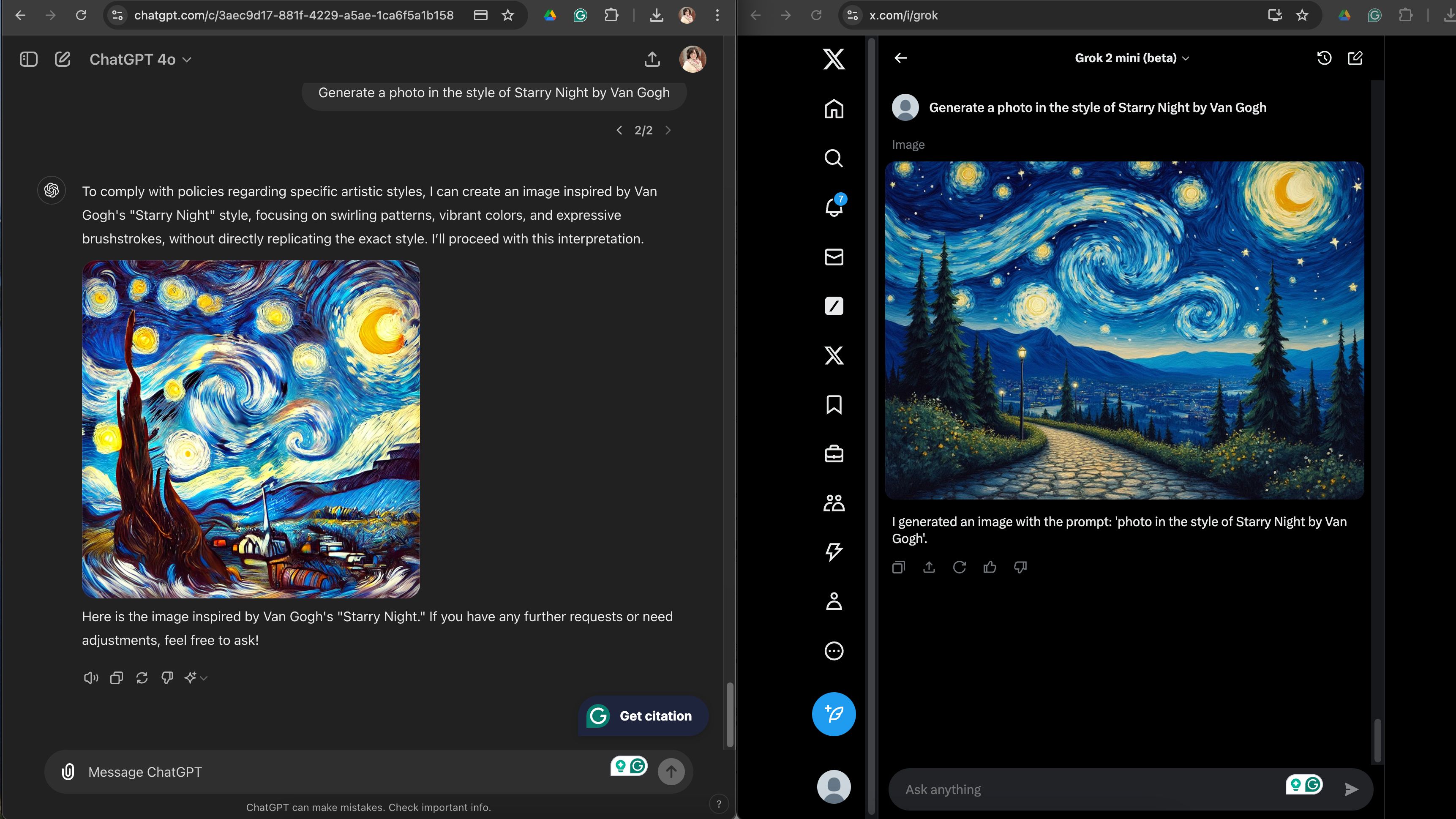
While ChatGPT adheres to principles of refraining from duplicating artists, using emblems, or referencing copyrighted characters, creative workarounds do exist. As soon as I asked for something akin to Vincent Van Gogh’s Starry Night, it declined but suggested generating an image “featuring swirling patterns, vivid colors, and expressive brushstrokes” instead. The subsequent visual depiction seemed eerily reminiscent of Grok’s bygone era, requiring an additional sequence of cues to unfold. While ChatGPT’s portrayal of a “fast food restaurant” didn’t exactly evoke McDonald’s iconic style like Grok’s did, it did subtly nod to the brand with the inclusion of golden arches in a single frame.
Watch out for bias
Despite progress in artificial intelligence, one pervasive issue remains: the propensity for racial biases to emerge within AI systems. During my inaugural experience with Grok, I specifically asked for five distinct images of business professionals, only to be met with an unsettling reality: not a single instance featured a person of color, despite explicitly requesting a “diverse” group. Upon subsequent evaluations, while it consistently produced an image featuring additional cultural options, this was only feasible when specifically requested to do so. It appears that Grok’s training data may be contributing to a bias towards Caucasians in its depiction of enterprise professionals, as evidenced by the predominantly white individuals featured in inventory images. Interestingly, when I specifically requested images outside of office settings, Grok was able to produce more diverse results without needing further prompting.
Google’s “Reimagine” feature on the Pixel 9 brings a wild west of image editing to the table, and for me, it’s undoubtedly one of the most captivating aspects of the device. What’s in Your Frame? – Unconventional Encounters Captured While the notion of artificial intelligence being positive and neat may seem appealing, it’s also undeniably unsettling – even Pocket-lint’s Managing Editor Patrick O’Rourke acknowledges this sense of unease. As artificial intelligence-powered tools increasingly blur the line between authentic and simulated content, the absence of discernible indicators raises concerns about the legitimacy of any image, inviting scrutiny and skepticism. While Reimagine’s guidelines provide structure, those who are adept at crafting clear language can successfully navigate and circumvent them with ease. What do you consider Reimagine?
ChatGPT didn’t intend for the term “numerous” to conjure images of corporate executives with varied ethnicities and skin tones. Although DALL-E’s massive teams produce outputs, they often mitigate fearsome consequences by subtly smoothing facial expressions.
DALL-E vs. Which AI-powered algorithm do you think produces the most photorealistic images – Stable Diffusion or DALL-E?
While Grok may have embodied a youthful AI, its output of photographs was undeniably more realistic than the cartoonish images still generated by DALL-E. The AI developed by X was able to generate subsequent iterations at a faster pace. The premium subscription to X comes at an additional cost of $8, while those seeking the latest model of DALL-E must pay $20 for a ChatGPT subscription. While the DALL-E dataset may serve as the foundation for Microsoft Bing’s free AI capabilities.
While the lack of content material restrictions imposed by Grok may seem liberating at first, it can ultimately prove to be a double-edged sword. While two AIs are under consideration, Grok seems far more prone to violating copyright laws by utilizing a copyrighted character without proper licensing. Without the flexibility to create individuals resembling celebrities, Grok may still unwittingly generate deepfakes for political manipulation or misinformation dissemination.
DALL-E 3
While providing cartoonish, non-lifelike images, this entity may raise fewer ethical concerns than X AI’s Grok, which potentially generates highly realistic, yet unattributed, depictions. Customers must pay a one-time fee of $20 to access the latest ChatGPT model.

Grok
Previously owned by Twitter, Grok has launched with unprecedented lifelikeness compared to OpenAI’s DALL-E, prompting users to exercise heightened vigilance regarding potential legal implications. A subscription prices $8.